Published online by Cambridge University Press: 16 March 2010
Let k ∈ ℕ and let E be a Banach space such that every k-homogeneous polynomial defined on a subspace of E has an extension to E. We prove that every norm one k-homogeneous polynomial, defined on a subspace, has an extension with a uniformly bounded norm. The analogous result for holomorphic functions of bounded type is obtained. We also prove that given an arbitrary subspace F ⊂ E, there exists a continuous morphism φk, F: 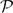 (kF) →
(kF) → 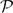 (kE) satisfying φk, F(P)|F = P, if and only E is isomorphic to a Hilbert space.
(kE) satisfying φk, F(P)|F = P, if and only E is isomorphic to a Hilbert space.