158 results
Effects of physical form of β-lactoglobulin and calcium ingestion on GLP-1 secretion, gastric emptying and energy intake in humans: a randomised crossover trial
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 January 2024, pp. 1-10
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
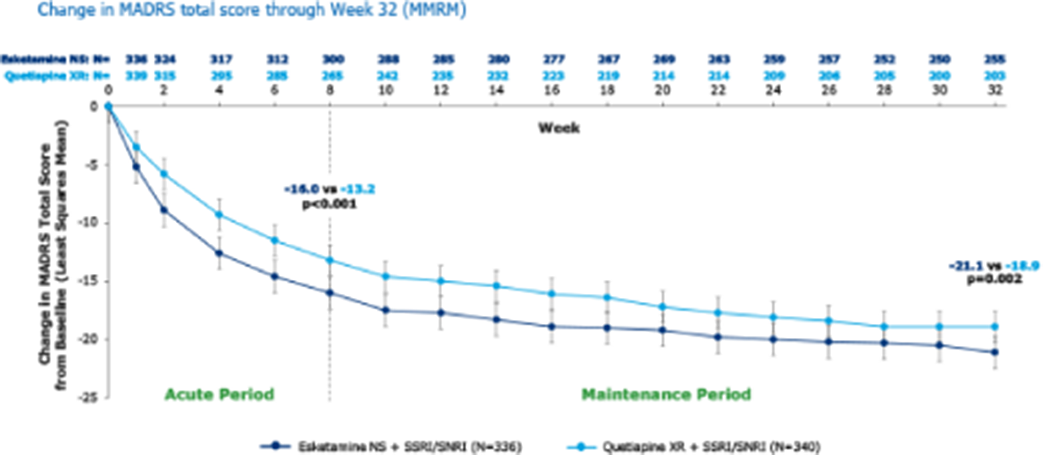
Esketamine nasal spray shows higher remission and response rates over 32 weeks of treatment compared with quetiapine extended-release in patients with treatment resistant depression: Results from ESCAPE-TRD, a randomised, phase IIIb clinical trial
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 66 / Issue S1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, pp. S90-S91
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Esketamine Nasal Spray Improves Rate and Time to Remission Versus Quetiapine Extended Release in Subgroups of Patients With Treatment Resistant Depression and Two or Three Plus Prior Treatment Failures: Results From ESCAPE-TRD, a Randomised Phase IIIb Trial
-
- Journal:
- BJPsych Open / Volume 9 / Issue S1 / July 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 July 2023, p. S75
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
SARS-CoV-2 and risk of psychiatric hospital admission and use of psychopharmaceuticals: A nationwide registry study of 4,585,083 adult Danish citizens
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 66 / Issue 1 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 June 2023, e50
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The effect of traditional diet on glucose homoeostasis in carriers and non-carriers of a common TBC1D4 variant in Greenlandic Inuit: a randomised crossover study
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 130 / Issue 11 / 14 December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 May 2023, pp. 1871-1884
- Print publication:
- 14 December 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Staying Good While Playing God - The Ethics of Breeding Farm Animals
-
- Journal:
- Animal Welfare / Volume 8 / Issue 4 / November 1999
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 January 2023, pp. 313-328
-
- Article
- Export citation
Letter of response to Nabi Z, Stansfeld J, Plöderl M, Wood L, Moncrieff J. Effects of lithium on suicide and suicidal behaviour: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised trials. Epidemiol Psychiatr Sci. 2022 Sep 16;31:e65. doi: 10.1017/S204579602200049X
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology and Psychiatric Sciences / Volume 31 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 November 2022, e84
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Relational Design
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Design Society / Volume 2 / May 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 May 2022, pp. 1061-1070
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Circulating sex-steroids and Staphylococcus aureus nasal carriage in a general male population
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 150 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 April 2022, e93
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Introducing antimicrobial stewardship to the outpatient clinics of a suburban academic health system
-
- Journal:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology / Volume 2 / Issue 1 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 January 2022, e9
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Translating RDoC to real-world impact in developmental psychopathology: A neurodevelopmental framework for application of mental health risk calculators
-
- Journal:
- Development and Psychopathology / Volume 33 / Issue 5 / December 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 December 2021, pp. 1665-1684
-
- Article
- Export citation
Reward disturbances in antipsychotic-naïve patients with first-episode psychosis and their association to glutamate levels
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 53 / Issue 4 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 August 2021, pp. 1629-1638
-
- Article
- Export citation
Feeding behaviour and energy balance in 4- to 6-month-old infants: adaptive changes during exclusive breast-feeding
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Nutrition Society / Volume 67 / Issue OCE6 / May 2008
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 June 2021, E220
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
EPA guidance on treatment of negative symptoms in schizophrenia
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 64 / Issue 1 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 March 2021, e21
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Liver fibrosis in patients with tetralogy of Fallot, an unrecognised complication?
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 31 / Issue 11 / November 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 March 2021, pp. 1796-1806
-
- Article
- Export citation
EPA guidance on assessment of negative symptoms in schizophrenia
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 64 / Issue 1 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 February 2021, e23
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Helminth infections in Italian donkeys: Strongylus vulgaris more common than Dictyocaulus arnfieldi
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Helminthology / Volume 95 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 February 2021, e4
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
EXPLORING HOW EXPERT BEHAVIOURAL DESIGNERS IDEATE IN THE BEHAVIOURAL DESIGN SPACE
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Design Society: DESIGN Conference / Volume 1 / May 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 June 2020, pp. 2541-2550
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Firn cold content evolution at nine sites on the Greenland ice sheet between 1998 and 2017
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Glaciology / Volume 66 / Issue 258 / August 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 April 2020, pp. 591-602
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Experience from the first ACT-programme in Denmark. III. The first 60 patients
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 17 / Issue S1 / May 2002
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 April 2020, p. 123s
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation