Article contents
P-Type Quantum Well Infrared Photodetectors Grown by OMVPE
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 26 February 2011
Abstract
We report on the growth and fabrication of p-doped long wavelength GaAs/AlxGa1−x As quantum well infrared photodetectors (QWIP) grown by organometallic vapor phase epitaxy. The operation of these devices is based on the photocurrent induced through valence band intersubband absorption by holes and, unlike n-doped QWIPs, can utilize normal incidence illumination. Carbon and zinc were used as the p-type dopants in a low-pressure (30 Torr) vertical-geometry reactor. The Zn-doped QWIP consisted of fifty periods of 48 nm-thick undoped Al0.36Ga0.64As barriers and nominally 4 nm-thick doped GaAs quantum wells. Using normal incidence, a quantum efficiency of η = 2.5% and a detectivity of 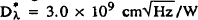 at 77K were obtained for a peak wavelength λp = 6.8 μm and a cutoff wavelength λ∫ =7.6 μm. The C-doped QWIP had 54 nm-thick Al0.31Ga0.69As barriers and exhibited a normal incidence
at 77K were obtained for a peak wavelength λp = 6.8 μm and a cutoff wavelength λ∫ =7.6 μm. The C-doped QWIP had 54 nm-thick Al0.31Ga0.69As barriers and exhibited a normal incidence 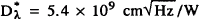 These initial studies indicate the superiority of carbon to zinc as the p-type dopant for these structures. The detectivity of the C-doped QWIPs is about four times less than n-doped QWIPs for the same λp but have the advantage of utilizing normal incidence illumination.
These initial studies indicate the superiority of carbon to zinc as the p-type dopant for these structures. The detectivity of the C-doped QWIPs is about four times less than n-doped QWIPs for the same λp but have the advantage of utilizing normal incidence illumination.
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 1992
References
REFERENCES
- 1
- Cited by


