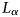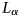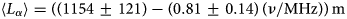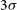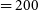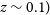261 results
546 Using Contingency Management to Understand the Cardiovascular, Immune and Psychosocial Benefits of Reduced Cocaine Use: A Protocol for a Randomized Controlled Trial
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 8 / Issue s1 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 April 2024, p. 163
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
16 Superior Verbal Learning and Memory in Pediatric Brain Tumor Survivors Treated with Proton Versus Photon Radiotherapy
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 29 / Issue s1 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 December 2023, pp. 17-18
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
71 Treatment with TMS Improves Aspects of Attention in Depression: A Pilot Study
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 29 / Issue s1 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 December 2023, pp. 476-477
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Agricultural Research Service Weed Science Research: Past, Present, and Future
-
- Journal:
- Weed Science / Volume 71 / Issue 4 / July 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 August 2023, pp. 312-327
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Making inroads to precision medicine for the treatment of autoimmune diseases: Harnessing genomic studies to better diagnose and treat complex disorders
-
- Journal:
- Cambridge Prisms: Precision Medicine / Volume 1 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 May 2023, e25
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A report of Bilharziella polonica cercariae in Knowsley Safari, Prescot, United Kingdom, with notes on other trematodes implicated in human cercarial dermatitis
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Helminthology / Volume 96 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 October 2022, e79
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Epidemiology and genomics of a slow outbreak of methicillin-resistant Staphyloccus aureus (MRSA) in a neonatal intensive care unit: Successful chronic decolonization of MRSA-positive healthcare personnel
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 44 / Issue 4 / April 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 June 2022, pp. 589-596
- Print publication:
- April 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
In situ, broadband measurement of the radio frequency attenuation length at Summit Station, Greenland
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Glaciology / Volume 68 / Issue 272 / December 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 May 2022, pp. 1234-1242
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Occupational risk factors for severe acute respiratory coronavirus virus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection among healthcare personnel: A 6-month prospective analysis of the COVID-19 Prevention in Emory Healthcare Personnel (COPE) Study
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 43 / Issue 11 / November 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 February 2022, pp. 1664-1671
- Print publication:
- November 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Seed-shattering phenology at soybean harvest of economically important weeds in multiple regions of the United States. Part 3: Drivers of seed shatter
-
- Journal:
- Weed Science / Volume 70 / Issue 1 / January 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 November 2021, pp. 79-86
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Characterisation of age and polarity at onset in bipolar disorder
-
- Journal:
- The British Journal of Psychiatry / Volume 219 / Issue 6 / December 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 August 2021, pp. 659-669
- Print publication:
- December 2021
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Pharmacological approaches of ADHD
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 64 / Issue S1 / April 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 August 2021, p. S73
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Nomenclature for Pediatric and Congenital Cardiac Care: Unification of Clinical and Administrative Nomenclature – The 2021 International Paediatric and Congenital Cardiac Code (IPCCC) and the Eleventh Revision of the International Classification of Diseases (ICD-11)
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 31 / Issue 7 / July 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 July 2021, pp. 1057-1188
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Successful management of invasive rats across a fragmented landscape
-
- Journal:
- Environmental Conservation / Volume 48 / Issue 3 / September 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 June 2021, pp. 200-207
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Murchison Widefield Array rapid-response observations of the short GRB 180805A
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 38 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 June 2021, e026
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Chronic effects of wild blueberry (poly)phenols on cognitive function in healthy older individuals: the BluFlow study
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Nutrition Society / Volume 80 / Issue OCE2 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 May 2021, E69
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Development of an online food database for the Batwa and Bakiga communities living in south-western Uganda
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Nutrition Society / Volume 80 / Issue OCE1 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 April 2021, E19
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
A history of high-power laser research and development in the United Kingdom
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 9 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 April 2021, e18
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Outbreak of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) among operating room staff of a tertiary referral center: An epidemiologic and environmental investigation
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 43 / Issue 3 / March 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 March 2021, pp. 319-325
- Print publication:
- March 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Occupational risk factors for severe acute respiratory coronavirus virus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection among healthcare personnel: A cross-sectional analysis of subjects enrolled in the COVID-19 Prevention in Emory Healthcare Personnel (COPE) study
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 43 / Issue 3 / March 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 February 2021, pp. 381-386
- Print publication:
- March 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation