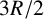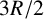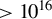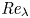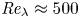774 results
Seasonality in regional brain glucose metabolism
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 April 2024, pp. 1-9
-
- Article
- Export citation
A molecular perspective on the genera Paragonimus Braun, Euparagonimus Chen and Pagumogonimus Chen
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Helminthology / Volume 73 / Issue 4 / April 1999
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 April 2024, pp. 295-299
-
- Article
- Export citation
426 A Beat Away from Precision Medicine: Characterizing Human Cardiac Fibroblast Responsiveness to Hemodynamic Unloading in Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 8 / Issue s1 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 April 2024, p. 127
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
The Effect of Clay Dispersion on the Sorption of Acetonitrile
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 40 / Issue 3 / June 1992
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 February 2024, pp. 355-358
-
- Article
- Export citation
Characterization of Iron-Manganese Concretions in Kentucky Alfisols with Perched Water Tables
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 45 / Issue 3 / June 1997
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 February 2024, pp. 428-439
-
- Article
- Export citation
Fixed-time anti-saturation control with concise system structure for the 6-DOF motion of spacecraft
-
- Journal:
- The Aeronautical Journal , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 February 2024, pp. 1-25
-
- Article
- Export citation
Racial and ethnic differences in the degree of participation and retention in a decentralized cohort study of COVID-19 immunization in patients with inflammatory bowel diseases
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 8 / Issue 1 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 January 2024, e31
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Patterns of polysomnography parameters in 27 neuropsychiatric diseases: An umbrella review – CORRIGENDUM
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 54 / Issue 2 / January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 January 2024, p. 435
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
58 Preliminary Development of a Virtual Reality Neuropsychological Assessment System
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 29 / Issue s1 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 December 2023, pp. 735-736
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
4 - No-Boundary Course Developments
-
-
- Book:
- Integrative Bioinformatics for Biomedical Big Data
- Published online:
- 14 September 2023
- Print publication:
- 28 September 2023, pp 45-66
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
NUMERICAL ANALYSIS OF APPARATUS-INDUCED DISPERSION FOR DENSITY-DEPENDENT SOLUTE TRANSPORT IN POROUS MEDIA
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- The ANZIAM Journal / Volume 65 / Issue 1-2 / January 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 August 2023, pp. 178-194
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Competition among the two-plasmon decay of backscattered light, filamentation of the electron-plasma wave and side stimulated Raman scattering
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 11 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 August 2023, e76
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Anxiety and depressive disorders in patients with Covid-19
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 66 / Issue S1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, pp. S339-S340
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Consider Early ECT Treatment for Chronic Insomnia-Induced Suicidal Ideation
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 66 / Issue S1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, p. S1100
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
The Parkes Pulsar Timing Array third data release
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 40 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, e049
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Preterm birth associated alterations in brain structure, cognitive functioning and behavior in children from the ABCD dataset
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 54 / Issue 2 / January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 June 2023, pp. 409-418
-
- Article
- Export citation
Multi-objective reward shaping for global and local trajectory planning of wing-in-ground crafts based on deep reinforcement learning
-
- Journal:
- The Aeronautical Journal / Volume 128 / Issue 1320 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 June 2023, pp. 371-397
-
- Article
- Export citation
Lagrangian model for passive scalar gradients in turbulence
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 964 / 10 June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 June 2023, A39
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Groundstates of the planar Schrödinger–Poisson system with potential well and lack of symmetry
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 May 2023, pp. 1-31
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The unusual atrypide brachiopod Qilianotryma suspectum (Popov, 1982) from the Upper Ordovician of the South China paleoplate
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Paleontology / Volume 97 / Issue 3 / May 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 May 2023, pp. 539-548
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation