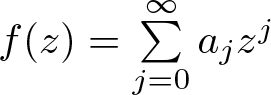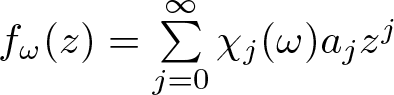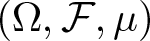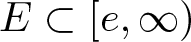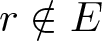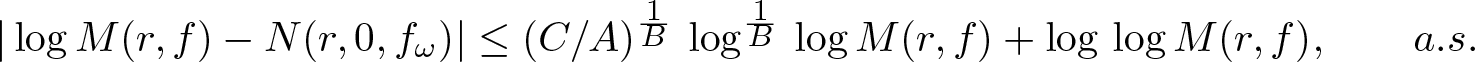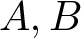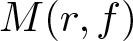261 results
Mediterranean diet for cardiovascular disease: an evidence mapping study
-
- Journal:
- Public Health Nutrition / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 April 2024, pp. 1-22
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Automatic extrinsic calibration for structured light camera and repetitive LiDARs
-
- Journal:
- Robotica , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 April 2024, pp. 1-19
-
- Article
- Export citation
Antimicrobial peptide cecropin B functions in pathogen resistance of Mythimna separata
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of Entomological Research , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 April 2024, pp. 1-12
-
- Article
- Export citation
Structure-function coupling and hierarchy-specific antidepressant response in major depressive disorder
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 April 2024, pp. 1-10
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Distribution and Isotopic Compositions of n-Alkanes and n-Alkenes in Cryoconites from the Glaciers of Tibetan Plateau
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Glaciology / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 March 2024, pp. 1-29
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Revealing complexity: Segmentation of hippocampal subfields in adolescents with major depressive disorder reveals specific links to cognitive dysfunctions
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 February 2024, pp. 1-31
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
East Asian monsoon variations in the loess–desert transitional zone (northern China) during the past 14 ka and their comparison with TraCE21K simulation results
-
- Journal:
- Quaternary Research , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 February 2024, pp. 1-9
-
- Article
- Export citation
Contributing Risk Factors to Self-Contamination During the Process of Donning and Doffing Personal Protective Equipment
-
- Journal:
- Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness / Volume 18 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 February 2024, e19
-
- Article
- Export citation
DNA Methylation Mediated the Association of Body Mass Index With Blood Pressure in Chinese Monozygotic Twins
-
- Journal:
- Twin Research and Human Genetics , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 January 2024, pp. 1-12
-
- Article
- Export citation
Laterite as a Potential Seepage Barrier From a Karst-Depression Tailings Impoundment
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 69 / Issue 1 / February 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 1-22
-
- Article
- Export citation
Characterization of Energetic Protons Generated in the ShenGuang-II UP Petawatt Laser Interactions with Foil Targets
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 2021 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e7
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Effect of Mechanical Activation on the Pozzolanic Activity of Muscovite
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 67 / Issue 3 / June 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 209-216
-
- Article
- Export citation
Advanced Glycation End Products’ Receptor DNA Methylation Associated with Immune Infiltration and Prognosis of Lung Adenocarcinoma and Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma
-
- Journal:
- Genetics Research / Volume 2023 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e4
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Hydration Properties of Mechanically Activated Muscovite in the Presence of Calcium Oxide
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 68 / Issue 6 / December 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 580-587
-
- Article
- Export citation
Identification of Glucose Metabolism-Related Genes in the Progression from Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease to Hepatocellular Carcinoma
-
- Journal:
- Genetics Research / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e13
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Identification of Key Biomarkers and Candidate Molecules in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer by Integrated Bioinformatics Analysis
-
- Journal:
- Genetics Research / Volume 2023 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e29
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Model of a 5-MA Linear-Transformer-Driver Accelerator: Comparison of MITL Performance for Bremsstrahlung Electron Beam Diodes and Z-Pinch Loads
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 2023 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e13
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Prospect of ultrahigh-resolution fast neutron absorption spectroscopy based on a laser plasma electron accelerator
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 12 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 November 2023, e11
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
8 - Assimilation by Names: A Mechanism of Pantheon Development in Local Religion
-
-
- Book:
- Chinese Popular Religion in Text and Acts
- Published by:
- Amsterdam University Press
- Published online:
- 26 March 2024
- Print publication:
- 28 November 2023, pp 189-208
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Inequalities concerning maximum modulus and zeros of random entire functions
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society / Volume 67 / Issue 1 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 October 2023, pp. 57-78
-
- Article
- Export citation