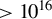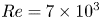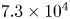644 results
Generation of polarized electron beams through self-injection in the interaction of a laser with a pre-polarized plasma
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 February 2024, pp. 1-7
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
China’s prevention and control experience of echinococcosis: A 19-year retrospective
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Helminthology / Volume 98 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 February 2024, e16
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Competition among the two-plasmon decay of backscattered light, filamentation of the electron-plasma wave and side stimulated Raman scattering
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 11 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 August 2023, e76
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Internal shear layer and vortex shedding development of a structured porous coated cylinder using tomographic particle image velocimetry
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 967 / 25 July 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 July 2023, A17
-
- Article
- Export citation
Multi-objective reward shaping for global and local trajectory planning of wing-in-ground crafts based on deep reinforcement learning
-
- Journal:
- The Aeronautical Journal / Volume 128 / Issue 1320 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 June 2023, pp. 371-397
-
- Article
- Export citation
Distributed fixed-time control for six-degree-of-freedom spacecraft formation with event-triggered observer
-
- Journal:
- The Aeronautical Journal / Volume 127 / Issue 1317 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 June 2023, pp. 1968-1992
-
- Article
- Export citation
Riboflavin intake associated with decreased risk of all-cause mortality among adults attending NHANES 2005-2016
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Nutrition Society / Volume 82 / Issue OCE2 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 March 2023, E145
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Resistant starch structure, food processing, and glycaemic control: investigating how the synergy of starch synthesis variation and processing influences glycaemia
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Nutrition Society / Volume 82 / Issue OCE1 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 March 2023, E33
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Depolarization of intense laser beams by dynamic plasma density gratings
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 11 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 February 2023, e37
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A deep learning-based approach to time-coordination entry guidance for multiple hypersonic vehicles
-
- Journal:
- The Aeronautical Journal / Volume 127 / Issue 1310 / April 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 February 2023, pp. 604-626
-
- Article
- Export citation
A machine learning model for predicting the three-year survival status of patients with hypopharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma using multiple parameters
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Laryngology & Otology / Volume 137 / Issue 9 / September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 January 2023, pp. 1041-1047
- Print publication:
- September 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Should mild obstructive sleep apnoea be treated? A systematic review from the standpoint of disease progression
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Laryngology & Otology / Volume 137 / Issue 8 / August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 November 2022, pp. 828-839
- Print publication:
- August 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
An Interactive Simulation and Visualization Tool for Conventional and Aberration-Corrected Transmission Electron Microscopy
-
- Journal:
- Microscopy Today / Volume 30 / Issue 6 / November 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 November 2022, pp. 20-27
- Print publication:
- November 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Remote Assessment of Disease and Relapse in Major Depressive Disorder (RADAR-MDD): Recruitment, retention, and data availability in a longitudinal remote measurement study
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 65 / Issue S1 / June 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 September 2022, p. S112
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Prediction and copy number variation identification of ZNF146 gene related to growth traits in Chinese cattle
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Agricultural Science / Volume 160 / Issue 5 / October 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 August 2022, pp. 404-412
-
- Article
- Export citation
Acceleration of 60 MeV proton beams in the commissioning experiment of the SULF-10 PW laser
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 10 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 August 2022, e26
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
AbGradCon 2021: lessons in digital meetings, international collaboration, and interdisciplinarity in astrobiology
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Astrobiology / Volume 21 / Issue 6 / December 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 July 2022, pp. 497-523
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Management of paediatric laryngotracheal trauma
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Laryngology & Otology / Volume 136 / Issue 11 / November 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 July 2022, pp. 1125-1129
- Print publication:
- November 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
An efficient reduced-order framework for active/passive hybrid flutter suppression
-
- Journal:
- The Aeronautical Journal / Volume 127 / Issue 1307 / January 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 May 2022, pp. 24-40
-
- Article
- Export citation
An unsteady aerodynamic model for three-dimensional wing based on augmented lifting-line method
-
- Journal:
- The Aeronautical Journal / Volume 127 / Issue 1307 / January 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 April 2022, pp. 97-115
-
- Article
- Export citation