Published online by Cambridge University Press: 10 June 2021
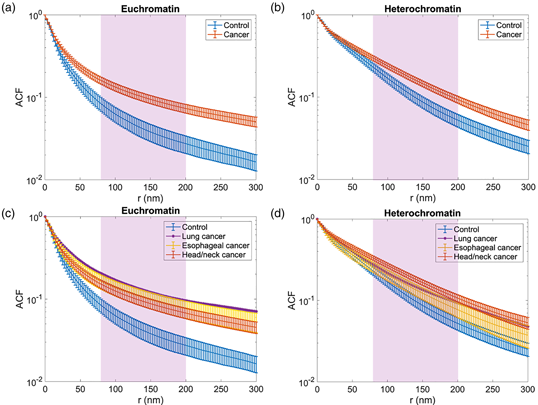
A profound characteristic of field cancerization is alterations in chromatin packing. This study aimed to quantify these alterations using electron microscopy image analysis of buccal mucosa cells of laryngeal, esophageal, and lung cancer patients. Analysis was done on normal-appearing mucosa, believed to be within the cancerization field, and not tumor itself. Large-scale electron microscopy (nanotomy) images were acquired of cancer patients and controls. Within the nuclei, the chromatin packing of euchromatin and heterochromatin was characterized. Furthermore, the chromatin organization was quantified through chromatin packing density scaling. A significant difference was found between the cancer and control groups in the chromatin packing density scaling parameter for length scales below the optical diffraction limit (200 nm) in both the euchromatin (p = 0.002) and the heterochromatin (p = 0.006). The chromatin packing scaling analysis also indicated that the chromatin organization of cancer patients deviated significantly from the control group. They might allow for novel strategies for cancer risk stratification and diagnosis with high sensitivity. This could aid clinicians in personalizing screening strategies for high-risk patients and follow-up strategies for treated cancer patients.
The first two authors contributed equally to this work.