Article contents
A Study of Damage in Silicon Created By 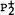 and P+ Implantation
and P+ Implantation
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 26 February 2011
Abstract
The damage and annealing behavior of <100> Si implanted at room temperature by 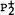 and P+ at different energies (5-600KeV) and intermediate dose (∼1014/cm2) has been investigated. Experimental results show that the damage created by
and P+ at different energies (5-600KeV) and intermediate dose (∼1014/cm2) has been investigated. Experimental results show that the damage created by 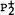 implantation is always greater than that of P+ implantation. The ratio of total displaced atoms of the target cuased by molecular and atomic implantation, ND(mol)d/ND(atom) reached a maximal value at 100KeV (
implantation is always greater than that of P+ implantation. The ratio of total displaced atoms of the target cuased by molecular and atomic implantation, ND(mol)d/ND(atom) reached a maximal value at 100KeV (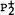 ) and 50KeV (P+) after rapid thermal annealing, the carrier concentration profiles measured by spreading resistance measurements are also different for the
) and 50KeV (P+) after rapid thermal annealing, the carrier concentration profiles measured by spreading resistance measurements are also different for the 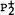 and P+ implanted samples. We attribute essentially this phenomenon to the displacement spike, but the multiple collision effect and the interaction between two molecular fragments should be considered while the incident energy is high.
and P+ implanted samples. We attribute essentially this phenomenon to the displacement spike, but the multiple collision effect and the interaction between two molecular fragments should be considered while the incident energy is high.
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 1988
References
REFERENCES
- 3
- Cited by


