Published online by Cambridge University Press: 26 February 2011
The interface between an a-axis oriented YBa2Cu3O7-x film and a NdGaO3(110) substrate has been investigated by cross-section transmission electron microscopy (TEM). The orientational relationship between the a-axis oriented film and substrate is YBa2Cu3O7-x[001] / NdGaO3[001]. This preferentially c-axis aligned direction of the YBa2Cu3O7-x film would be caused by a very small lattice mismatch (0.1%) between b(=a) lattice constant of YBa2Cu3O7-x and 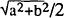 of the pseudo-cubic sub-lattices in NdGaO3 at a substrate temperature of 750°C. Two kinds of imperfections have been observed in the crystal lattice of YBa2Cu3O7-x near the interface; One is the deviation of YBa2Cu3O7-x [301] from NdGaO3 [111]. The other type is pair dislocations with a positive and negative Burgers vectors in the YBa2Cu3O7-x (103) planes. These two kinds of defects at the interface would be act to reduce the tensile stress within a distance of about l.lnm from the substrate interface.
of the pseudo-cubic sub-lattices in NdGaO3 at a substrate temperature of 750°C. Two kinds of imperfections have been observed in the crystal lattice of YBa2Cu3O7-x near the interface; One is the deviation of YBa2Cu3O7-x [301] from NdGaO3 [111]. The other type is pair dislocations with a positive and negative Burgers vectors in the YBa2Cu3O7-x (103) planes. These two kinds of defects at the interface would be act to reduce the tensile stress within a distance of about l.lnm from the substrate interface.