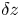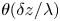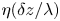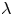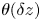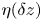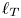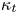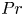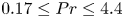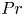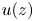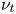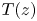50 results
Preparation of Organo-Montmorillonites and the Relationship Between Microstructure and Swellability
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 65 / Issue 6 / December 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 417-430
-
- Article
- Export citation
Origin and Mineralogy of Sepiolite and Palygorskite From the Tuluanshan Formation, Eastern Taiwan
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 57 / Issue 5 / October 2009
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 521-530
-
- Article
- Export citation
Tuning the Acidity of Montmorillonite by H3PO4-Activation and Supporting WO3 for Catalytic Dehydration of Glycerol to Acrolein
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 70 / Issue 3 / June 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 460-479
-
- Article
- Export citation
Association Among Negative Life Events, Sense of Security, and Depressive Symptoms in Chinese Adolescents After the 2013 Ya’an Earthquake
-
- Journal:
- Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness / Volume 17 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 March 2023, e352
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Fluctuation-induced slip of thermal boundary layers at a stable liquid–liquid interface
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 951 / 25 November 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 November 2022, A10
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Profiles of interpersonal relationship qualities and trajectories of internalizing problems among Chinese adolescents
-
- Journal:
- Development and Psychopathology / Volume 36 / Issue 1 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 November 2022, pp. 196-207
-
- Article
- Export citation
A comparison between three-dimensional, transient, thermomechanically coupled first-order and Stokes ice flow models
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Glaciology / Volume 69 / Issue 275 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 October 2022, pp. 513-524
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Long-term psychological profile of general population following COVID-19 outbreak: symptom trajectories and evolution of psychopathological network
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology and Psychiatric Sciences / Volume 31 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 September 2022, e69
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Designing a toroidal crystal for monochromatic X-ray imaging of a laser-produced He-like plasma
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 10 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 September 2022, e37
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Dynamic Observation of Nanovoid Formation in Lithium- Manganese-rich Cathode Materials with Solid Electrolyte
-
- Journal:
- Microscopy and Microanalysis / Volume 28 / Issue S1 / August 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 July 2022, pp. 1928-1929
- Print publication:
- August 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
The Early Cretaceous tectonic evolution of the Neo-Tethys: constraints from zircon U–Pb geochronology and geochemistry of the Liuqiong adakite, Gongga, Tibet
-
- Journal:
- Geological Magazine / Volume 159 / Issue 10 / October 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 June 2022, pp. 1647-1662
-
- Article
- Export citation
Collective effect of thermal plumes on temperature fluctuations in a closed Rayleigh–Bénard convection cell
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 934 / 10 March 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 January 2022, A13
-
- Article
- Export citation
Investigation of three-scalar subgrid-scale mixing in turbulent coaxial jets
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 924 / 10 October 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 August 2021, A40
-
- Article
- Export citation
Atomic-scale mechanisms for fluorination-enhanced cycling stability of cation-disordered rocksalt cathodes
-
- Journal:
- Microscopy and Microanalysis / Volume 27 / Issue S1 / August 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 July 2021, pp. 1256-1258
- Print publication:
- August 2021
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Mean velocity and temperature profiles in turbulent Rayleigh–Bénard convection at low Prandtl numbers
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 918 / 10 July 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 May 2021, A1
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Bacillus amyloliquefaciens ameliorates high-carbohydrate diet-induced metabolic phenotypes by restoration of intestinal acetate-producing bacteria in Nile Tilapia
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 127 / Issue 5 / 14 March 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 April 2021, pp. 653-665
- Print publication:
- 14 March 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
18 - Translanguaging and Momentarity in Social Interaction
- from Part IV - (Trans)Locations and Intersections
-
-
- Book:
- The Cambridge Handbook of Discourse Studies
- Published online:
- 28 September 2020
- Print publication:
- 15 October 2020, pp 394-416
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Fabrication of anti-icing surface with halloysite spherical microcapsule
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 35 / Issue 21 / 16 November 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 October 2020, pp. 2887-2896
- Print publication:
- 16 November 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
Synthesis and characterization of single-bond fullerene dimer derivatives
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 35 / Issue 20 / 28 October 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 September 2020, pp. 2676-2683
- Print publication:
- 28 October 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation