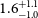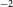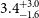54 results
546 Using Contingency Management to Understand the Cardiovascular, Immune and Psychosocial Benefits of Reduced Cocaine Use: A Protocol for a Randomized Controlled Trial
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 8 / Issue s1 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 April 2024, p. 163
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Anxiety in late-life depression: Associations with brain volume, amyloid beta, white matter lesions, cognition, and functional ability
-
- Journal:
- International Psychogeriatrics , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 January 2024, pp. 1-12
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Rapid ASKAP Continuum Survey III: Spectra and Polarisation In Cutouts of Extragalactic Sources (SPICE-RACS) first data release
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 40 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 August 2023, e040
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Towards a global sustainable development agenda built on social–ecological resilience
-
- Journal:
- Global Sustainability / Volume 6 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 April 2023, e8
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Characterisation of age and polarity at onset in bipolar disorder
-
- Journal:
- The British Journal of Psychiatry / Volume 219 / Issue 6 / December 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 August 2021, pp. 659-669
- Print publication:
- December 2021
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Qualitative Transparency Deliberations: Insights and Implications
-
- Journal:
- Perspectives on Politics / Volume 19 / Issue 1 / March 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 January 2021, pp. 171-208
- Print publication:
- March 2021
-
- Article
- Export citation
The effects of callous-unemotional traits and aggression subtypes on amygdala activity in response to negative faces – ERRATUM
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 53 / Issue 1 / January 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 August 2020, p. 304
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
The effects of callous-unemotional traits and aggression subtypes on amygdala activity in response to negative faces
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 52 / Issue 3 / February 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 July 2020, pp. 476-484
-
- Article
- Export citation
100 Olanzapine/Samidorphan for Schizophrenia: Weight Gain and Metabolic Outcomes in Phase 3 ENLIGHTEN-2 and Subsequent Long-Term, Open-Label Safety Study
-
- Journal:
- CNS Spectrums / Volume 25 / Issue 2 / April 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 April 2020, p. 265
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Petawatt and exawatt class lasers worldwide
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 7 / 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 August 2019, e54
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Structure and Function of the Proteasome Activator PA28 of the Malaria Parasite Plasmodium falciparum
-
- Journal:
- Microscopy and Microanalysis / Volume 25 / Issue S2 / August 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 August 2019, pp. 1324-1325
- Print publication:
- August 2019
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Stop the Bleed: The Effect of Hemorrhage Control Education on Laypersons’ Willingness to Respond During a Traumatic Medical Emergency
-
- Journal:
- Prehospital and Disaster Medicine / Volume 33 / Issue 2 / April 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 February 2018, pp. 127-132
- Print publication:
- April 2018
-
- Article
- Export citation
The Impact of a Computerized Clinical Decision Support Tool on Inappropriate Clostridium difficile Testing
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 38 / Issue 10 / October 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 August 2017, pp. 1204-1208
- Print publication:
- October 2017
-
- Article
- Export citation
A ground-based radar for measuring vertical strain rates and time-varying basal melt rates in ice sheets and shelves
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Glaciology / Volume 61 / Issue 230 / 2015
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 July 2017, pp. 1079-1087
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Life events and escape in conversion disorder
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 46 / Issue 12 / September 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 July 2016, pp. 2617-2626
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Twin's Birth-Order Differences in Height and Body Mass Index From Birth to Old Age: A Pooled Study of 26 Twin Cohorts Participating in the CODATwins Project
-
- Journal:
- Twin Research and Human Genetics / Volume 19 / Issue 2 / April 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 March 2016, pp. 112-124
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Zygosity Differences in Height and Body Mass Index of Twins From Infancy to Old Age: A Study of the CODATwins Project
-
- Journal:
- Twin Research and Human Genetics / Volume 18 / Issue 5 / October 2015
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 September 2015, pp. 557-570
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
The CODATwins Project: The Cohort Description of Collaborative Project of Development of Anthropometrical Measures in Twins to Study Macro-Environmental Variation in Genetic and Environmental Effects on Anthropometric Traits
-
- Journal:
- Twin Research and Human Genetics / Volume 18 / Issue 4 / August 2015
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 May 2015, pp. 348-360
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Contributors
-
-
- Book:
- The Cambridge Dictionary of Philosophy
- Published online:
- 05 August 2015
- Print publication:
- 27 April 2015, pp ix-xxx
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Contributors
-
-
- Book:
- Trauma Anesthesia
- Published online:
- 05 April 2015
- Print publication:
- 09 April 2015, pp vii-x
-
- Chapter
- Export citation