Article contents
FINITE ELEMENT APPROXIMATION OF A TIME-FRACTIONAL DIFFUSION PROBLEM FOR A DOMAIN WITH A RE-ENTRANT CORNER
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 05 April 2017
Abstract
An initial-boundary value problem for a time-fractional diffusion equation is discretized in space, using continuous piecewise-linear finite elements on a domain with a re-entrant corner. Known error bounds for the case of a convex domain break down, because the associated Poisson equation is no longer 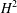 $H^{2}$-regular. In particular, the method is no longer second-order accurate if quasi-uniform triangulations are used. We prove that a suitable local mesh refinement about the re-entrant corner restores second-order convergence. In this way, we generalize known results for the classical heat equation.
$H^{2}$-regular. In particular, the method is no longer second-order accurate if quasi-uniform triangulations are used. We prove that a suitable local mesh refinement about the re-entrant corner restores second-order convergence. In this way, we generalize known results for the classical heat equation.
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- © 2017 Australian Mathematical Society
References
- 3
- Cited by




