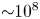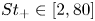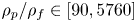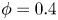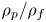766 results
Intestinal anisakiasis in Italy: case report
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Helminthology / Volume 78 / Issue 3 / September 2004
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 April 2024, pp. 271-273
-
- Article
- Export citation
Pomphorhynchus laevis in its intermediate host Echinogammarus stammeri in the River Brenta, Italy
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Helminthology / Volume 73 / Issue 2 / February 1999
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 April 2024, pp. 95-102
-
- Article
- Export citation
Metrology for sub-Rayleigh-length target positioning in ~1022 W/cm2 laser-plasma experiments
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 March 2024, pp. 1-58
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Development of the conversation tool “I-HARP for COPD” for early identification of palliative care needs in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
-
- Journal:
- Palliative & Supportive Care , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 February 2024, pp. 1-9
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Restoration of postictal cortical activity after electroconvulsive therapy relates to recovery of orientation in person, place, and time
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 67 / Issue 1 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 February 2024, e16
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Diet quality scores in childhood and arterial stiffness and carotid artery intima-media thickness in adolescence/early adulthood: findings from the ALSPAC cohort
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Nutrition Society / Volume 82 / Issue OCE5 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 January 2024, E281
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
65 Learning Ability in Relation to Everyday Activities in Patients with Korsakoff’s Syndrome, Other Alcohol-Related Cognitive Impairments, or Uncomplicated Alcohol Use Disorder
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 29 / Issue s1 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 December 2023, pp. 269-270
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
A buffer-gas trap for the NEPOMUC positron beam: optimization studies with electrons
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Plasma Physics / Volume 89 / Issue 6 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 December 2023, 935890602
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Effect of Stokes number and particle-to-fluid density ratio on turbulence modification in channel flows
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 974 / 10 November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 October 2023, A26
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Magnetic field considerations for a multi-cell Penning–Malmberg trap for positrons
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Plasma Physics / Volume 89 / Issue 4 / August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 September 2023, 935890405
-
- Article
- Export citation
Biocultural aspects of species extinctions
-
- Journal:
- Cambridge Prisms: Extinction / Volume 1 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 August 2023, e22
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Sticky criticism? Affective and neural responses to parental criticism and praise in adolescents with depression
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 54 / Issue 3 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 August 2023, pp. 507-516
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A novel workflow for streamflow prediction in the presence of missing gauge observations
-
- Journal:
- Environmental Data Science / Volume 2 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 July 2023, e23
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Australian consumer concern about food waste and packaging: a cross-sectional survey about environmentally sustainable food choices.
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Nutrition Society / Volume 82 / Issue OCE2 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 March 2023, E157
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Associations between data-driven lifestyle profiles and cognitive function
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Nutrition Society / Volume 82 / Issue OCE2 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 March 2023, E57
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Protocol of a policy intervention with local governments to improve access to healthier foods and beverages at community events
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Nutrition Society / Volume 82 / Issue OCE2 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 March 2023, E195
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Polymer-coated urea application can increase both grain yield and nitrogen use efficiency in japonica-indica hybrid rice
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Agricultural Science / Volume 161 / Issue 1 / January 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 November 2022, pp. 51-59
-
- Article
- Export citation
Assessing the core microbial symbionts of jellyfish in Indonesian and Vietnamese marine lakes
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom / Volume 102 / Issue 7 / November 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 October 2022, pp. 486-495
-
- Article
- Export citation
Poor adherence to UK dietary guidelines in school-aged children, measured using a children's Eatwell Guide score, is associated with lower socio-economic status
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Nutrition Society / Volume 81 / Issue OCE5 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 October 2022, E223
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Effectiveness of national guidance on foods and drinks to limit or avoid in pregnancy in England
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Nutrition Society / Volume 81 / Issue OCE5 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 October 2022, E201
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation