Published online by Cambridge University Press: 28 December 2016
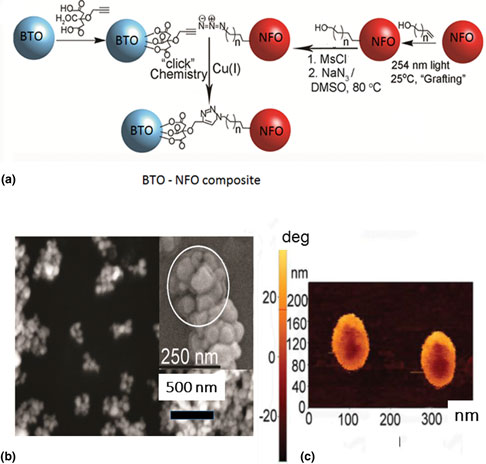
Self-assembly of multiferroic oxide composites by chemical and biochemical methodology is discussed. The approach involves covalently attaching organic functional groups or oligomeric DNA/RNA to the nanoparticles (NPs). The organic functional groups are only reactive toward functional groups located on different NPs. Using oligomeric DNA/RNA, one could program NPs to only interact with particles possessing complementary DNA/RNA. We have applied both concepts to the assembly of nanostructures with ferrites for the ferromagnetic phase and barium titanate for the ferroelectric phase. The assembled core–shell particles and superstructures obtained in a magnetic field show evidence for strong interactions between the magnetic and ferroelectric subsystems.