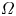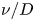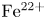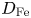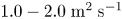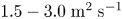53 results
Establishment of a secondary infection laboratory model of Echinococcus shiquicus metacestode using BALB/c mice and Mongolian jirds (Meriones unguiculatus)
-
- Journal:
- Parasitology / Volume 150 / Issue 9 / August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 July 2023, pp. 813-820
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Factual and counterfactual learning in major adolescent depressive disorder, evidence from an instrumental learning study
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 54 / Issue 2 / January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 May 2023, pp. 256-266
-
- Article
- Export citation
Experimental study on the oscillatory Kelvin–Helmholtz instability of a planar liquid sheet in the presence of axial oscillating gas flow
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 959 / 25 March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 March 2023, A18
-
- Article
- Export citation
Variation in placental microRNA expression associates with maternal family history of cardiovascular disease
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Developmental Origins of Health and Disease / Volume 14 / Issue 1 / February 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 July 2022, pp. 132-139
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Ordering the Myriad Things: From Traditional Knowledge to Scientific Botany By Nicholas K. Menzies. Seattle: University of Washington Press, 2021. 312 pp. $ 99.00 (cloth) $30.00 (paper)
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Chinese History / Volume 6 / Issue 2 / July 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 May 2022, pp. 386-388
-
- Article
- Export citation
Depressive symptoms and cognitive impairment: A 10-year follow-up study from the Survey of Health, Ageing and Retirement in Europe
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 64 / Issue 1 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 August 2021, e55
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Protocol for a pharmacogenomic study on individualised antipsychotic drug treatment for patients with schizophrenia
-
- Journal:
- BJPsych Open / Volume 7 / Issue 4 / July 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 June 2021, e121
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Experimental and simulation study of impurity transport response to RMPs in RF-heated H-mode plasmas at EAST
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Plasma Physics / Volume 87 / Issue 2 / April 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 March 2021, 905870213
-
- Article
- Export citation
Echinococcus shiquicus in Qinghai–Tibet plateau: population structure and confirmation of additional endemic areas
-
- Journal:
- Parasitology / Volume 148 / Issue 7 / June 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 March 2021, pp. 879-886
-
- Article
- Export citation
CLASS NUMBERS OF CM ALGEBRAIC TORI, CM ABELIAN VARIETIES AND COMPONENTS OF UNITARY SHIMURA VARIETIES
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Nagoya Mathematical Journal / Volume 245 / March 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 October 2020, pp. 74-99
- Print publication:
- March 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
A new molecular nomenclature for Taenia hydatigena: mitochondrial DNA sequences reveal sufficient diversity suggesting the assignment of major haplotype divisions
-
- Journal:
- Parasitology / Volume 148 / Issue 3 / March 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 October 2020, pp. 311-326
-
- Article
- Export citation
Herbicidal activity and molecular docking study of novel PPO inhibitors
-
- Journal:
- Weed Science / Volume 68 / Issue 6 / November 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 August 2020, pp. 565-574
-
- Article
- Export citation
One-dimensional steady-state model for stimulated Raman and Brillouin backscatter processes in laser-irradiated plasmas
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 38 / Issue 3 / September 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 July 2020, pp. 169-175
-
- Article
- Export citation
1433 – Study On The Influence Of Genetic And Environmental Factor On Personality Of Chongqing Twins Children
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 28 / Issue S1 / 2013
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 April 2020, 28-E754
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
1418 – How Do The Genetic And Environmental Factor Influence The Mental Health Of Chongqing Twins Children
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 28 / Issue S1 / 2013
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 April 2020, 28-E741
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
First report of Echinococcus granulosus sensu stricto (G1) in Nigeria, West Africa
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Helminthology / Volume 94 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 November 2019, e109
-
- Article
- Export citation
Shotgun metagenomics reveals both taxonomic and tryptophan pathway differences of gut microbiota in major depressive disorder patients
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 51 / Issue 1 / January 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 November 2019, pp. 90-101
-
- Article
- Export citation
Association between edible mushroom intake and the prevalence of newly diagnosed non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: results from the Tianjin Chronic Low-Grade Systemic Inflammation and Health Cohort Study in China
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 123 / Issue 1 / 14 January 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 October 2019, pp. 104-112
- Print publication:
- 14 January 2020
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Calibration and verification of streaked optical pyrometer system used for laser-induced shock experiments
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 7 / 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 August 2019, e49
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Association of dietary patterns with depressive symptoms in Chinese postmenopausal women
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 122 / Issue 10 / 28 November 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 July 2019, pp. 1168-1174
- Print publication:
- 28 November 2019
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation