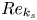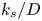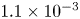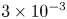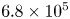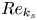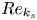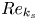1560 results
A longitudinal network analysis of suicide risk factors among service members and veterans sampled for suicidal ideation or attempt
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 April 2024, pp. 1-11
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Psychological Aspects of Vestibular Disorders: A National Survey of Clinical Practice
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Laryngology & Otology / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 April 2024, pp. 1-35
-
- Article
- Export citation
(Small D-democratic) vacation, all I ever wanted? The effect of democratic backsliding on leisure travel in the American states
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Experimental Political Science , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 April 2024, pp. 1-11
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The equitable impact of sugary drink taxation structures on sugary drink consumption among Canadians: a modelling study using the 2015 Canadian Community Health Survey-Nutrition
-
- Journal:
- Public Health Nutrition / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 April 2024, pp. 1-27
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
The Intellectual History of Milton Friedman's Criticism of Corporate Social Responsibility
-
- Journal:
- Modern Intellectual History , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 March 2024, pp. 1-27
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The influence of surface roughness on postcritical flow over circular cylinders revisited – CORRIGENDUM
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 979 / 25 January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 January 2024, E1
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The predictive role of symptoms in COVID-19 diagnostic models: A longitudinal insight
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 152 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 January 2024, e37
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Helium as a Surrogate for Deuterium in LPI Studies
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 2023 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
56 Dunning-Kruger Effect and Anxiety in a Mexican population
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 29 / Issue s1 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 December 2023, pp. 841-842
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
8 The Dunning-Kruger Effect on a Latinx Population
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 29 / Issue s1 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 December 2023, pp. 423-424
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
42 Lexical Retrieval and Acculturation in Generation Z Mexicans
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 29 / Issue s1 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 December 2023, p. 453
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
22 Cordoba Naming Test Performance and Acculturation in a Geriatric Population
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 29 / Issue s1 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 December 2023, pp. 335-336
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
30 Analyzing Spanish Speakers Cordoba Naming Test Performance
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 29 / Issue s1 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 December 2023, pp. 443-444
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
The influence of surface roughness on postcritical flow over circular cylinders revisited
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 975 / 25 November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 November 2023, A36
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Persistence of potential ST398 MSSA in outpatient settings among US veterans, 2010–2019
-
- Journal:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology / Volume 3 / Issue 1 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 October 2023, e177
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Radiofrequency ice dielectric measurements at Summit Station, Greenland
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Glaciology , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 October 2023, pp. 1-12
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
1 - Thomas Frederick Simmons and The Lay Folks’ Mass Book
-
- Book:
- Reinventing Medieval Liturgy in Victorian England
- Published by:
- Boydell & Brewer
- Published online:
- 02 March 2024
- Print publication:
- 03 October 2023, pp 13-26
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Appendix II - The Lay Folks’ Mass Book and the Sarum Rite
-
- Book:
- Reinventing Medieval Liturgy in Victorian England
- Published by:
- Boydell & Brewer
- Published online:
- 02 March 2024
- Print publication:
- 03 October 2023, pp 221-234
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
4 - Simmons as Editor: The Philologist
-
- Book:
- Reinventing Medieval Liturgy in Victorian England
- Published by:
- Boydell & Brewer
- Published online:
- 02 March 2024
- Print publication:
- 03 October 2023, pp 67-94
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Preface
-
-
- Book:
- Reinventing Medieval Liturgy in Victorian England
- Published by:
- Boydell & Brewer
- Published online:
- 02 March 2024
- Print publication:
- 03 October 2023, pp xiii-xiv
-
- Chapter
- Export citation