When Bamileke women in urban Cameroon give birth, older women often recall the ‘troubles’, the period between 1955 and 1974 when the UPC (Union des Populations du Cameroun) waged a battle of national independence, as a way of teaching their daughters about the hazards of reproduction and threats to Bamileke integrity as a people (Feldman-Savelsberg et al.). Slightly to the north-west, in the Nigerian city of Kano, Igbo talk constantly about their memories of the Biafran war, using them to forge a sense of Igbo ethnic distinctiveness that reinforces patterns of patron-client relations critical to the maintenance of transregional connections (Smith), while further to the south many Yoruba are reassessing the meaning of the old practice of pawning children (Renne). Meanwhile in Botswana, where the AIDS epidemic exacts a high death toll, members of an Apostolic church create distinctive practices of remembering what caused a person's death. In so doing, they counter the attenuation of care and support that often occurs when people interpret death as due to illnesses transmitted through blood and improper sexual relations (Klaits). By contrast in a Samburu community in Kenya, the cultural practice of ntotoi, a complex board game, reproduces a male-dominated history of kinship, while systematically erasing a female narrative of adulterous births and forced infanticide. And among rural Beng in Côte d'Ivoire, beliefs and practices that structure infant care serve as an indirect critique of the violence of French colonialism and of its aftermath that continues to interfere in Beng lives in the form of high rates of infant mortality (Gottlieb). As these examples taken from this volume indicate, the papers gathered together in this special issue examine the complex and often contradictory ways in which the reproduction of memories shapes the social and biological reproduction of people.

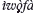 , these children would work for the lender until their kinsmen had repaid the debts they had incurred. British colonial officials came to view this practice as a form of slavery and eventually outlawed it. This paper considers the life history of one older man who worked as an
, these children would work for the lender until their kinsmen had repaid the debts they had incurred. British colonial officials came to view this practice as a form of slavery and eventually outlawed it. This paper considers the life history of one older man who worked as an 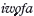 in a small Ekiti Yoruba town, focusing on his memories of child-pawning and how this practice has been interpreted by his children. The paper then examines the process whereby people's changed thinking about the moral bases of pawning parallels contemporary reassessments of the practice of child-fostering by young parents, some of whom claim that it is ‘like slavery’. How subsequent generations of townspeople remember slavery, child-pawning and, more recently, child-fostering, have implications for reproduction, since what it means to have the number of children who can be ‘raised well’ may contribute to social and economic pressures to limit family size. This study of memories of pawning and child-fostering, which support reduced fertility, underscores the ways that distinctive historical experiences have had different consequences for how reproduction is perceived and practised.
in a small Ekiti Yoruba town, focusing on his memories of child-pawning and how this practice has been interpreted by his children. The paper then examines the process whereby people's changed thinking about the moral bases of pawning parallels contemporary reassessments of the practice of child-fostering by young parents, some of whom claim that it is ‘like slavery’. How subsequent generations of townspeople remember slavery, child-pawning and, more recently, child-fostering, have implications for reproduction, since what it means to have the number of children who can be ‘raised well’ may contribute to social and economic pressures to limit family size. This study of memories of pawning and child-fostering, which support reduced fertility, underscores the ways that distinctive historical experiences have had different consequences for how reproduction is perceived and practised.