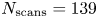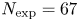308 results
From Indigenous philosophy in environmental education to Indigenous planetary futures: what would it take?
-
- Journal:
- Australian Journal of Environmental Education / Volume 39 / Issue 3 / September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 September 2023, pp. 320-335
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Advocacy at the Eighth World Congress of Pediatric Cardiology and Cardiac Surgery
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 33 / Issue 8 / August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 August 2023, pp. 1277-1287
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Chapter 2 - Letters
- from Part I - Life and Works
-
-
- Book:
- Wilkie Collins in Context
- Published online:
- 27 July 2023
- Print publication:
- 10 August 2023, pp 11-18
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Preliminary evaluation of a smartphone application (DelApp) for identification of delirium in sub-Saharan Africa
-
- Journal:
- Acta Neuropsychiatrica , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 June 2023, pp. 1-9
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
1 - Improving public policy and administration: exploring the potential of design
-
-
- Book:
- Policy-Making as Designing
- Published by:
- Bristol University Press
- Published online:
- 20 January 2024
- Print publication:
- 24 May 2023, pp 1-17
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography and endoscopic ultrasound endoscope reprocessing: Variables impacting contamination risk
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 44 / Issue 9 / September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 January 2023, pp. 1485-1489
- Print publication:
- September 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Statistical characterization of experimental magnetized liner inertial fusion stagnation images using deep-learning-based fuel–background segmentation
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Plasma Physics / Volume 88 / Issue 5 / October 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 September 2022, 895880501
-
- Article
- Export citation
Pharmacological interventions for treatment-resistant depression in adults: a Cochrane Review
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- BJPsych Advances / Volume 28 / Issue 1 / January 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 December 2021, pp. 2-3
- Print publication:
- January 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Nomenclature for Pediatric and Congenital Cardiac Care: Unification of Clinical and Administrative Nomenclature – The 2021 International Paediatric and Congenital Cardiac Code (IPCCC) and the Eleventh Revision of the International Classification of Diseases (ICD-11)
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 31 / Issue 7 / July 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 July 2021, pp. 1057-1188
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Preserving last resort antibiotics: A meropenem reduction strategy
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 43 / Issue 10 / October 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 July 2021, pp. 1516-1517
- Print publication:
- October 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
A history of high-power laser research and development in the United Kingdom
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 9 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 April 2021, e18
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Prevalence and 1-year incidence of HIV-associated neurocognitive disorder (HAND) in adults aged ≥50 years attending standard HIV clinical care in Kilimanjaro, Tanzania
-
- Journal:
- International Psychogeriatrics / Volume 35 / Issue 7 / July 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 March 2021, pp. 339-350
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Responding to Natural and Industrial Disasters: Partnerships and Lessons Learned
-
- Journal:
- Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness / Volume 16 / Issue 3 / June 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 March 2021, pp. 885-888
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
On the Ethics of Reconstructing Destroyed Cultural Heritage Monuments
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the American Philosophical Association / Volume 6 / Issue 4 / Winter 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 November 2020, pp. 483-501
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Characteristics of Cases With Polymicrobial Bloodstream Infections Involving Candida in Multisite Surveillance, 2017
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 41 / Issue S1 / October 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 November 2020, p. s163
- Print publication:
- October 2020
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Onsite-Assessment of Infection Prevention Preparedness in Community Healthcare Settings
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 41 / Issue S1 / October 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 November 2020, pp. s335-s336
- Print publication:
- October 2020
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Psychological therapies for treatment-resistant depression in adults: a Cochrane Review
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- BJPsych Advances / Volume 26 / Issue 5 / September 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 August 2020, p. 254
- Print publication:
- September 2020
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Diagnosis to death: family experiences of paediatric heart disease
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 30 / Issue 11 / November 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 August 2020, pp. 1672-1678
-
- Article
- Export citation
24 - Precision Behavioral Management (PBM): A Novel Genetically Guided Therapy to Combat Reward Deficiency Syndrome (RDS) Relevant to the Opiate Crisis
- from Part V - Ongoing and Future Research Directions
-
-
- Book:
- The Cambridge Handbook of Substance and Behavioral Addictions
- Published online:
- 13 July 2020
- Print publication:
- 06 August 2020, pp 297-306
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Universal masking is an effective strategy to flatten the severe acute respiratory coronavirus virus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) healthcare worker epidemiologic curve
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 41 / Issue 12 / December 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 June 2020, pp. 1466-1467
- Print publication:
- December 2020
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation