Published online by Cambridge University Press: 01 August 2013
Instabilities and long-term evolution of two-dimensional circular flows around a rigid circular cylinder (island) are studied analytically and numerically. For that we consider a base flow consisting of two concentric neighbouring rings of uniform but different vorticity, with the inner ring touching the cylinder. We first study the inviscid linear stability of such flows to perturbations of the free edges of the rings. For a given ratio of the vorticity in the rings, the governing parameters of the problem are the radii of the inner and outer rings scaled on the cylinder radius. In this two-dimensional parameter space, we determine analytically the regions of linear stability/instability of each azimuthal mode  $m= 1, 2, \ldots . $ In the physically most meaningful case of zero net circulation, for each mode
$m= 1, 2, \ldots . $ In the physically most meaningful case of zero net circulation, for each mode 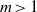 $m\gt 1$, two regions are identified: a regular instability region where mode
$m\gt 1$, two regions are identified: a regular instability region where mode 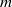 $m$ is unstable along with some other modes, and a unique instability region where only mode
$m$ is unstable along with some other modes, and a unique instability region where only mode 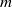 $m$ is unstable. After the conditions of linear instability are established, inviscid contour-dynamics and high-Reynolds-number finite-element simulations are conducted. In the regular instability regions, simulations of both kinds typically result in the formation of vortical dipoles or multipoles. In the unique instability regions, where the inner vorticity ring is much thinner than the outer ring, the inviscid contour-dynamics simulations do not reveal dipole emission. In the viscous simulation, because viscosity has time to widen the inner ring, the instability develops in the same manner as in the regular instability regions.
$m$ is unstable. After the conditions of linear instability are established, inviscid contour-dynamics and high-Reynolds-number finite-element simulations are conducted. In the regular instability regions, simulations of both kinds typically result in the formation of vortical dipoles or multipoles. In the unique instability regions, where the inner vorticity ring is much thinner than the outer ring, the inviscid contour-dynamics simulations do not reveal dipole emission. In the viscous simulation, because viscosity has time to widen the inner ring, the instability develops in the same manner as in the regular instability regions.