22 results
The connective
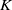 $K$-theory of the Eilenberg–MacLane space
$K$-theory of the Eilenberg–MacLane space 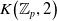 $K\!\left({\mathbb{Z}}_p,\textrm{2}\right)$
$K\!\left({\mathbb{Z}}_p,\textrm{2}\right)$
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Glasgow Mathematical Journal / Volume 66 / Issue 1 / January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 December 2023, pp. 188-220
- Print publication:
- January 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
338 The Alabama Genomic Health Initiative: Integrating Genomic Medicine into Primary Care
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 7 / Issue s1 / April 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 April 2023, pp. 100-101
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Planning for patient-reported outcome implementation: Development of decision tools and practical experience across four clinics
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 4 / Issue 6 / December 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 April 2020, pp. 498-507
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
An n-dimensional Klein bottle
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 149 / Issue 5 / October 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 January 2019, pp. 1207-1221
- Print publication:
- October 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
Metolachlor and Alachlor Effects on Membrane Permeability and Lipid Synthesis
-
- Journal:
- Weed Science / Volume 30 / Issue 4 / July 1982
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 June 2017, pp. 399-404
-
- Article
- Export citation
Contributors
-
-
- Book:
- The Cambridge Dictionary of Philosophy
- Published online:
- 05 August 2015
- Print publication:
- 27 April 2015, pp ix-xxx
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Coordinated Microanalyses of Seven Particles of Probable Interstellar Origin from the Stardust Mission.
-
- Journal:
- Microscopy and Microanalysis / Volume 20 / Issue S3 / August 2014
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 August 2014, pp. 1692-1693
- Print publication:
- August 2014
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Effects of kiwifruit extracts on colonic gene and protein expression levels in IL-10 gene-deficient mice
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 108 / Issue 1 / 14 July 2012
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 December 2011, pp. 113-129
- Print publication:
- 14 July 2012
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Contributors
-
-
- Book:
- Behavioral and Psychopharmacologic Pain Management
- Published online:
- 10 January 2011
- Print publication:
- 25 November 2010, pp ix-xii
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Contributors
-
-
- Book:
- The Cambridge Dictionary of Christianity
- Published online:
- 05 August 2012
- Print publication:
- 20 September 2010, pp xi-xliv
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Contributors
-
-
- Book:
- Antipsychotic Trials in Schizophrenia
- Published online:
- 03 May 2010
- Print publication:
- 01 April 2010, pp ix-x
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
17 - The use of EEG in assessing acute and chronic brain damage in the newborn
- from Section 3 - Diagnosis of the infant with brain injury
-
-
- Book:
- Fetal and Neonatal Brain Injury
- Published online:
- 12 January 2010
- Print publication:
- 18 June 2009, pp 196-208
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
The developmental pathways to schizophrenia: Potential moderating effects of stress
-
- Journal:
- Development and Psychopathology / Volume 8 / Issue 4 / Fall 1996
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 March 2009, pp. 647-665
-
- Article
- Export citation
SOME NEW IMMERSION RESULTS FOR COMPLEX PROJECTIVE SPACE
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society / Volume 51 / Issue 1 / February 2008
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 February 2008, pp. 45-56
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Ostracodes as Hydrologic Indicators in Springs, Streams and Wetlands: A Tool for Environmental and Paleoenvironmental Assessment
-
- Journal:
- The Paleontological Society Papers / Volume 9 / November 2003
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 July 2017, pp. 203-222
- Print publication:
- November 2003
-
- Article
- Export citation
5 - Some remarks on υ1 -periodic homotopy groups
-
-
- Book:
- Adams Memorial Symposium on Algebraic Topology
- Published online:
- 18 January 2010
- Print publication:
- 07 May 1992, pp 55-72
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
6 - The unstable Novikov spectral sequence for Sp(n), and the power series sinh−1(x)
-
-
- Book:
- Adams Memorial Symposium on Algebraic Topology
- Published online:
- 18 January 2010
- Print publication:
- 07 May 1992, pp 73-86
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Elliptical Galaxies and Large-Scale Velocity Flows
-
- Journal:
- Symposium - International Astronomical Union / Volume 130 / 1988
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 August 2017, pp. 169-176
- Print publication:
- 1988
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Non-Uniformities in the Hubble Flow: Results from a Survey of Elliptical Galaxies
-
- Journal:
- Symposium - International Astronomical Union / Volume 124 / 1987
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2016, pp. 223-227
- Print publication:
- 1987
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
The spectrum (P ⋀ bo) −∞
-
- Journal:
- Mathematical Proceedings of the Cambridge Philosophical Society / Volume 96 / Issue 1 / July 1984
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 October 2008, pp. 85-93
- Print publication:
- July 1984
-
- Article
- Export citation



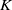
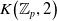
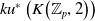
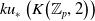
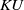
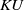
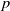
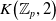
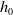
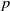
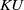
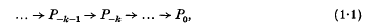
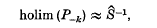
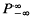 this holim (
this holim (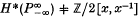 , but rather
, but rather