With an increase in adult disease relating to poor diet choices, the early years are a crucial time for intervention. Obesity in childhood is more likely to lead to obesity in adulthood and the associated risks of age-related diseases such as CVD and diabetes. These and other age-related diseases including osteoporosis and bone fracture have been linked to specific nutrients such as particular fats, cholesterol, GI, fibre, fruits, vegetables, calcium and vitamin D( Reference Everitt, Hilmer, Brand-Miller, Jamieson, Truswell, Sharma, Mason, Morris and Le Couteur 1 ). The nursery setting offers an excellent opportunity to deliver food messages and practices that can either have a positive or a negative effect on the child's health( Reference Jacobi, Agras, Bryson and Hammer 2 ) with long-lasting consequences. The current project was a pilot study comprising 12 nurseries from the NE of England; food provision comparisons were made between nurseries who had received council-run nutrition training (group A) with those that had no training (group B) using ANOVA and T tests. Data was compared with the Caroline Walker Trust( 3 ) dietary requirement guidelines for children between the ages of 1–4.
Significant differences (p=.000) were found between nursery group A and group B in fruit provision but not for vegetable provision and for the provision of sodium, group B having a significantly lower (p=0.039) content of sodium provision (Fig. 1). No significant difference was reported for total energy provision or for fat, protein and carbohydrate as percentage of energy provision between groups A and B. No significant differences were noted between A and B with respect to the provision of carbohydrate, total fat, SFA, MUFA, PUFA, omegas 3 and 6, vitamin D, iron or zinc. However, both groups were deficient in iron and zinc provision and both groups failed to achieve half of the required daily RNI for vitamin D.
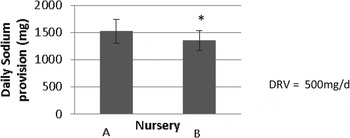
Fig. 1. Comparison of average sodium provision for nurseries in group A (n=6) and group B (n=6)±stdev where significance is denoted by *(p<0.05). DRV for sodium for 1–3 yrs=500 mg/4.
Sodium provision for all nurseries was more than twice the DRV of 500 mg/d for a child aged 1–3 years, with some group A nurseries providing over 1500 mg/d. Total fat and SFA were higher in group A than B and trans fat was significantly higher in group B than A (p=0.010). The daily mean values for both groups A and B were higher than the recommended % of total energy intake and both groups were below the recommended level for omega 3. The study will be extended to incorporate a larger number of nurseries within other areas of NE of England.





