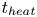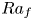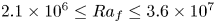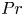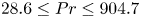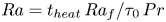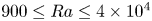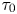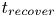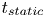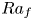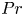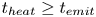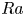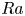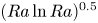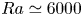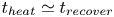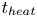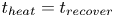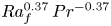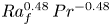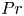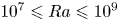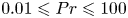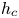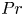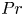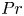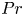35 results
Formation and evolution of laminar thermal structures: correlation to the thermal boundary layer and effects of heating time
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 984 / 10 April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 April 2024, A60
-
- Article
- Export citation
Compact Thomson Scattering Source Based on a Mixed Injection Assisted Laser Wakefield Accelerator
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e9
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The egg ribonuclease SjCP1412 accelerates liver fibrosis caused by Schistosoma japonicum infection involving damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs)
-
- Journal:
- Parasitology / Volume 151 / Issue 3 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 December 2023, pp. 260-270
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Epidemiological characteristics, spatial clusters and monthly incidence prediction of hand, foot and mouth disease from 2017 to 2022 in Shanxi Province, China
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 151 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 March 2023, e54
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Investigation of a Fused in Sarcoma Splicing Mutation in a Chinese Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Patient
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 50 / Issue 6 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 December 2022, pp. 891-896
-
- Article
- Export citation
Late Palaeozoic tectonic evolution of the eastern Palaeo-Asian Ocean: new evidence from the early Permian arc magmatic suites in the Kulun region
-
- Journal:
- Geological Magazine / Volume 159 / Issue 9 / September 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 July 2022, pp. 1513-1528
-
- Article
- Export citation
The Early Cretaceous tectonic evolution of the Neo-Tethys: constraints from zircon U–Pb geochronology and geochemistry of the Liuqiong adakite, Gongga, Tibet
-
- Journal:
- Geological Magazine / Volume 159 / Issue 10 / October 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 June 2022, pp. 1647-1662
-
- Article
- Export citation
Red Alert: It Is Time to Strengthen the Medical Knowledge of Noncompressible Torso Hemorrhage Among Health-Care Workers
-
- Journal:
- Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness / Volume 16 / Issue 5 / October 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 October 2021, pp. 2020-2028
-
- Article
- Export citation
Glucosamine use, smoking and risk of incident chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a large prospective cohort study
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 128 / Issue 4 / 28 August 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 September 2021, pp. 721-732
- Print publication:
- 28 August 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Impacts of lockdown on dietary patterns among youths in China: the COVID-19 Impact on Lifestyle Change Survey
-
- Journal:
- Public Health Nutrition / Volume 24 / Issue 11 / August 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 May 2021, pp. 3221-3232
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Associations of spicy food flavour and intake frequency with blood lipid levels and risk of abnormal serum lipid levels in Chinese rural population: a cross-sectional study
-
- Journal:
- Public Health Nutrition / Volume 24 / Issue 18 / December 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 April 2021, pp. 6201-6210
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Early Cretaceous crust–mantle interaction linked to rollback of the Palaeo-Pacific flat-subducting slab: constraints from the intermediate–felsic volcanic rocks of the northern Great Xing’an Range, NE China
-
- Journal:
- Geological Magazine / Volume 158 / Issue 9 / September 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 March 2021, pp. 1617-1638
-
- Article
- Export citation
The
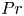 $Pr$-dependence of the critical roughness height in two-dimensional turbulent Rayleigh–Bénard convection
$Pr$-dependence of the critical roughness height in two-dimensional turbulent Rayleigh–Bénard convection
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 911 / 25 March 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 February 2021, A52
-
- Article
- Export citation
One-step synthesis of nitrogen-decorated CeO2/reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite and its electrocatalytic activity for triiodide/iodide reduction
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 35 / Issue 11 / 15 June 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 May 2020, pp. 1461-1471
- Print publication:
- 15 June 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
The VNTR of the AS3MT gene is associated with brain activations during a memory span task and their training-induced plasticity
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 51 / Issue 11 / August 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 April 2020, pp. 1927-1932
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A pilot study on the association between the blood oxygen level-dependent signal in the reward system and dopamine transporter availability in adults with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder
-
- Journal:
- CNS Spectrums / Volume 26 / Issue 3 / June 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 April 2020, pp. 299-306
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Microstructure and corrosion resistance of Ni–P gradient coating/stannate conversion film on magnesium alloy
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 34 / Issue 6 / 28 March 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 February 2019, pp. 1064-1072
- Print publication:
- 28 March 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
New species and new records of Ophioparmaceae (lichenized Ascomycota) from China
-
- Journal:
- The Lichenologist / Volume 50 / Issue 1 / January 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 January 2018, pp. 89-99
- Print publication:
- January 2018
-
- Article
- Export citation
Significant changes in ITIH4, AHSG, ORM1, and CD46 content in milk fat globule membrane proteins of ketotic dairy cows
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Dairy Research / Volume 84 / Issue 4 / November 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 November 2017, pp. 407-413
- Print publication:
- November 2017
-
- Article
- Export citation