51 results
Sustained Antibacterial Effect of Levofloxacin Drug in a Polymer Matrix by Hybridization With A Layered Double Hydroxide
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 69 / Issue 4 / August 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 443-452
-
- Article
- Export citation
Safety Outcomes of Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors in Adolescent Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder with Comorbid Depression: The ASSURE Study – CORRIGENDUM
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 53 / Issue 10 / July 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 April 2023, p. 4831
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Safety outcomes of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors in adolescent attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder with comorbid depression: the ASSURE study
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 53 / Issue 10 / July 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 February 2023, pp. 4811-4819
-
- Article
- Export citation
Perceptions of the meaning of life among Korean patients with advanced cancer: A mixed-methods study
-
- Journal:
- Palliative & Supportive Care / Volume 21 / Issue 4 / August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 August 2022, pp. 658-669
-
- Article
- Export citation
Identifying Possible Two-Level-System Sources in Superconducting Qubit with Advanced Electron Microscopy
-
- Journal:
- Microscopy and Microanalysis / Volume 28 / Issue S1 / August 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 July 2022, pp. 1716-1717
- Print publication:
- August 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Is spiritual well-being related to survival time of inpatients with advanced cancer? An East Asian cohort study
-
- Journal:
- Palliative & Supportive Care / Volume 21 / Issue 3 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 June 2022, pp. 483-491
-
- Article
- Export citation
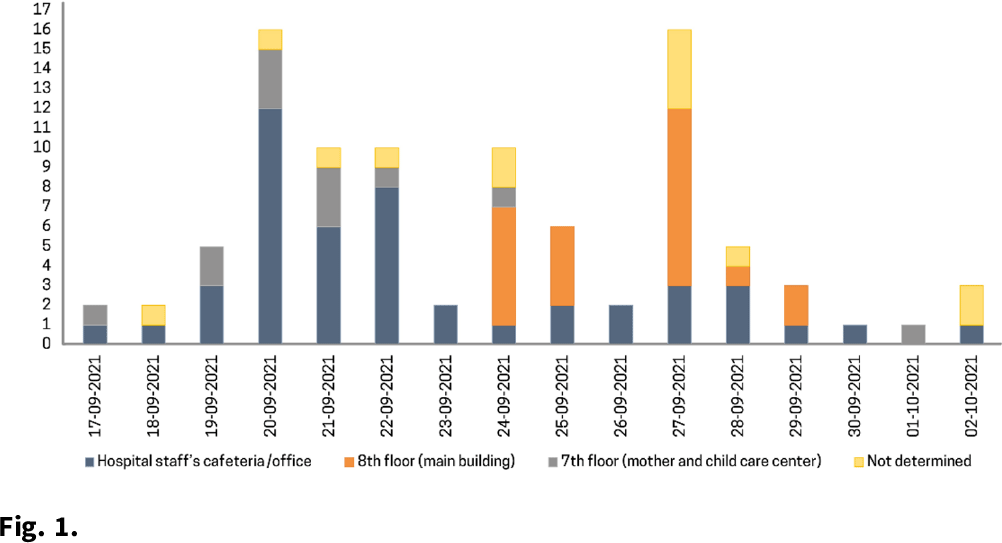
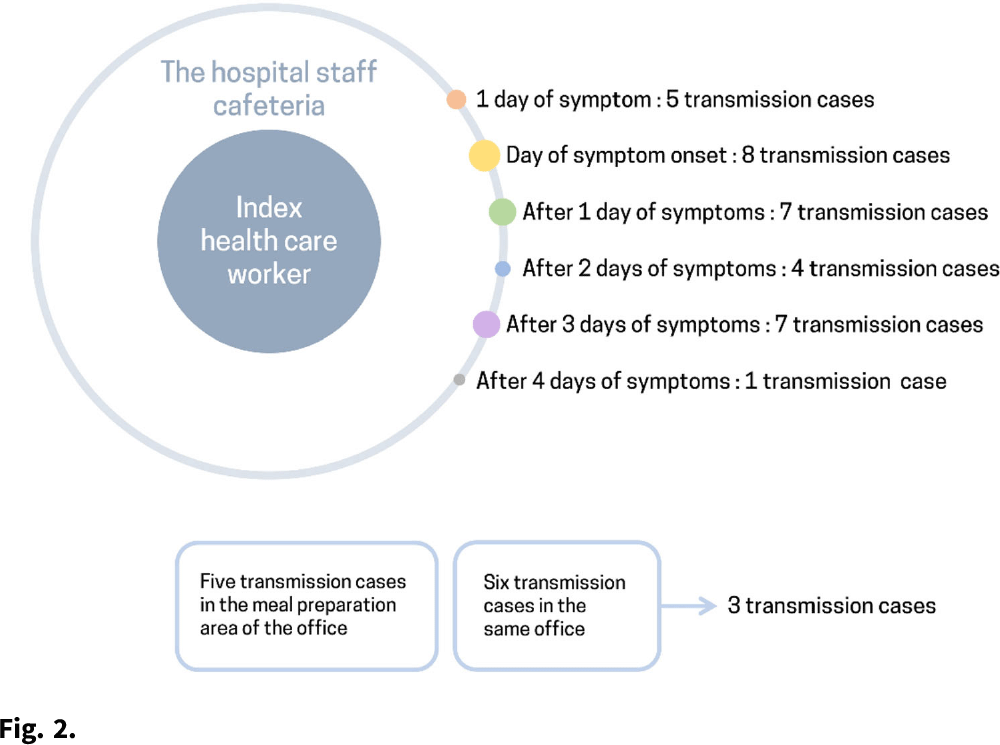
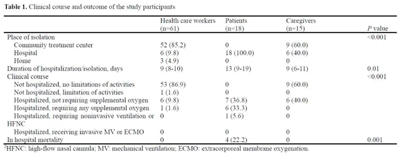
A SARS-CoV-2 outbreak due to vaccine breakthrough in an acute-care hospital
-
- Journal:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology / Volume 2 / Issue S1 / July 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 May 2022, p. s83
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Comparison of Objective Prognostic Score and Palliative Prognostic Score performance in inpatients with advanced cancer in Japan and Korea
-
- Journal:
- Palliative & Supportive Care / Volume 20 / Issue 5 / October 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 October 2021, pp. 662-670
-
- Article
- Export citation
Effectiveness of Steroid Treatment for SARS-CoV-2 Pneumonia With Cryptogenic Organizing Pneumonia-Like Reaction: A Case Report
-
- Journal:
- Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness / Volume 16 / Issue 2 / April 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 October 2020, pp. 491-494
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Kawasaki disease with tsutsugamushi disease: two case reports
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 30 / Issue 6 / June 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 May 2020, pp. 877-879
-
- Article
- Export citation
Concealed resuscitation-related injuries as reversible cause of recurrent arrest following extracorporeal cardiopulmonary resuscitation
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Emergency Medicine / Volume 19 / Issue 5 / September 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 November 2016, pp. 404-409
- Print publication:
- September 2017
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Perioperative Strain Changes of Chronic Otitis Media Surgery: Presenting Author: Su Hee Jeong
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Laryngology & Otology / Volume 130 / Issue S3 / May 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 June 2016, pp. S182-S183
- Print publication:
- May 2016
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Communication for end-of-life care planning among Korean patients with terminal cancer: A context-oriented model
-
- Journal:
- Palliative & Supportive Care / Volume 14 / Issue 1 / February 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 July 2015, pp. 69-76
-
- Article
- Export citation
The preventive effect of breast-feeding for longer than 6 months on early pubertal development among children aged 7–9 years in Korea
-
- Journal:
- Public Health Nutrition / Volume 18 / Issue 18 / December 2015
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 March 2015, pp. 3300-3307
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Borna disease virus and deficit schizophrenia
-
- Journal:
- Acta Neuropsychiatrica / Volume 15 / Issue 5 / October 2003
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 June 2014, pp. 262-265
-
- Article
- Export citation
No borna disease virus-specific RNA detected in blood of race horses and jockeys
-
- Journal:
- Acta Neuropsychiatrica / Volume 18 / Issue 3-4 / June 2006
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 June 2014, pp. 177-180
-
- Article
- Export citation
Microstructural Analysis of Dehydrogenation Products of the Ca(BH4)2–MgH2 Composite
-
- Journal:
- Microscopy and Microanalysis / Volume 19 / Issue S5 / August 2013
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 August 2013, pp. 149-151
- Print publication:
- August 2013
-
- Article
- Export citation
Association of Adiponectin Gene Polymorphism With Birth Weight in Korean Neonates
-
- Journal:
- Twin Research and Human Genetics / Volume 16 / Issue 3 / June 2013
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 April 2013, pp. 732-738
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation