38 results
C. auris and neighborhood socioeconomic vulnerability in the state of Maryland from 2019 to 2022
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 July 2024, pp. 1-7
-
- Article
- Export citation
Highly pathogenic avian influenza causes mass mortality in Sandwich Tern Thalasseus sandvicensis breeding colonies across north-western Europe
-
- Journal:
- Bird Conservation International / Volume 34 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 February 2024, e6
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
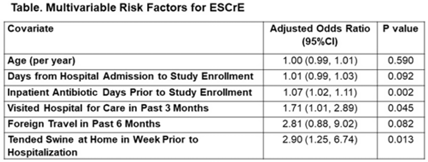
Colonization with extended-spectrum cephalosporin-resistant Enterobacterales (ESCrE) in hospitalized patients in Botswana
-
- Journal:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology / Volume 3 / Issue S2 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 September 2023, p. s81
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Healthcare personnel interactive pathogen exposure response system
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 44 / Issue 8 / August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 April 2023, pp. 1358-1360
- Print publication:
- August 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Imaging and Molecular Annotation of Xenographs and Tumours (IMAXT): High throughput data and analysis infrastructure
-
- Journal:
- Biological Imaging / Volume 3 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 April 2023, e11
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Cabbage and Caviar: A History of Food in Russia. By Alison K. Smith. Foods and Nations. London: Reaktion Books, 2021. 352 pp. Notes. Bibliography. Glossary. Index. Illustrations. Plates. Photographs. Tables. $39.00, hard bound.
-
- Journal:
- Slavic Review / Volume 82 / Issue 1 / Spring 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 August 2023, pp. 242-243
- Print publication:
- Spring 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
17 - The Global Alzheimer’s Platform Foundation®: Delivering New Medicines Faster by Accelerating Clinical Trials
- from Section 3 - Alzheimer’s Disease Clinical Trials
-
-
- Book:
- Alzheimer's Disease Drug Development
- Published online:
- 03 March 2022
- Print publication:
- 31 March 2022, pp 207-215
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Severe acute respiratory coronavirus virus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) exposure investigations using genomic sequencing among healthcare workers and patients in a large academic center
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 44 / Issue 5 / May 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 March 2022, pp. 798-801
- Print publication:
- May 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Transmission of severe acute respiratory coronavirus virus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), delta variant, between two fully vaccinated healthcare personnel
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 43 / Issue 12 / December 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 November 2021, pp. 1983-1985
- Print publication:
- December 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Impact of weekly asymptomatic testing for severe acute respiratory coronavirus virus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) in inpatients at an academic hospital
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 44 / Issue 1 / January 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 August 2021, pp. 99-101
- Print publication:
- January 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Hospital-acquired infections among adult patients admitted for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 43 / Issue 8 / August 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 April 2021, pp. 1054-1057
- Print publication:
- August 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
Inter-individual variation shapes the human microbiome
-
- Journal:
- Behavioral and Brain Sciences / Volume 42 / 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 July 2019, e79
-
- Article
- Export citation
New VIRAC proper motion maps show signature of galactic boxy/peanut bulge
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the International Astronomical Union / Volume 14 / Issue S353 / June 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 May 2020, pp. 29-30
- Print publication:
- June 2019
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Transverse bar/bulge kinematics with Gaia and VVV
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the International Astronomical Union / Volume 14 / Issue S353 / June 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 May 2020, pp. 38-42
- Print publication:
- June 2019
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Are long-term trends in Bewick’s Swan Cygnus columbianus bewickii numbers driven by changes in winter food resources?
-
- Journal:
- Bird Conservation International / Volume 29 / Issue 3 / September 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 November 2018, pp. 479-496
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Challenging the assertion of comparability of surveillance and administrative data
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 39 / Issue 11 / November 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 October 2018, pp. 1391-1392
- Print publication:
- November 2018
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Chronology of Inland Eolian Dunes on the Coastal Plain of Georgia, USA
-
- Journal:
- Quaternary Research / Volume 55 / Issue 3 / May 2001
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 January 2017, pp. 293-302
-
- Article
- Export citation
‘All these negative thoughts come flooding in’: how young people with depression describe their experience of rumination
-
- Journal:
- The Cognitive Behaviour Therapist / Volume 8 / 2015
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 July 2015, e15
-
- Article
- Export citation
Appraisals of Internal States and their Consequences: Relationship to Adolescent Analogue Bipolar Symptoms
-
- Journal:
- Behavioural and Cognitive Psychotherapy / Volume 44 / Issue 2 / March 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 April 2015, pp. 214-224
- Print publication:
- March 2016
-
- Article
- Export citation
The Sanctuary Model, Creating Safety for an Out-of-home Care Community
-
- Journal:
- Children Australia / Volume 39 / Issue 4 / December 2014
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 December 2014, pp. 232-236
- Print publication:
- December 2014
-
- Article
- Export citation