Article contents
Growth process and morphology control of SBA-15 particles: synergistic effects of tetraethoxysilane and Pluronic-123 concentrations
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 21 November 2016
Abstract
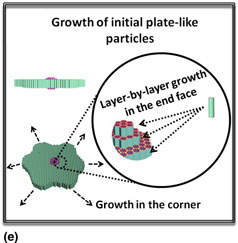
The synergistic effects of the template [Pluronic-123 (P123)] and the silica source [tetraethoxysilane (TEOS)] concentrations on the SBA-15 mesoporous silica morphology were investigated through adjusting the system initial solution volume with the same amounts of silica source and template. It found interestingly that the SBA-15 morphology changed from the hexagonal plate-like shape to the gear-like shape with the decrease of the P123 and TEOS concentration. Based on the morphology variations, the growth of the gear-like morphology was speculated to be formed through the preferential growth at the corner and the layer-by-layer growth in the end face of the ordinary hexagonal plate-like particle.
- Type
- Research Letters
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2016
References
- 7
- Cited by





