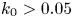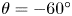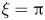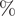239 results
Variation of millet grain size and cooking techniques across Asia between the late fourth and first millennia BC
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Workshop for the protection of Chinese giant salamanders
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Modulational instability of the interacting electron whistlers and magnetosonic perturbations
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Plasma Physics / Volume 90 / Issue 1 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 February 2024, 905900121
-
- Article
- Export citation
Guiding-centre orbit-following simulations of charge exchange loss of NBI ions with the finite Larmor radius effect
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Plasma Physics / Volume 89 / Issue 6 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 November 2023, 905890601
-
- Article
- Export citation
Design, performance and application of a line-imaging velocity interferometer system for any reflector coupled with a streaked optical pyrometer system at the Shenguang-II upgrade laser facility
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 12 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 November 2023, e6
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Sociome Data Commons: A scalable and sustainable platform for investigating the full social context and determinants of health
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 7 / Issue 1 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 November 2023, e255
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Potential neuropsychological mechanism involved in the transition from suicide ideation to action – a resting-state fMRI study implicating the insula
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 66 / Issue 1 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 September 2023, e69
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Social mixing and network characteristics of COVID-19 patients before and after widespread interventions: A population-based study
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 151 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 August 2023, e141
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Optical rectification in 4H-SiC: paving the way to generate strong terahertz fields with ultra-wide bandwidth
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 11 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 June 2023, e62
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Some observations on the temporal patterns in the surplus process of an insurer
-
- Journal:
- British Actuarial Journal / Volume 28 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 May 2023, e4
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Design and optimization of a decoupled serial constant force microgripper for force sensitive objects manipulation
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
ABO blood groups and nosocomial infection
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 151 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 April 2023, e64
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A machine learning model for predicting the three-year survival status of patients with hypopharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma using multiple parameters
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Laryngology & Otology / Volume 137 / Issue 9 / September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 January 2023, pp. 1041-1047
- Print publication:
- September 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Hazardous use of benzodiazepine receptor agonists in psychiatric clinics in China: electronic prescription database study – CORRIGENDUM
-
- Journal:
- BJPsych Open / Volume 8 / Issue 6 / November 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 November 2022, e195
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Hazardous use of benzodiazepine receptor agonists in psychiatric clinics in China: electronic prescription database study
-
- Journal:
- BJPsych Open / Volume 8 / Issue 6 / November 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 October 2022, e188
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The global disease burden attributable to a diet low in fibre in 204 countries and territories from 1990 to 2019
-
- Journal:
- Public Health Nutrition / Volume 26 / Issue 4 / April 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 September 2022, pp. 854-865
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Timing of gestational weight gain in association with birth weight outcomes: a prospective cohort study
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 129 / Issue 6 / 28 March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 July 2022, pp. 1058-1065
- Print publication:
- 28 March 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Early Cretaceous tectonic evolution of the Neo-Tethys: constraints from zircon U–Pb geochronology and geochemistry of the Liuqiong adakite, Gongga, Tibet
-
- Journal:
- Geological Magazine / Volume 159 / Issue 10 / October 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 June 2022, pp. 1647-1662
-
- Article
- Export citation
Machine-learning guided optimization of laser pulses for direct-drive implosions - CORRIGENDUM
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 10 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 May 2022, e17
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation