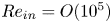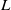48 results
Flow–acoustic resonance mechanism in tandem deep cavities coupled with acoustic eigenmodes in turbulent shear layers
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 984 / 10 April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 April 2024, A19
-
- Article
- Export citation
OPN Promotes Cell Proliferation and Invasion through NF-κB in Human Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma
-
- Journal:
- Genetics Research / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e5
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Impact of Implementing and Lifting COVID-19 Lockdown on Study and Physical Activity Patterns Among Youths in China
-
- Journal:
- Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness / Volume 17 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 January 2023, e383
-
- Article
- Export citation
Reply to ‘preconception paternal/maternal BMI and risk of small-/large-for-gestational age infant in over 4·7 million Chinese women aged 20–49 years: a population-based cohort study in China’
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 129 / Issue 2 / 28 January 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 April 2022, pp. 365-366
- Print publication:
- 28 January 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Preconception paternal/maternal BMI and risk of small/large for gestational age infant in over 4·7 million Chinese women aged 20–49 years: a population-based cohort study in China
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 129 / Issue 9 / 14 May 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 February 2022, pp. 1645-1655
- Print publication:
- 14 May 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Evaluation of paper-based and web-based food frequency questionnaires for 7-year-old children in Singapore
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 128 / Issue 8 / 28 October 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 November 2021, pp. 1626-1637
- Print publication:
- 28 October 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
The administration of a pre-digested fat-enriched formula prevents necrotising enterocolitis-induced lung injury in mice
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 128 / Issue 6 / 28 September 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 October 2021, pp. 1050-1063
- Print publication:
- 28 September 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
The association between meat consumption and the metabolic syndrome: a cross-sectional study and meta-analysis
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 127 / Issue 10 / 28 May 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 August 2021, pp. 1467-1481
- Print publication:
- 28 May 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Protocol for a pharmacogenomic study on individualised antipsychotic drug treatment for patients with schizophrenia
-
- Journal:
- BJPsych Open / Volume 7 / Issue 4 / July 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 June 2021, e121
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Impacts of lockdown on dietary patterns among youths in China: the COVID-19 Impact on Lifestyle Change Survey
-
- Journal:
- Public Health Nutrition / Volume 24 / Issue 11 / August 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 May 2021, pp. 3221-3232
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Dietary patterns of 5-year-old children and their correlates: findings from a multi-ethnic Asian cohort
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 127 / Issue 5 / 14 March 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 April 2021, pp. 763-772
- Print publication:
- 14 March 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Using manure for improving nitrogen fertilization and maize yield
-
- Journal:
- Experimental Agriculture / Volume 56 / Issue 6 / December 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 January 2021, pp. 901-914
-
- Article
- Export citation
Blunted reward prediction error signals in internet gaming disorder
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 52 / Issue 11 / August 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 November 2020, pp. 2124-2133
-
- Article
- Export citation
Iodine nutrition status of women after 10 years of Lipiodol supplementation: a cross-sectional study in Xinjiang, China
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 126 / Issue 1 / 14 July 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 October 2020, pp. 9-21
- Print publication:
- 14 July 2021
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
COVID-19 pandemic: study on simple, easy, and practical relaxation techniques while wearing medical protective equipment
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 52 / Issue 7 / May 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 August 2020, pp. 1386-1392
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
HUMAN DIETARY COMPLEXITY IN TIANSHAN REGION AND THE INFLUENCE OF CLIMATE ON HUMAN PALEODIET
-
- Journal:
- Radiocarbon / Volume 62 / Issue 5 / October 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 June 2020, pp. 1489-1502
- Print publication:
- October 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
Associations between taste preferences and chronic diseases: a population-based exploratory study in China
-
- Journal:
- Public Health Nutrition / Volume 24 / Issue 8 / June 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 June 2020, pp. 2021-2032
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Influence of the solenoid magnetic field on the self-modulation mechanism
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 38 / Issue 2 / June 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 May 2020, pp. 135-140
-
- Article
- Export citation
Underground nuclear astrophysics experiment JUNA in China
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the International Astronomical Union / Volume 15 / Issue S350 / April 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 October 2020, pp. 313-320
- Print publication:
- April 2019
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation