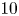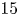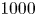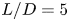317 results
Calorie restriction improves serum lipid metabolism, colon metabolites and microbiota in pigs
-
- Journal:
- Animal Nutriomics / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 September 2024, pp. 1-35
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
What determines respondents’ valuation uncertainty? Impact of subjective perceptions from the demand and supply sides
-
- Journal:
- Environment and Development Economics , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 June 2024, pp. 1-26
-
- Article
- Export citation
Compression and acceleration processes of spherical shells in gold cones
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 12 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 April 2024, e43
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Structure-function coupling and hierarchy-specific antidepressant response in major depressive disorder
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 April 2024, pp. 1-10
-
- Article
- Export citation
Shared genetic basis and causality between schizophrenia and inflammatory bowel disease: evidence from a comprehensive genetic analysis
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 April 2024, pp. 1-11
-
- Article
- Export citation
Dynamic aberrances of substantia nigra-relevant coactivation patterns in first-episode treatment-naïve patients with schizophrenia
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 March 2024, pp. 1-11
-
- Article
- Export citation
Vortex dynamics and boundary layer transition in flow around a rectangular cylinder with different aspect ratios at medium Reynolds number
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 982 / 10 March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 February 2024, A5
-
- Article
- Export citation
P31: Prescribing patterns for older age bipolar disorder patients discharged from two public mental hospitals in Taiwan, 2006-2019
-
- Journal:
- International Psychogeriatrics / Volume 35 / Issue S1 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 February 2024, p. 199
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Therapeutic efficacy of probiotics for symptoms of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder in children and adolescents: meta-analysis
-
- Journal:
- BJPsych Open / Volume 10 / Issue 1 / January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 January 2024, e36
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Contract noncompliance in agricultural conservation programs: Panel evidence from Louisiana, USA
-
- Journal:
- Agricultural and Resource Economics Review , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 January 2024, pp. 1-26
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Voltage-gated sodium channel gene mutation and P450 gene expression are associated with the resistance of Aphis spiraecola Patch (Hemiptera: Aphididae) to lambda-cyhalothrin
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of Entomological Research / Volume 114 / Issue 1 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 January 2024, pp. 49-56
-
- Article
- Export citation
Synthesis and Adsorption Desulfurization Performance of Modified Mesoporous Silica Materials M-MCM-41 (M = Fe, Co, Zn)
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 67 / Issue 4 / August 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 325-333
-
- Article
- Export citation
Preparation of Organo-Montmorillonites and the Relationship Between Microstructure and Swellability
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 65 / Issue 6 / December 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 417-430
-
- Article
- Export citation
Dispersion and Swellability of Ternary Surfactant Co-Modified Montmorillonites
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 69 / Issue 6 / December 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 759-771
-
- Article
- Export citation
Identification of a Novel 15q21.1 Microdeletion in a Family with Marfan Syndrome
-
- Journal:
- Genetics Research / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e65
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
TPX2 Serves as a Cancer Susceptibility Gene and Is Closely Associated with the Poor Prognosis of Endometrial Cancer
-
- Journal:
- Genetics Research / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e70
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Dynamic structure–function coupling across three major psychiatric disorders
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 54 / Issue 8 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 December 2023, pp. 1629-1640
-
- Article
- Export citation
Is auditory processing measured by the N100 an endophenotype for psychosis? A family study and a meta-analysis
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 54 / Issue 8 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 November 2023, pp. 1559-1572
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Protective factors for children with autism spectrum disorder during COVID-19-related strict lockdowns: a Shanghai autism early developmental cohort study
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 54 / Issue 6 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 November 2023, pp. 1102-1112
-
- Article
- Export citation