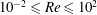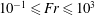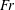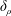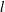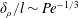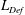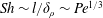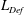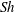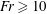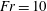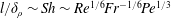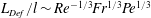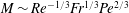116 results
New integrated molecular approaches for investigating lake settlements in north-western Europe
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
309 MYC Inhibition Overcomes IMiD Resistance in Heterogeneous Multiple Myeloma Populations
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 6 / Issue s1 / April 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 April 2022, p. 54
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Addressing personal protective equipment (PPE) decontamination: Methylene blue and light inactivates severe acute respiratory coronavirus virus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) on N95 respirators and medical masks with maintenance of integrity and fit
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 43 / Issue 7 / July 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 May 2021, pp. 876-885
- Print publication:
- July 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A conceptual framework to address administrative and infection control barriers for animal-assisted intervention programs in healthcare facilities: Perspectives from a qualitative study
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 43 / Issue 4 / April 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 January 2021, pp. 531-533
- Print publication:
- April 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Validation and calibration of the Eating Assessment in Toddlers FFQ (EAT FFQ) for children, used in the Growing Up Milk – Lite (GUMLi) randomised controlled trial
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 125 / Issue 2 / 28 January 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 August 2020, pp. 183-193
- Print publication:
- 28 January 2021
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Part I - Identifying priorities and collating the evidence
-
- Book:
- Conservation Research, Policy and Practice
- Published online:
- 18 April 2020
- Print publication:
- 16 April 2020, pp 27-142
-
- Chapter
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Chapter One - Making a difference in conservation: linking science and policy
- from Introduction and scene setting
-
-
- Book:
- Conservation Research, Policy and Practice
- Published online:
- 18 April 2020
- Print publication:
- 16 April 2020, pp 3-8
-
- Chapter
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Chapter Twenty - Successfully translating conservation research into practice and policy: concluding thoughts
- from Conclusion
-
-
- Book:
- Conservation Research, Policy and Practice
- Published online:
- 18 April 2020
- Print publication:
- 16 April 2020, pp 325-328
-
- Chapter
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Part II - Influencing and making decisions
-
- Book:
- Conservation Research, Policy and Practice
- Published online:
- 18 April 2020
- Print publication:
- 16 April 2020, pp 143-262
-
- Chapter
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Contents
-
- Book:
- Conservation Research, Policy and Practice
- Published online:
- 18 April 2020
- Print publication:
- 16 April 2020, pp vii-ix
-
- Chapter
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Contributors
-
- Book:
- Conservation Research, Policy and Practice
- Published online:
- 18 April 2020
- Print publication:
- 16 April 2020, pp x-xvi
-
- Chapter
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Part III - Communicating the message
-
- Book:
- Conservation Research, Policy and Practice
- Published online:
- 18 April 2020
- Print publication:
- 16 April 2020, pp 263-322
-
- Chapter
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Introduction and scene setting
-
- Book:
- Conservation Research, Policy and Practice
- Published online:
- 18 April 2020
- Print publication:
- 16 April 2020, pp 1-26
-
- Chapter
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Plate Section (PDF Only)
-
- Book:
- Conservation Research, Policy and Practice
- Published online:
- 18 April 2020
- Print publication:
- 16 April 2020, pp 337-356
-
- Chapter
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation

Conservation Research, Policy and Practice
-
- Published online:
- 18 April 2020
- Print publication:
- 16 April 2020
-
- Book
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Copyright page
-
- Book:
- Conservation Research, Policy and Practice
- Published online:
- 18 April 2020
- Print publication:
- 16 April 2020, pp vi-vi
-
- Chapter
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Conclusion
-
- Book:
- Conservation Research, Policy and Practice
- Published online:
- 18 April 2020
- Print publication:
- 16 April 2020, pp 323-328
-
- Chapter
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Index
-
- Book:
- Conservation Research, Policy and Practice
- Published online:
- 18 April 2020
- Print publication:
- 16 April 2020, pp 329-336
-
- Chapter
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Deformation of ambient chemical gradients by sinking spheres
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 892 / 10 June 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 April 2020, A33
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Physiological responses to maximal eating in men
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 124 / Issue 4 / 28 August 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 April 2020, pp. 407-417
- Print publication:
- 28 August 2020
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation