Civil unrest results from unresolved disputes and can lead to organized mass gatherings and protests with resulting riots or violent public disturbances, destruction of property, and compromised safety of bystanders or participating individuals. Riots can challenge the emergency medical system because of the large number of casualties involvedReference Lee, Ooi and Phua1, Reference Schwartz and Bar-Dayan2 and the lack of physician familiarity with the full extent of injuries caused by weapons used by security forces to incapacitate rioters.Reference Schep, Slaughter and McBride3
In the summer of 2015, Beirut, the capital city of Lebanon, experienced a garbage crisis resulting from failure to collect and dispose of the local rubbish; this eventually resulted in huge piles of garbage in the streets.Reference Samaha4 The government’s failure to address this crisis triggered a series of demonstrations in Martyrs’ Square in downtown Beirut, which led to civil unrest and a major riot at the end of August of the same year.Reference Samaha4 Riot control forces and military police used less-lethal weapons such as water cannons, tear gas, and rubber bullets.Reference Samaha4 Approximately ten thousand rioters faced hundreds of policemen in riot gear, and violent eruptionsReference Samaha4 took place over 24 hours and resulting in dozens of casualties. The emergency department (ED) at the American University of Beirut Medical Center (AUBMC), the largest tertiary care center in Lebanon, was the main ED in the area to receive riot-related casualties because of geographic proximity to the events.
Existing literature that describes the impact of riots on the medical system is setting specific, in that the types of less-lethal weapons used to contain rioters determine the resulting types of injuries and, accordingly, the hospital resources that are utilized.Reference Lee, Ooi and Phua1, Reference Schwartz and Bar-Dayan2, Reference Suyama, Panagos and Sztajnkrycer5 To date, riot-related mass casualty events have not been previously described in Beirut, Lebanon. This study describes the impact of a riot-type mass casualty event. Patient characteristics, injury patterns, ED management, and clinical outcomes of affected victims are examined.
METHODS
Study Design and Sample
A retrospective observational study was performed in which the charts of patients presenting to the emergency room at AUBMC between August 22 and August 30, 2015, when major riots were taking place, were reviewed. Charts of all patients arriving to the ED during this period were reviewed, and patients with riot-induced injuries were identified and included in our study. The study was approved by the institutional review board at AUBMC.
Data Collection and Statistical Analysis
A chart review of all patients included in the study was conducted. Investigators retrieved the following information from the patients’ charts:
patient demographics (age, sex, marital status, citizenship, role in riot)
administrative elements (mode of arrival to ED, emergency severity index (ESI) score (1-5, with a score of 1 being the most urgent and 5 being least urgent), patient disposition from ED, and ED length of stay
clinical elements (chief complaint, type of injury, mechanism of injury, body region of injury, and medical interventions (laboratory test, imaging, procedures, medications)
Descriptive analysis was performed using SPSS 23 (Statistical Package for Social Sciences). Categorical variables were presented as frequencies and percentages, whereas continuous variables were summarized as means plus or minus standard deviations, medians, and interquartile ranges.
RESULTS
Out of 1302 charts reviewed, 95 patients presented to the ED at AUBMC with reported injuries as a consequence of the riots that took place in Beirut between August 22 and August 29, 2015. Of these patients, 90.5% were male, 94.7% were Lebanese, most (84.2%) were single, and the majority were protestors (92.6%). The mean age of the victims was 28.0 (± 8.7) years. Patient baseline characteristics are shown on Table 1.
TABLE 1 Patient Characteristics and Variables
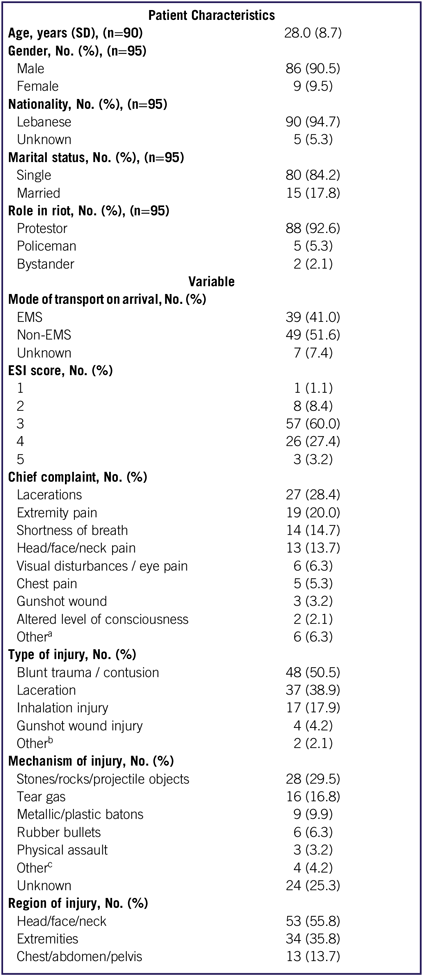
Abbreviations: EMS, emergency medical services; ESI, triage acuity score.
