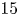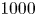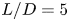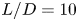585 results
Macrolide-Resistance of Mycoplasma pneumoniae in Several Regions of China from 2013 to 2019
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 April 2024, pp. 1-18
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Effectiveness of GLIM and SGA for diagnosing malnutrition and predicting wound healing in patients with diabetic foot ulcers
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 April 2024, pp. 1-30
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Trauma diagnostic-related target proteins and their detection techniques
-
- Journal:
- Expert Reviews in Molecular Medicine / Volume 26 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 April 2024, e7
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Immune control in Kawasaki disease knowledge mapping: a bibliometric analysis
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 April 2024, pp. 1-16
-
- Article
- Export citation
Age-atypical brain functional networks in autism spectrum disorder: a normative modeling approach
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 April 2024, pp. 1-12
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Effect of dietary selenium intake on cardiovascular disease: A retrospective cohort study based on China Health and Nutrition Survey (CHNS) data
-
- Journal:
- Public Health Nutrition / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 March 2024, pp. 1-23
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Turbulent wake characteristics for a circular cylinder in proximity to a moving wall
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 983 / 25 March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 March 2024, A18
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
How top leaders’ support affects open government data (OGD)-driven innovation capacity of firms: Based on the TOE framework perspective
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Management & Organization , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 March 2024, pp. 1-17
-
- Article
- Export citation
Vortex dynamics and boundary layer transition in flow around a rectangular cylinder with different aspect ratios at medium Reynolds number
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 982 / 10 March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 February 2024, A5
-
- Article
- Export citation
An exponential nonuniform Berry–Esseen bound of the maximum likelihood estimator in a Jacobi process
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Applied Probability , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 February 2024, pp. 1-18
-
- Article
- Export citation
Identification of Philaster apodigitiformis in aquaculture and functional characterization of its β-PKA gene and expression analysis of infected Poecilia reticulata
-
- Journal:
- Parasitology / Volume 151 / Issue 4 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 February 2024, pp. 370-379
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Renewable energy prosocial behavior, is it source dependent?
-
- Journal:
- Agricultural and Resource Economics Review / Volume 53 / Issue 1 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 February 2024, pp. 185-207
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
East Asian monsoon variations in the loess–desert transitional zone (northern China) during the past 14 ka and their comparison with TraCE21K simulation results
-
- Journal:
- Quaternary Research , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 February 2024, pp. 1-9
-
- Article
- Export citation
A Theoretical Study of the Effect of Carboxyl Hydroxamic Acid on the Flotation Behavior of Diaspore and Aluminosilicate Minerals
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 60 / Issue 1 / February 2012
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 52-62
-
- Article
- Export citation
Effect of Viscosity on Stopping Power for a Charged Particle Moving above Two-Dimensional Electron Gas
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e19
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Formation and Transformation of Manganese Oxide Minerals on the Surface of Kaolinite
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 71 / Issue 1 / February 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 106-118
-
- Article
- Export citation
Comprehensive Multiomics Analysis of Monozygotic Twin Discordant for Double Outlet Right Ventricle
-
- Journal:
- Twin Research and Human Genetics / Volume 26 / Issue 6 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 December 2023, pp. 370-378
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Theoretical analysis of frequency modulation-to-amplitude modulation on the final optics and target of the SG II-Up laser facility
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 12 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 December 2023, e9
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation