No CrossRef data available.
Article contents
Kinetics Of The Growth Of Copper Clusters On The Alumina (0001) Surface : Influence Of Surface Structure
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 10 February 2011
Abstract
The kinetics of the growth of copper clusters on the alumina (0001) surface was studied as a function of surface structure, using EXAFS at the Cu K edge. Equivalent Cu coverages ranging from 0.5 to 4 equivalent monolayers were deposited in situ, at room temperature, on alumina (0001) surfaces exhibiting the (1×1) or the 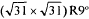 reconstructed structure. The evolution of mean cluster size with deposition time was followed from the mean Cu coordination number in the clusters deduced from the EXAFS data. The increase of the mean cluster radius with deposition time is characteristic of a coalescence mechanism on both surfaces. The growth is quicker on the reconstructed surface, likely due to different surface diffusion properties of both surfaces.
reconstructed structure. The evolution of mean cluster size with deposition time was followed from the mean Cu coordination number in the clusters deduced from the EXAFS data. The increase of the mean cluster radius with deposition time is characteristic of a coalescence mechanism on both surfaces. The growth is quicker on the reconstructed surface, likely due to different surface diffusion properties of both surfaces.
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 1998


