Published online by Cambridge University Press: 20 September 2019
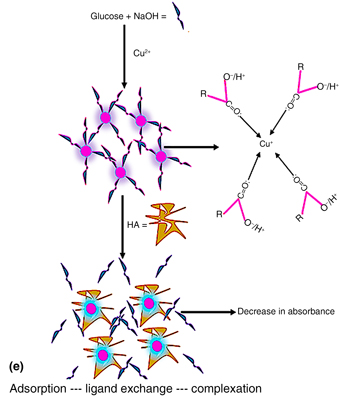
A glucose-reduced, room temperature-synthesized colloidal Cu2O solution (CCS) was used for the first time to detect humic acid (HA), a carcinogen-promoting substance in aqueous solution. The CCS sensor was characterized using standard spectroscopy and microscopy techniques. The sensor evolved as a carboxylic acid-capped peach-pink solution after synthesis. The result of the interaction of the sensor with HA in phosphate buffer solution (pH 7) showed a detection limit of 1.5891 × 10−2 mg/L over a concentration range of 0.00–0.41 mg/L. This finding suggests that the sensor may be useful for monitoring low levels of HA in aqueous environments.