a Includes: (1) epistaxis, (2) testicular pain, (4) finger amputation, (5) polytrauma, (6) back pain.
b Includes: (1) posterior vitreous detachment and (2) finger amputation.
c Includes injuries caused by: (1) water cannons, (2) barbed wire, (3) mechanical falls.
The highest influx of patients arriving to the ED occurred on August 23, 2015 (62 patients), with the peak arrival of patients occurring between 9:00 pm and 10:00 pm (24 patients). More than half (53.7%) of the ED admissions occurred between 8:00 pm and 11:00 pm on the second day of the riots at a rate of approximately 1 patient every 3.5 minutes. The most common mode of transport to the ED was non-EMS (51.6%). On arrival to the ED, the majority of patients had a medium to low triage acuity score (ESI score of 3 or 4). Laceration injury was the most common chief complaint (28.4%), and contusion / blunt trauma was the most common type of injury (50.5%). The most common reported mechanism of injury was by stones, rocks, and other projectile objects (29.5%). The mechanism of injury was missing in 25.3% of cases. The head/face/neck was the most frequently injured body region (55.8%), followed by the extremities (35.8%). Characteristics of patient injuries are reported on Table 1.
Most of the patients who presented to the ED did not require any laboratory tests (92.6%) or procedures (61.0%). For patients who underwent a procedure in the ED, the most common procedure was laceration repair (81.1%), followed by a focused assessment with sonography for trauma (FAST) exam (35.1%). More than half of the patients underwent imaging tests, mainly radiography (66.7%). Medications were administered to 67.4% of the patients. The most frequently administered medication was tetanus vaccine (54.7%), followed by pain medication (39.1%). Most patients were treated in the ED and discharged home (91.6%). Only 1 patient required ICU admission, and 1 patient died in the ED from a penetrating head injury. The average ED length of stay was 124.8 ± 199.1 minutes. Medical interventions and patient dispositions are displayed on Table 2.
TABLE 2 Patient Disposition and Emergency Department Medical Interventions
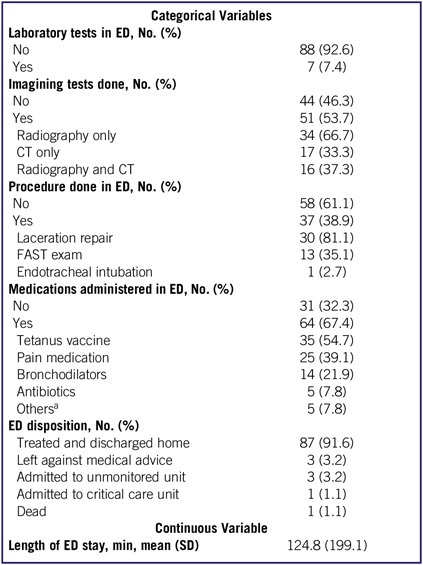
Abbreviations: CT, computed tomography; ED, emergency department; FAST, focused assessment with sonography for trauma.
a Includes (1) proton-pump inhibitors and (2) neuromuscular blockers.
DISCUSSION
This retrospective study is the first to describe a riot-type mass casualty event in Beirut, Lebanon. Riots are setting-specific, and their impact is important to describe for better planning and mitigation. The mortality rate of 1.1% in this study is lower than rates reported in previous studies examining this topic. Previously reported mortality ratesReference Mahajna, Aboud and Harbaji6 from riots range from 2.0% to 6.1% on arrival to the ED. Other studies examining this topic do not report mortality rates.Reference Lee, Ooi and Phua1, Reference Suyama, Panagos and Sztajnkrycer5 This variation in mortality rates among patients with riot-related injuries may be a result of the numerous available forms of less-lethal weapons that can be used to incapacitate rioters and which may result in different types of injuries and subsequently different rates of deaths that are setting- and country-specific.
