Article contents
RIGID ORBITS AND SHEETS IN REDUCTIVE LIE ALGEBRAS OVER FIELDS OF PRIME CHARACTERISTIC
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 04 April 2016
Abstract
Let 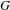 $G$ be a simple simply connected algebraic group over an algebraically closed field
$G$ be a simple simply connected algebraic group over an algebraically closed field 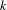 $k$ of characteristic
$k$ of characteristic 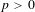 $p>0$ with
$p>0$ with 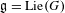 $\mathfrak{g}=\text{Lie}(G)$. We discuss various properties of nilpotent orbits in
$\mathfrak{g}=\text{Lie}(G)$. We discuss various properties of nilpotent orbits in 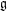 $\mathfrak{g}$, which have previously only been considered over
$\mathfrak{g}$, which have previously only been considered over  $\mathbb{C}$. Using computational methods, we extend to positive characteristic various calculations of de Graaf with nilpotent orbits in exceptional Lie algebras. In particular, we classify those orbits which are reachable as well as those which satisfy a certain related condition due to Panyushev, and determine the codimension of the derived subalgebra
$\mathbb{C}$. Using computational methods, we extend to positive characteristic various calculations of de Graaf with nilpotent orbits in exceptional Lie algebras. In particular, we classify those orbits which are reachable as well as those which satisfy a certain related condition due to Panyushev, and determine the codimension of the derived subalgebra 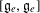 $[\mathfrak{g}_{e},\mathfrak{g}_{e}]$ in the centraliser
$[\mathfrak{g}_{e},\mathfrak{g}_{e}]$ in the centraliser 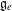 $\mathfrak{g}_{e}$ of any nilpotent element
$\mathfrak{g}_{e}$ of any nilpotent element 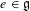 $e\in \mathfrak{g}$. Some of these calculations are used to show that the list of rigid nilpotent orbits in
$e\in \mathfrak{g}$. Some of these calculations are used to show that the list of rigid nilpotent orbits in 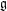 $\mathfrak{g}$, the classification of sheets of
$\mathfrak{g}$, the classification of sheets of 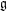 $\mathfrak{g}$ and the distribution of the nilpotent orbits amongst them are independent of good characteristic, remaining the same as in the characteristic zero case. We also give a comprehensive account of the theory of sheets in reductive Lie algebras over algebraically closed fields of good characteristic.
$\mathfrak{g}$ and the distribution of the nilpotent orbits amongst them are independent of good characteristic, remaining the same as in the characteristic zero case. We also give a comprehensive account of the theory of sheets in reductive Lie algebras over algebraically closed fields of good characteristic.
MSC classification
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Journal of the Institute of Mathematics of Jussieu , Volume 17 , Issue 3 , June 2018 , pp. 583 - 613
- Copyright
- © Cambridge University Press 2016
References
- 11
- Cited by




