Article contents
Counter-flow orbiting of the vortex centre in turbulent thermal convection
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 26 January 2022
Abstract
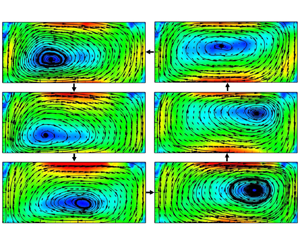
We present an experimental study of the large-scale vortex (or large-scale circulation, LSC) in turbulent Rayleigh–Bénard convection in a  $\varGamma =\text {diameter}/\text {height}=2$ cylindrical cell. The working fluid is deionized water with Prandtl number (
$\varGamma =\text {diameter}/\text {height}=2$ cylindrical cell. The working fluid is deionized water with Prandtl number ( $Pr$) around 5.7, and the Rayleigh number (
$Pr$) around 5.7, and the Rayleigh number ( $Ra$) ranges from
$Ra$) ranges from  $7.64\times 10^7$ to
$7.64\times 10^7$ to  $6.06\times 10^8$. We measured the velocity field in various vertical cross-sectional planes by using the planar particle image velocimetry technique. The velocity measurement in the LSC central plane shows that the flow is in the single-roll form, and the centre of the single-roll (vortex) does not always stay at the centre of the cell; instead, it orbits periodically in the direction opposite to the flow direction of the LSC, with its trajectory in the shape of an ellipse. The velocity measurements in the three vertical planes in parallel to the LSC central plane indicate that the flow is in the vortex tube form horizontally filling almost the whole cell, and the centre line of the vortex tube is consistent with the so-called ‘jump rope’ form proposed by a previous study that combined numerical simulation and local velocity measurements in the low
$6.06\times 10^8$. We measured the velocity field in various vertical cross-sectional planes by using the planar particle image velocimetry technique. The velocity measurement in the LSC central plane shows that the flow is in the single-roll form, and the centre of the single-roll (vortex) does not always stay at the centre of the cell; instead, it orbits periodically in the direction opposite to the flow direction of the LSC, with its trajectory in the shape of an ellipse. The velocity measurements in the three vertical planes in parallel to the LSC central plane indicate that the flow is in the vortex tube form horizontally filling almost the whole cell, and the centre line of the vortex tube is consistent with the so-called ‘jump rope’ form proposed by a previous study that combined numerical simulation and local velocity measurements in the low  $Pr$ case (Vogt et al., Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA, vol. 115, 2018, pp. 12674–12679). In addition, we found that the oscillation of the local velocity in
$Pr$ case (Vogt et al., Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA, vol. 115, 2018, pp. 12674–12679). In addition, we found that the oscillation of the local velocity in  $\varGamma =2$ cells originates from the periodical orbiting of the vortex centre. Our velocity measurements further indicate that the vortex centre orbiting is absent in
$\varGamma =2$ cells originates from the periodical orbiting of the vortex centre. Our velocity measurements further indicate that the vortex centre orbiting is absent in  $\varGamma =1$ cells, at least in the
$\varGamma =1$ cells, at least in the  $Ra$ range of our experiments.
$Ra$ range of our experiments.
JFM classification
- Type
- JFM Papers
- Information
- Copyright
- © The Author(s), 2022. Published by Cambridge University Press
References
REFERENCES
- 7
- Cited by