Temporary incapacitating agents used to control rioters often appear to have more than temporary effects: previous studies and case reports have documented pulmonary contusions and penetrating ocular injuriesReference Mahajna, Aboud and Harbaji6 from rubber bullets and ocular, cutaneous, and respiratory reactions and myocardial infarctionsReference Kim, Payal and Daly7 from tear gas. These unfamiliar complications, as well as the lack of evidence-based management of patients with riot injuries,Reference Kim, Payal and Daly7 could result in higher-than-expected mortality rates from seemingly nonlethal injuries, particularly in patients with chronic respiratory or cardiac diseases who are more likely to develop severe systemic sequelae from riot control agents.Reference Smith and Greaves8
The most common mode of transport of patients arriving to the ED was non-EMS, however, EMS use in this study (41.0%) is higher than previously reported local EMS use. A study carried out at the ED of AUBMC showed that only 23.3% of the study population used EMS for all-cause presentations and that EMS use was associated with higher illness severity during routine daily operations.Reference El Sayed, Tamim and Chehadeh9 During civil unrest and rioting, however, EMS are expected to increase their readiness by deploying additional ambulances and teams to the conflict zones. Additionally, EMS agencies in Lebanon are well adapted to quick transport and care of trauma-related cases because of the recurrent armed conflicts that occur in the region.Reference El Sayed and Bayram10
Injury patterns and severity in this study mirror findings from other studies examining this topic. Riot victims are usually hemodynamically stable on presentation (medium to low triage severity score)Reference Lee, Ooi and Phua1, Reference Schwartz and Bar-Dayan2 and are predominantly male.Reference Lee, Ooi and Phua1, Reference Suyama, Panagos and Sztajnkrycer5, Reference Mahajna, Aboud and Harbaji6 Patients present mainly with abrasions and lacerationsReference Lee, Ooi and Phua1 affecting the head/neck and extremities, which are the most commonly injured body regions.Reference Lee, Ooi and Phua1, Reference Schwartz and Bar-Dayan2, Reference Suyama, Panagos and Sztajnkrycer5, Reference Mahajna, Aboud and Harbaji6 This study was also consistent with the existing medical literature regarding hospital resource utilization, diagnostic measures, and patient disposition.Reference Lee, Ooi and Phua1, Reference Schwartz and Bar-Dayan2, Reference Suyama, Panagos and Sztajnkrycer5
Casualties often arrive at emergency departments in large numbers over short periods of time.Reference Lee, Ooi and Phua1 This was demonstrated in our study, which showed that 53.7% of the ED admissions occurred over a 3-hour period at a rate of 1 patient arrival every 3.5 minutes. This resulted in the activation of our hospital disaster preparedness plan. This incident revealed that ED personnel need to be better prepared for high patient influx during rioting events. Disaster planning strategies could involve collaboration with EMS to allow for more balanced casualty distribution among the hospitals that are close to the riot scene. In Lebanon, the EMS system is composed of multiple volunteer agencies that lack prehospital standards and a lead agency. Effective communication between EMS personnel and ED staff is lacking.Reference El Sayed and Bayram10 This was made even more apparent when, during these riots, almost all patients were routed to our ED by EMS. Additionally, more advanced EMS systems often establish policies and protocols that allow them to treat and release patients on the field or transport them to appropriate EDs. Our EMS system has no such polices, which resulted in unnecessary ED admissions.
The limitations of this study are related to its retrospective nature. During mass casualty events, documentation in the ED records is often missing, and this might have led to underestimation of some injuries. No follow-up was obtained on patients, and as a result we could not comment on missing injuries or delayed complications of initial injuries. It is worth noting that, because of the fluctuating nature of the rioting crowd, estimating the crowd size was difficult. It is possible that larger rioting crowds may have resulted in different injury profiles. Although the study results mirror those of previous studies examining this topic in other countries, this study is innovative in reporting on the impact of riots out of a developing country that has not previously experienced such events.
CONCLUSION
Patients’ characteristics and patterns of injuries in riots in Lebanon were similar to those from other countries. Patients are usually young and present with low-severity injuries mostly related to lacerations. High patient influx over a short period of time was observed. Additionally, although nonlethal or less-lethal weapons are used during rioting, deaths do occur. This highlights the need for effective prehospital and hospital mass casualty planning in Lebanon for improved response to such events.




