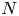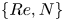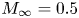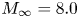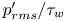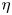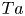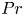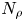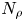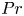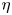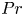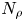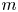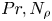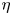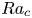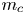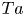114 results
Shared genetic basis and causality between schizophrenia and inflammatory bowel disease: evidence from a comprehensive genetic analysis
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 April 2024, pp. 1-11
-
- Article
- Export citation
Voltage-gated sodium channel gene mutation and P450 gene expression are associated with the resistance of Aphis spiraecola Patch (Hemiptera: Aphididae) to lambda-cyhalothrin
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of Entomological Research / Volume 114 / Issue 1 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 January 2024, pp. 49-56
-
- Article
- Export citation
Dispersion and Swellability of Ternary Surfactant Co-Modified Montmorillonites
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 69 / Issue 6 / December 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 759-771
-
- Article
- Export citation
TPX2 Serves as a Cancer Susceptibility Gene and Is Closely Associated with the Poor Prognosis of Endometrial Cancer
-
- Journal:
- Genetics Research / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e70
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Promoting conservation of fireflies in Kuala Lumpur's urban park through experiential learning
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Analysis of Destructive Effects with Electron Bombardment in Slow-Wave Structures
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e25
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The egg ribonuclease SjCP1412 accelerates liver fibrosis caused by Schistosoma japonicum infection involving damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs)
-
- Journal:
- Parasitology / Volume 151 / Issue 3 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 December 2023, pp. 260-270
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Conditional analysis on extreme wall shear stress and heat flux events in compressible turbulent boundary layers
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 974 / 10 November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 November 2023, A38
-
- Article
- Export citation
Genetic and Environmental Influences on Blood Pressure and Serum Lipids Across Age-Groups
-
- Journal:
- Twin Research and Human Genetics / Volume 26 / Issue 3 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 August 2023, pp. 223-230
-
- Article
- Export citation
Linear global stability of a flow past a sphere under a streamwise magnetic field
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 970 / 10 September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 August 2023, A16
-
- Article
- Export citation
Geochemistry, zircon U–Pb geochronology and Hf isotope of the early Permian gabbro and high-Mg diorites from the Zhusileng–Hangwula Belt in the northern Alxa area: Petrogenesis and tectonic implications
-
- Journal:
- Geological Magazine / Volume 160 / Issue 7 / July 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 August 2023, pp. 1417-1427
-
- Article
- Export citation
Exploring the Genetic Association between Obesity and Serum Lipid Levels Using Bivariate Methods
-
- Journal:
- Twin Research and Human Genetics / Volume 25 / Issue 6 / December 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 January 2023, pp. 234-244
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Wall-cooling effects on pressure fluctuations in compressible turbulent boundary layers from subsonic to hypersonic regimes
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 946 / 10 September 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 August 2022, A14
-
- Article
- Export citation
Risk factors for underlying comorbidities and complications in patients with hepatitis B virus-related acute-on-chronic liver failure
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 150 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 July 2022, e147
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Dietary inflammatory index, inflammation biomarkers and preeclampsia risk: a hospital-based case–control study
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 129 / Issue 9 / 14 May 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 May 2022, pp. 1528-1536
- Print publication:
- 14 May 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Noise reduction mechanisms for insert-type serrations of the NACA-0012 airfoil
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 941 / 25 June 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 May 2022, A57
-
- Article
- Export citation
Consistent brain structural abnormalities and multisite individualised classification of schizophrenia using deep neural networks
-
- Journal:
- The British Journal of Psychiatry / Volume 221 / Issue 6 / December 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 February 2022, pp. 732-739
- Print publication:
- December 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
COVID-19-Related Knowledge and Practices of Cancer Patients and Their Anxiety and Depression During the Early Surge Phase of the Pandemic: A Cross-sectional Online Survey
-
- Journal:
- Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness / Volume 17 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 January 2022, e73
-
- Article
- Export citation
A Comparison of Preterm Birth Rate and Growth from Birth to 18 Years Old between in Vitro Fertilization and Spontaneous Conception of Twins
-
- Journal:
- Twin Research and Human Genetics / Volume 24 / Issue 4 / August 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 September 2021, pp. 228-233
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Radius ratio dependency of the instability of fully compressible convection in rapidly rotating spherical shells
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 925 / 25 October 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 September 2021, A40
-
- Article
- Export citation