Article contents
Transport characteristics of type II Weyl semimetal MoTe2 thin films grown by chemical vapor deposition
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 04 November 2019
Abstract
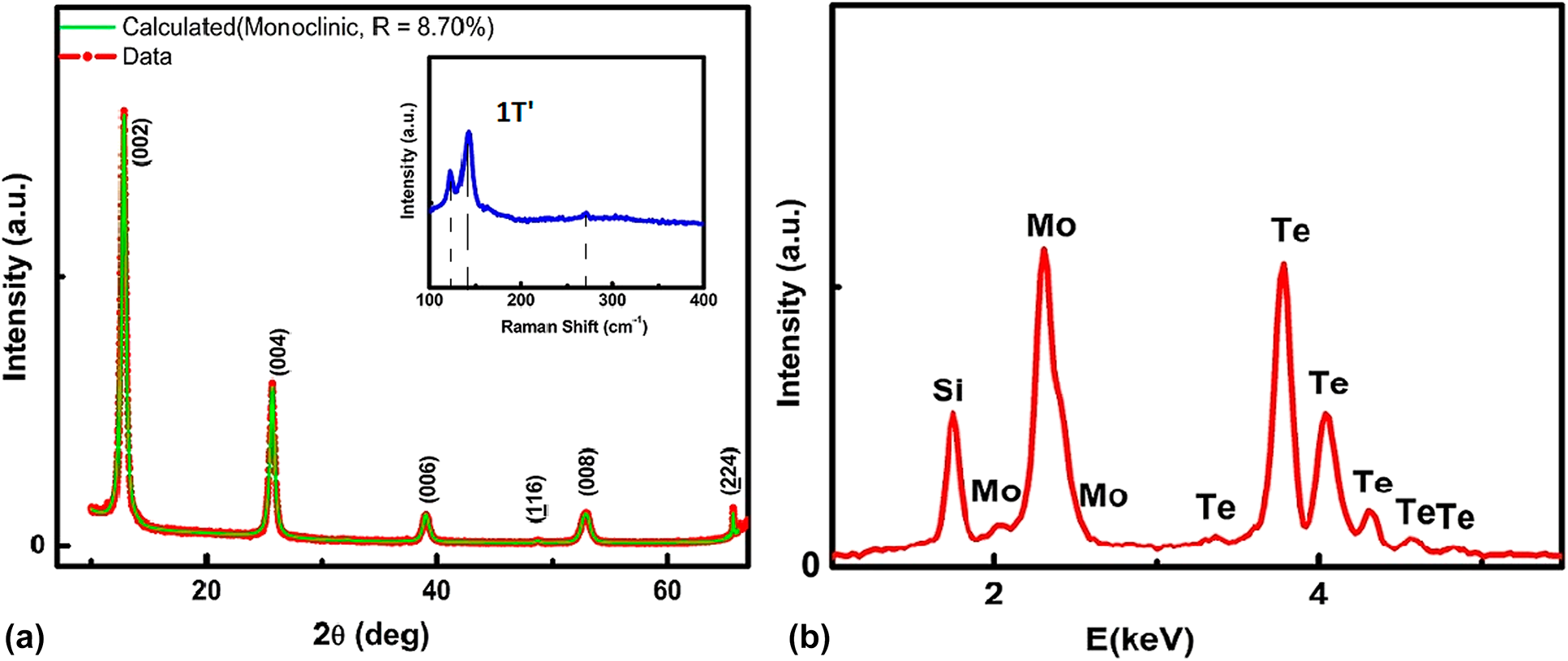
Theoretical calculations and experimental observations show MoTe2 is a type II Weyl semimetal, along with many members of transition metal dichalcogenides family. We have grown highly crystalline large-area MoTe2 thin films on Si/SiO2 substrates by chemical vapor deposition. Very uniform, continuous, and smooth films were obtained as confirmed by scanning electron microscopy and atomic force microscopy analyses. Measurements of the temperature dependence of longitudinal resistivity and current–voltage characteristics at different temperature are discussed. Unsaturated, positive quadratic magnetoresistance of the as-grown thin films has been observed from 10 to 200 K. Hall resistivity measurements confirm the majority charge carriers are hole.
- Type
- Article
- Information
- Journal of Materials Research , Volume 35 , Issue 5: Focus Issue: The Science and Technology of Vapor Phase Processing and Modification of Surfaces , 16 March 2020 , pp. 454 - 461
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2019
References
- 4
- Cited by




