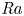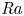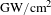54 results
Brain transcriptome-wide association study implicates novel risk genes underlying schizophrenia risk
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 53 / Issue 14 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 April 2023, pp. 6867-6877
-
- Article
- Export citation
Food Sources May Affect the Symptom Rates of COVID-19, an Epidemiological Analysis Based on the Public Data in Gansu Province, China, During the Summer Epidemic Cycle in 2022
-
- Journal:
- Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness / Volume 17 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 April 2023, e393
-
- Article
- Export citation
Morphometric analysis of stem-group mollusks from the northern Yangtze Craton, China
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Paleontology / Volume 96 / Issue 5 / September 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 May 2022, pp. 1024-1036
-
- Article
- Export citation
CYP4CJ6-mediated resistance to two neonicotinoid insecticides in Sitobion miscanthi (Takahashi)
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of Entomological Research / Volume 112 / Issue 5 / October 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2022, pp. 646-655
-
- Article
- Export citation
Relapse risk revealed by degree centrality and cluster analysis in heroin addicts undergoing methadone maintenance treatment
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 53 / Issue 6 / April 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 October 2021, pp. 2216-2228
-
- Article
- Export citation
Enhanced heat transport in thermal convection with suspensions of rod-like expandable particles
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 928 / 10 December 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 October 2021, R1
-
- Article
- Export citation
Meal frequency and incidence of type 2 diabetes: a prospective study
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 128 / Issue 2 / 28 July 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 August 2021, pp. 273-278
- Print publication:
- 28 July 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Longitudinal trajectory analysis of antipsychotic response in patients with schizophrenia: 6-week, randomised, open-label, multicentre clinical trial – CORRIGENDUM
-
- Journal:
- BJPsych Open / Volume 7 / Issue 5 / September 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 August 2021, e153
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A novel Fabry–Pérot (FP) antenna with high gain, low radar-cross-section (RCS), and wideband circular polarization
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Microwave and Wireless Technologies / Volume 14 / Issue 7 / September 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 July 2021, pp. 871-878
-
- Article
- Export citation
Identity recognition on waterways: a novel ship information tracking method based on multimodal data
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Navigation / Volume 74 / Issue 6 / November 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 June 2021, pp. 1336-1352
- Print publication:
- November 2021
-
- Article
- Export citation
1178 J, 527 nm near diffraction limited laser based on a complete closed-loop adaptive optics controlled off-axis multi-pass amplification laser system
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 9 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 May 2021, e22
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Warming affects water use, yield and crop quality of a potato–broad bean–winter wheat rotation system in semi-arid regions of China
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Agricultural Science / Volume 158 / Issue 7 / September 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 December 2020, pp. 543-557
-
- Article
- Export citation
Resistance switching behaviors of continuous-thick hBN films fabricated by radio-frequency-sputtering
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 35 / Issue 23-24 / 14 December 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 November 2020, pp. 3247-3256
- Print publication:
- 14 December 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
Longitudinal trajectory analysis of antipsychotic response in patients with schizophrenia: 6-week, randomised, open-label, multicentre clinical trial
-
- Journal:
- BJPsych Open / Volume 6 / Issue 6 / November 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 October 2020, e126
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
METHOD OF MOMENTS ESTIMATION FOR LÉVY-DRIVEN ORNSTEIN–UHLENBECK STOCHASTIC VOLATILITY MODELS
-
- Journal:
- Probability in the Engineering and Informational Sciences / Volume 35 / Issue 4 / October 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 June 2020, pp. 975-1004
-
- Article
- Export citation
Fabrication of iron carbide by plasma-enhanced atomic layer deposition
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 35 / Issue 7 / 14 April 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 November 2019, pp. 813-821
- Print publication:
- 14 April 2020
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Indium tin oxide nanowires as voltage self-stabilizing supercapacitor electrodes
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 34 / Issue 18 / 30 September 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 August 2019, pp. 3195-3203
- Print publication:
- 30 September 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
Amplification of 200-ps high-intensity laser pulses via frequency matching stimulated Brillouin scattering
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 7 / 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 July 2019, e41
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Prediction of psychosis in prodrome: development and validation of a simple, personalized risk calculator
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 49 / Issue 12 / September 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 September 2018, pp. 1990-1998
-
- Article
- Export citation
Preparation and characterization of monosized Cu–Sn spherical alloy particles by pulsated orifice ejection method
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 33 / Issue 18 / 28 September 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 June 2018, pp. 2835-2843
- Print publication:
- 28 September 2018
-
- Article
- Export citation