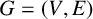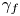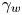62 results
On the interfacial instabilities of a ventilation cavity induced by gaseous injection into liquid crossflow
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 980 / 10 February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 February 2024, A44
-
- Article
- Export citation
Cavitation bubble dynamics inside a droplet suspended in a different host fluid
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 979 / 25 January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 January 2024, A47
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
First-Principles Study of Isomorphic (‘Dual-Defect’) Substitution in Kaolinite
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 59 / Issue 5 / October 2011
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 501-506
-
- Article
- Export citation
SOME GLOBAL EXISTENCE RESULTS ON LOCALLY FINITE GRAPHS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 November 2023, pp. 1-17
-
- Article
- Export citation
8 - Narratives and Voices of Cultural Revolution “Perpetrators”
- from Part IV - Memory
-
-
- Book:
- Justice After Mao
- Published online:
- 31 August 2023
- Print publication:
- 14 September 2023, pp 193-215
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Dissociation between neuroanatomical and symptomatic subtypes in schizophrenia
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 66 / Issue 1 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 September 2023, e78
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Axisymmetric column collapses of bi-frictional granular mixtures
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 963 / 25 May 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 May 2023, A4
-
- Article
- Export citation
Vertically neutral collapse of a pulsating bubble at the corner of a free surface and a rigid wall
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 962 / 10 May 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 May 2023, A28
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Programmable polymers with shape memory for biomedical applications
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Programmable Materials / Volume 1 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 April 2023, e2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Investigation of hydrodynamics of water impact and tail slamming of high-speed water entry with a novel immersed boundary method
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 958 / 10 March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 March 2023, A42
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Effect of high-pressure sintering on snow density evolution. Part I: experiments and results – CORRIGENDUM
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Glaciology / Volume 68 / Issue 272 / December 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 November 2022, p. 1116
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Non-modal growth of finite-amplitude disturbances in oscillatory boundary layer
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 943 / 25 July 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 June 2022, A45
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Multiphase large-eddy simulations of human cough jet development and expiratory droplet dispersion
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 942 / 10 July 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 May 2022, A12
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Global, regional and national burden of autism spectrum disorder from 1990 to 2019: results from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology and Psychiatric Sciences / Volume 31 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 May 2022, e33
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Effect of high-pressure sintering on snow density evolution: experiments and results
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Glaciology / Volume 68 / Issue 272 / December 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 April 2022, pp. 1107-1115
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Interaction of cavitation bubbles with the interface of two immiscible fluids on multiple time scales
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 932 / 10 February 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 December 2021, A8
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
ATP-binding cassette transporters ABCF2 and ABCG9 regulate rice black-streaked dwarf virus infection in its insect vector, Laodelphax striatellus (Fallén)
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of Entomological Research / Volume 112 / Issue 3 / June 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 September 2021, pp. 327-334
-
- Article
- Export citation
A prospective epidemiological analysis of controlling nutritional status score with the poor functional outcomes in Chinese patients with haemorrhagic stroke
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 128 / Issue 2 / 28 July 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 August 2021, pp. 192-199
- Print publication:
- 28 July 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Associations between early thiamine administration and clinical outcomes in critically ill patients with acute kidney injury
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 128 / Issue 2 / 28 July 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 August 2021, pp. 183-191
- Print publication:
- 28 July 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation