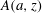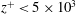33 results
Detection of the β-lactoglobulin genotype in zebu cattle (Gangatiri) milk using high-resolution accurate mass spectroscopy
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Dairy Research / Volume 90 / Issue 3 / August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 August 2023, pp. 287-291
- Print publication:
- August 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Analysis of genetic diversity and population structure using glutenin protein markers in various wheat varieties
-
- Journal:
- Plant Genetic Resources / Volume 21 / Issue 1 / February 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 June 2023, pp. 28-36
-
- Article
- Export citation
Generation of terahertz radiation by a Hermite–Gaussian laser beam inside magnetoplasma with a density ramp
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Plasma Physics / Volume 89 / Issue 2 / April 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 April 2023, 905890207
-
- Article
- Export citation
Probing of alpha, beta and kappa-caseins polymorphic variants in Gangatiri cow milk with the use of polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and HRAMS
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Dairy Research / Volume 90 / Issue 1 / February 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 February 2023, pp. 54-57
- Print publication:
- February 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Assessment of Health Status of Newborns Discharged From Sick Newborn Care Units of the Five Cyclone Fani Affected Districts of Odisha, India
-
- Journal:
- Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness / Volume 17 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 October 2022, e214
-
- Article
- Export citation
A velocity-variation-based formulation for bedload particle hops in rivers
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 912 / 10 April 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 February 2021, A33
-
- Article
- Export citation
Collection, characterization, conservation and utilization of Cordia sinensis Lam.: An underexploited multipurpose fruit species of hot arid regions
-
- Journal:
- Plant Genetic Resources / Volume 18 / Issue 6 / December 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 December 2020, pp. 427-436
-
- Article
- Export citation
Shales of Palaeo-Mesoproterozoic Vindhyan Basin, central India: insight into sedimentation dynamics of Proterozoic shelf
-
- Journal:
- Geological Magazine / Volume 159 / Issue 2 / February 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 November 2020, pp. 247-268
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Multi-modality management of extraosseous Ewing sarcoma: 10-year experience from a tertiary care centre
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Radiotherapy in Practice / Volume 20 / Issue 2 / June 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 March 2020, pp. 189-195
-
- Article
- Export citation
Neuroendocrine carcinoma of the uterine cervix: 15-year experience from a tertiary care centre in Southern India
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Radiotherapy in Practice / Volume 20 / Issue 2 / June 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 February 2020, pp. 164-167
-
- Article
- Export citation
Second-harmonic generation by a chirped laser pulse with the exponential density ramp profile in the presence of a planar magnetostatic wiggler
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 37 / Issue 4 / December 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 December 2019, pp. 442-447
-
- Article
- Export citation
Generation of second harmonics of intense Hermite–Gaussian laser beam in relativistic plasma
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 37 / Issue 1 / March 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 March 2019, pp. 79-85
-
- Article
- Export citation
A measure of scale-dependent asymmetry in turbulent boundary layer flows: scaling and Reynolds number similarity
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 797 / 25 June 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 May 2016, pp. 549-563
-
- Article
- Export citation
Electron plasma wave excitation by beating of two q-Gaussian laser beams in collisionless plasma
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 34 / Issue 2 / June 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 February 2016, pp. 230-241
-
- Article
- Export citation
Late desaturation due to giant azygous vein 16 years after bidirectional cavopulmonary anastomosis
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 26 / Issue 3 / March 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 December 2015, pp. 569-570
-
- Article
- Export citation
Second-harmonic generation by relativistic self-focusing of cosh-Gaussian laser beam in underdense plasma
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 34 / Issue 1 / March 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 November 2015, pp. 1-10
-
- Article
- Export citation
Beat wave excitation of electron plasma wave by coaxial cosh-Gaussian laser beams in collisional plasma
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 33 / Issue 4 / December 2015
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 July 2015, pp. 621-632
-
- Article
- Export citation
Higher harmonic generation by self-focused q-Gaussian laser beam in preformed collisionless plasma channel
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 32 / Issue 4 / December 2014
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 October 2014, pp. 621-629
-
- Article
- Export citation
Connector-less test setup for measurement of passive inter-modulation products at UHF band
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Microwave and Wireless Technologies / Volume 5 / Issue 6 / December 2013
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 August 2013, pp. 689-698
-
- Article
- Export citation
Contributors
-
-
- Book:
- Economic Reform in India
- Published online:
- 05 February 2013
- Print publication:
- 21 January 2013, pp vii-viii
-
- Chapter
- Export citation