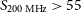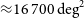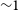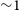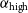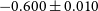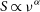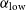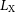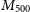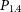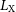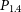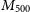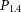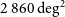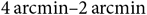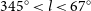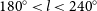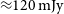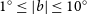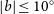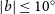91 results
Competition among the two-plasmon decay of backscattered light, filamentation of the electron-plasma wave and side stimulated Raman scattering
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 11 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 August 2023, e76
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The GLEAM 200-MHz local radio luminosity function for AGN and star-forming galaxies
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 38 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 September 2021, e041
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Diffuse galaxy cluster emission at 168 MHz within the Murchison Widefield Array Epoch of Reionization 0-h field
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 38 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 March 2021, e010
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
LINEARLY IMPLICIT ENERGY-PRESERVING FOURIER PSEUDOSPECTRAL SCHEMES FOR THE COMPLEX MODIFIED KORTEWEG–DE VRIES EQUATION
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- The ANZIAM Journal / Volume 62 / Issue 3 / July 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 January 2021, pp. 256-273
-
- Article
- Export citation
Effects of guanidinoacetic acid and coated folic acid supplementation on growth performance, nutrient digestion and hepatic gene expression in Angus bulls
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 126 / Issue 4 / 28 August 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 November 2020, pp. 510-517
- Print publication:
- 28 August 2021
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Laboratory findings and a combined multifactorial approach to predict death in critically ill patients with COVID-19: a retrospective study
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 148 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 June 2020, e129
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
1393 – The Study On Validity And Reliability Of Questionnaires Related To Family Environment
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 28 / Issue S1 / 2013
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 April 2020, 28-E723
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Healthcare resource use of paliperidone palmitate 3-month injection vs. paliperidone palmitate 1-month injection: An analysis of phase III clinical trial hospital data
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 33 / Issue S1 / March 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 March 2020, pp. s265-s266
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
New candidate radio supernova remnants detected in the GLEAM survey over 345° < l < 60°, 180° < l < 240°
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 36 / 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 November 2019, e045
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
GaLactic and Extragalactic All-sky Murchison Widefield Array (GLEAM) survey II: Galactic plane 345° < l < 67°, 180° < l < 240°
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 36 / 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 November 2019, e047
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Candidate radio supernova remnants observed by the GLEAM survey over 345° < l < 60° and 180° < l < 240°
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 36 / 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 November 2019, e048
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Burst behavior due to the quasimode excited by stimulated Brillouin scattering in high-intensity laser–plasma interactions
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 7 / 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 November 2019, e58
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Potential use of spectroscopic techniques for assessing table eggs and hatching eggs
-
- Journal:
- World's Poultry Science Journal / Volume 75 / Issue 3 / September 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 August 2019, pp. 445-456
- Print publication:
- September 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
Gridded and direct Epoch of Reionisation bispectrum estimates using the Murchison Widefield Array
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 36 / 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 July 2019, e023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Enhancement of the surface emission at the fundamental frequency and the transmitted high-order harmonics by pre-structured targets
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 7 / 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 June 2019, e36
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The identification and expression analysis of candidate chemosensory genes in the bird cherry-oat aphid Rhopalosiphum padi (L.)
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of Entomological Research / Volume 108 / Issue 5 / October 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 December 2017, pp. 645-657
-
- Article
- Export citation
Calibration and Stokes Imaging with Full Embedded Element Primary Beam Model for the Murchison Widefield Array
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 34 / 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 November 2017, e062
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Genotype and genetic variation of HCV infections with low-risk factors in Putian coastal regions, China
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 145 / Issue 16 / December 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 October 2017, pp. 3385-3397
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
A High-Resolution Foreground Model for the MWA EoR1 Field: Model and Implications for EoR Power Spectrum Analysis
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 34 / 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 August 2017, e033
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation