No CrossRef data available.
Article contents
Improved axial confinement in the open trap by the combination of helical and short mirrors
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 18 September 2024
Abstract
The paper presents experimental results from the SMOLA device, which was built in the Budker Institute of Nuclear Physics for the verification of the helical mirror confinement idea. This concept involves active control of axial losses from the confinement zone in an open magnetic trap through the use of multiple mirrors that move in the plasma frame of reference. The discussed experiments focused on determining the cumulative effect of a helical mirror system in combination with a short segment of a stronger magnetic field. Combination of these two methods of axial flow suppression results in higher efficiency compared with each method individually. Different combinations of the mirrors were tested. The most effective flow suppression was observed if the short mirror was placed between the confinement region and the helical mirror. In this configuration, an effective mirror ratio of $R_{{\rm eff}} = 32.6\pm 7.8$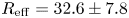 was achieved, along with a more than three-fold increase in plasma density within the confinement region. The possibility of a cumulative effect of different types of magnetic mirrors offers a way to improve the confinement performance of the reactor-grade mirror confinement devices.
was achieved, along with a more than three-fold increase in plasma density within the confinement region. The possibility of a cumulative effect of different types of magnetic mirrors offers a way to improve the confinement performance of the reactor-grade mirror confinement devices.
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © The Author(s), 2024. Published by Cambridge University Press



