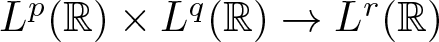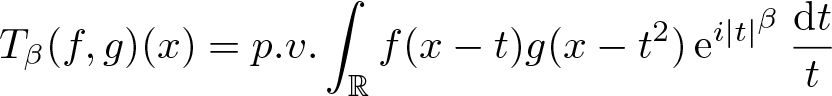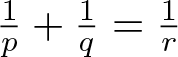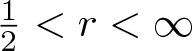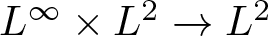8 results
The boundedness of the bilinear oscillatory integral along a parabola
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society / Volume 66 / Issue 1 / February 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 April 2023, pp. 54-88
-
- Article
- Export citation
The impact of self-efficacy on first onset and prognosis of major depressive disorder: Findings from a longitudinal study in a sample of Chinese first-year university students – Corrigendum
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 52 / Issue 1 / January 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 August 2021, p. 199
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
The impact of self-efficacy on first onset and prognosis of major depressive disorder: findings from a longitudinal study in a sample of Chinese first-year university students
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 52 / Issue 1 / January 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 August 2021, pp. 178-183
-
- Article
- Export citation
Dynamic risk prewarning in ship encounter process considering domain violation
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Navigation / Volume 74 / Issue 6 / November 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 August 2021, pp. 1416-1431
- Print publication:
- November 2021
-
- Article
- Export citation
On isolated millisecond pulsars formed by the coalescence of neutron stars and massive white dwarfs
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 36 / 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 February 2019, e005
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Nanoscopic imaging of energy transfer from single plasmonic particles to semiconductor substrates via STEM/EELS
-
- Journal:
- Microscopy and Microanalysis / Volume 21 / Issue S3 / August 2015
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 September 2015, pp. 1909-1910
- Print publication:
- August 2015
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Shape measurement by using basis functions
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the International Astronomical Union / Volume 8 / Issue S288 / August 2012
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 January 2013, pp. 306-308
- Print publication:
- August 2012
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
GW-level high-power CO2 laser system
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 10 / Issue 3 / September 1992
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 March 2009, pp. 413-419
-
- Article
- Export citation