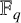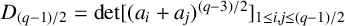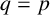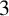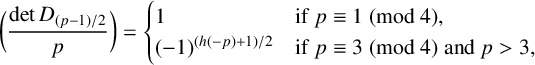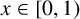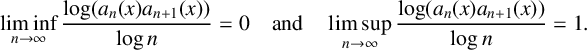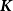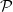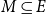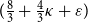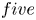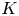14796 results

Spectral and Spectral Element Methods for Fractional Ordinary and Partial Differential Equations
- Coming soon
-
- Expected online publication date:
- September 2024
- Print publication:
- 30 September 2024
-
- Book
- Export citation

Negotiating Legality
- Chinese Companies in the US Legal System
- Coming soon
-
- Expected online publication date:
- June 2024
- Print publication:
- 30 June 2024
-
- Book
- Export citation

Translingual Practices
- Playfulness and Precariousness
- Coming soon
-
- Expected online publication date:
- May 2024
- Print publication:
- 09 May 2024
-
- Book
- Export citation
Facile preparation of sepiolite-based composites and their antibacterial/rheological properties
-
- Journal:
- Clay Minerals / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 April 2024, pp. 1-28
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Boundary mixing. Part 2. The impact of ventilation
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 985 / 25 April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 April 2024, A24
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
ON GENERALISED LEGENDRE MATRICES INVOLVING ROOTS OF UNITY OVER FINITE FIELDS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 April 2024, pp. 1-12
-
- Article
- Export citation
Modulating bilingual language production and cognitive control: how bilingual language experience matters
-
- Journal:
- Bilingualism: Language and Cognition , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 April 2024, pp. 1-15
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A visual SLAM-based lightweight multi-modal semantic framework for an intelligent substation robot
-
- Journal:
- Robotica , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 April 2024, pp. 1-15
-
- Article
- Export citation
Design and singularity analysis of a parallel mechanism with origami-inspired reconfigurable 5R closed-loop linkages
-
- Journal:
- Robotica , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 April 2024, pp. 1-24
-
- Article
- Export citation
Strategic underreporting and optimal deductible insurance
-
- Journal:
- ASTIN Bulletin: The Journal of the IAA , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 April 2024, pp. 1-24
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Integrating Cover Crops and Herbicides for Weed Control in Soybean
-
- Journal:
- Weed Technology / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 April 2024, pp. 1-25
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Macrolide-Resistance of Mycoplasma pneumoniae in Several Regions of China from 2013 to 2019
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 April 2024, pp. 1-18
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
ASYMPTOTIC BEHAVIOUR FOR PRODUCTS OF CONSECUTIVE PARTIAL QUOTIENTS IN CONTINUED FRACTIONS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 April 2024, pp. 1-12
-
- Article
- Export citation
An approximation algorithm for the
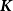 $\boldsymbol{K}$-prize-collecting multicut problem in trees with submodular penalties
$\boldsymbol{K}$-prize-collecting multicut problem in trees with submodular penalties
-
- Journal:
- Mathematical Structures in Computer Science , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 April 2024, pp. 1-18
-
- Article
- Export citation
Long-term outcomes after the arterial switch operation
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 April 2024, pp. 1-13
-
- Article
- Export citation
The homotopy decomposition of the suspension of a non-simply-connected five-manifold
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 April 2024, pp. 1-29
-
- Article
- Export citation
A coordinated switch in sucrose and callose metabolism enables enhanced symplastic unloading in potato tubers
-
- Journal:
- Quantitative Plant Biology / Volume 5 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 April 2024, e4
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Mood disorders influencing endometriosis and adenomyosis: Mendelian randomisation study
-
- Journal:
- BJPsych Open / Volume 10 / Issue 3 / May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 April 2024, e83
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Disarticulation, evisceration and excarnation: Neolithic mortuary practices at Dingsishan, southern China
-
- Journal:
- Antiquity , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 April 2024, pp. 1-20
-
- Article
- Export citation