Article contents
The wake structure and transition process of a flow past a sphere affected by a streamwise magnetic field
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 07 March 2018
Abstract
The wake structure and transition process of an incompressible viscous fluid flow past a sphere affected by an imposed streamwise magnetic field are investigated numerically over flow regimes that include steady and unsteady laminar flows at Reynolds numbers up to 300. For cases without a magnetic field, a subregion with the existence of a limit cycle is found in the range 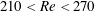 $210<Re<270$. The point of division is between
$210<Re<270$. The point of division is between 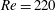 $Re=220$ and
$Re=220$ and 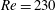 $Re=230$. For cases with a streamwise magnetic field, five wake patterns are the steady axisymmetric wake with an attached separation bubble, the steady plane symmetric wake with a small spiral dismissed, the steady plane symmetric wake with a limit cycle, the steady plane symmetric wake with a small spiral fed by the upstream fluid and the unsteady plane symmetric wake with a wave-like oscillation or vortex shedding. Under the influence of an imposed streamwise magnetic field, the wake will be transitioned to various patterns. An interesting ‘reversion phenomenon’, which describes the topological structure behind a sphere with a higher Reynolds number and a certain interaction parameter which corresponds to a lower Reynolds number case with a certain interaction parameter or a much lower Reynolds number case without a magnetic field, is also found. The principal results of the present work are summarized in a map of regimes in the
$Re=230$. For cases with a streamwise magnetic field, five wake patterns are the steady axisymmetric wake with an attached separation bubble, the steady plane symmetric wake with a small spiral dismissed, the steady plane symmetric wake with a limit cycle, the steady plane symmetric wake with a small spiral fed by the upstream fluid and the unsteady plane symmetric wake with a wave-like oscillation or vortex shedding. Under the influence of an imposed streamwise magnetic field, the wake will be transitioned to various patterns. An interesting ‘reversion phenomenon’, which describes the topological structure behind a sphere with a higher Reynolds number and a certain interaction parameter which corresponds to a lower Reynolds number case with a certain interaction parameter or a much lower Reynolds number case without a magnetic field, is also found. The principal results of the present work are summarized in a map of regimes in the 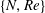 $\{N,Re\}$ plane.
$\{N,Re\}$ plane.
JFM classification
- Type
- JFM Papers
- Information
- Copyright
- © 2018 Cambridge University Press
References
- 15
- Cited by



