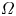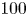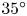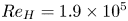149 results
Macrolide-Resistance of Mycoplasma pneumoniae in Several Regions of China from 2013 to 2019
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 April 2024, pp. 1-18
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
The role of deubiquitinases in cardiac disease
-
- Journal:
- Expert Reviews in Molecular Medicine / Volume 26 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 March 2024, e3
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Improving hen welfare on cage-free egg farms in Asia: Egg producers’ perspectives
-
- Journal:
- Animal Welfare / Volume 32 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 September 2023, e64
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Experimental study on the oscillatory Kelvin–Helmholtz instability of a planar liquid sheet in the presence of axial oscillating gas flow
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 959 / 25 March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 March 2023, A18
-
- Article
- Export citation
Metabolic signatures of immune cells in chronic kidney disease
-
- Journal:
- Expert Reviews in Molecular Medicine / Volume 24 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 October 2022, e40
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Sterility of Cydia pomonella by X ray irradiation as an alternative to gamma radiation for the sterile insect technique
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of Entomological Research / Volume 113 / Issue 1 / February 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 August 2022, pp. 72-78
-
- Article
- Export citation
Validity and reproducibility of a FFQ for assessing dietary intake among residents of northeast China: northeast cohort study of China
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 129 / Issue 7 / 14 April 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 August 2022, pp. 1252-1265
- Print publication:
- 14 April 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Long non-coding RNA-EN_181 potentially contributes to the protective effects of N-acetylcysteine against non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in mice
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 129 / Issue 6 / 28 March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 June 2022, pp. 921-935
- Print publication:
- 28 March 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Powder X-ray structural analysis and bandgap measurements for (CaxSr2−x)MnWO6 (x = 0.25, 0.5, 0.75, 1.5, 1.75)
-
- Journal:
- Powder Diffraction / Volume 37 / Issue 3 / September 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 June 2022, pp. 122-132
-
- Article
- Export citation
A fast and accurate transfer alignment method without relying on the empirical model of angular deformation
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Navigation / Volume 75 / Issue 4 / July 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 June 2022, pp. 878-900
- Print publication:
- July 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
Bottom wall shear stress fluctuations in shallow-water Langmuir turbulence
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 942 / 10 July 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 May 2022, A6
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
AlepPBP2, but not AlepPBP3, may involve in the recognition of sex pheromones and maize volatiles in Athetis lepigone
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of Entomological Research / Volume 112 / Issue 4 / August 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 February 2022, pp. 536-545
-
- Article
- Export citation
A high neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio is associated with poor nutritional status in chronic kidney disease patients
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 128 / Issue 10 / 28 November 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 January 2022, pp. 1990-1996
- Print publication:
- 28 November 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Petrogenesis, W metallogenic and tectonic implications of granitic intrusions in the southern Great Xing’an Range W belt, NE China: insights from the Narenwula Complex
-
- Journal:
- Geological Magazine / Volume 159 / Issue 4 / April 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 January 2022, pp. 593-627
-
- Article
- Export citation
Comparing 2 crystal structures and 12 AlphaFold2-predicted human membrane glucose transporters and their water-soluble glutamine, threonine and tyrosine variants
-
- Journal:
- QRB Discovery / Volume 3 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 June 2022, e5
- Print publication:
- 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Comparing 2 crystal structures and 12 AlphaFold2-predicted human membrane glucose transporters and their water-soluble glutamine, threonine and tyrosine variants – CORRIGENDUM
-
- Journal:
- QRB Discovery / Volume 3 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 July 2022, e8
- Print publication:
- 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Triassic trachytic volcanism in the Bangong–Nujiang Ocean: geochemical and geochronological constraints on a continental rifting event
-
- Journal:
- Geological Magazine / Volume 159 / Issue 4 / April 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 December 2021, pp. 519-534
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Explorative gradient method for active drag reduction of the fluidic pinball and slanted Ahmed body
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 932 / 10 February 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 December 2021, A7
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Triassic calc-alkaline lamprophyre dykes from the North Qiangtang, central Tibetan Plateau: evidence for a subduction-modified lithospheric mantle
-
- Journal:
- Geological Magazine / Volume 159 / Issue 3 / March 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 November 2021, pp. 407-420
-
- Article
- Export citation