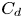64 results
11 - Localizing the Sustainable Development Goals
-
-
- Book:
- India Population Report
- Published online:
- 15 August 2023
- Print publication:
- 30 April 2024, pp 389-451
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Rare inheritance studies on yellow sarson for petalous and apetalous traits
-
- Journal:
- Plant Genetic Resources / Volume 22 / Issue 2 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 March 2024, pp. 125-130
-
- Article
- Export citation
Stimulated Raman Scattering of X-Mode Laser in a Plasma Channel
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 2021 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e12
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Flow past two rotationally oscillating cylinders
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 969 / 25 August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 August 2023, A16
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Shocked confined-granular flow over obstacles
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 960 / 10 April 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 March 2023, A21
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Droplet size distribution in a swirl airstream using in-line holography technique
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 954 / 10 January 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 January 2023, A39
-
- Article
- Export citation
Risk factors for mortality over 18 years in 317 ICUs in 9 Asian countries: The impact of healthcare-associated infections
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 44 / Issue 8 / August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 October 2022, pp. 1261-1266
- Print publication:
- August 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Experimental investigation of three-dimensional modes in the wake of a rotationally oscillating cylinder
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 950 / 10 November 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 October 2022, A10
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Neuromodulatory Effects of Adjunctive High Definition Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (HDtDCS) on Auditory Verbal Hallucinations in Schizophrenia Patients: A Sham Controlled Diffusion Tensor Imaging Study
-
- Journal:
- BJPsych Open / Volume 8 / Issue S1 / June 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 June 2022, p. S59
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
3 - Emerging living arrangements of older adults in India: patterns and welfare implications
-
-
- Book:
- Care for Older Adults in India
- Published by:
- Bristol University Press
- Published online:
- 13 October 2022
- Print publication:
- 31 May 2022, pp 25-42
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Identification of potential donors for false smut resistance in elite breeding lines of rice (Oryza sativa L.) under field conditions
-
- Journal:
- Plant Genetic Resources / Volume 20 / Issue 1 / February 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 May 2022, pp. 7-14
-
- Article
- Export citation
A numerical investigation of granular shock waves over a circular cylinder using the discrete element method
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 936 / 10 April 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 February 2022, A11
-
- Article
- Export citation
Detachment of strong shocks in confined granular flows
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 935 / 25 March 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 January 2022, A13
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A novel design of circularly polarized ring CDRA with wideband impedance bandwidth using slotted microstrip feed line for X-band applications
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Microwave and Wireless Technologies / Volume 14 / Issue 9 / November 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 December 2021, pp. 1149-1158
-
- Article
- Export citation
Flow past a rotationally oscillating cylinder with an attached flexible filament
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 930 / 10 January 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 November 2021, A3
-
- Article
- Export citation
Effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccine in preventing infection and disease severity: a case-control study from an Eastern State of India
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 149 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 October 2021, e224
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Surveillance of Healthcare-Associated Bloodstream and Urinary Tract Infections in a National Level Network of Indian Hospitals
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 41 / Issue S1 / October 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 November 2020, pp. s398-s399
- Print publication:
- October 2020
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
DATING ADOPTION AND INTENSIFICATION OF FOOD-CROPS: INSIGHTS FROM 4MSR (BINJOR), AN INDUS (HARAPPAN) SITE IN NORTHWESTERN INDIA
-
- Journal:
- Radiocarbon / Volume 62 / Issue 5 / October 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 June 2020, pp. 1349-1369
- Print publication:
- October 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
Shock–shock interactions in granular flows
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 884 / 10 February 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 December 2019, R4
-
- Article
- Export citation
Graphene/chitosan-functionalized iron oxide nanoparticles for biomedical applications
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 34 / Issue 20 / 28 October 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 September 2019, pp. 3389-3399
- Print publication:
- 28 October 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation