Introduction
The single-target biosensor evolution from laboratory to wearable functionality was demonstrated by the classical glucose oxidase (GOx) biosensor, first described by Clarke in 1962 and developed by Medtronic in 2005 for continuous blood glucose monitoring. Single-target sensors have extensively been researched and commercialized for metabolites, antibodies, and proteins, etc. Bio-fluids such as saliva, tear, sweat, and interstitial fluid generate significant research around disease-specific biomarkers. Such fluids are naturally secreted by the body and are painlessly sampled unlike invasive blood draw. Saliva incorporates protein biomarkers[Reference Yan, Apweiler, Balgley, Boontheung, Bundy, Cargile, Cole, Fang, Gonzalez-Begne, Griffin, Hagen, Hu, Wolinsky, Lee, Malamud, Melvin, Menon, Mueller, Qiao, Rhodus, Sevinsky, States, Stephenson, Than, Yates, Yu, Xie, Xie, Omenn, Loo and Wong1] relevant to local cell activity and biomolecular function. It is used to monitor creatine, fibrinogen, hemoglobin, triglyceride, glucose levels, and correlates to blood pressure.[Reference Soukup, Biesiada, Henderson, Idowu, Rodeback, Ridpath, Bridges, Nazar and Bridges2] Tear fluid contains lipids, electrolytes, metabolites, and proteins[Reference Semba, Enghild, Venkatraman, Dyrlund and Van Eyk3] suitable for disease monitoring. Sweat is extensively used to measure physiologic parameters[Reference Huang, Chen, Huang and Mao4–Reference Shirreffs, Aragon-Vargas, Chamorro, Maughan, Serratosa and Zachwieja6] and incorporates protein biomarkers associated with genetic diseases.[Reference Zeng, Shu, Li, Chen, Wang and Tao7] While single-target assays monitor specific conditions such as diabetes, multiplex protein screening offers improved diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment for cancer. Recent reviews[Reference Choi, Lee, Ghaffari, Hyeon and Kim8–Reference Raiszadeh, Ross and Russo10] have highlighted wearable technology progress around materials, assays, and instrumentation. Flexible substrates offer mechanical properties suitable for wearable devices with Young's moduli compatible with skin applications.[Reference Park, Ahn, Feng, Wang, Huang and Rogers11] Device structure typically consists of flexible layers, including support substrate, active layer, and electrical connections. Careful design[Reference Silver, Freeman and DeVore12] avoids device failure (cracking and delamination), caused by stretching and bending. Flexible substrate materials include paper, polymer, and textiles. All offer biocompatibility and robustness during device fabrication and biomolecule immobilization. Natural polymers include cellulose, silk, wool, and cotton, while synthetic polymers include nylon, polyethylene, polyester, and teflon. Wearable biosensors progressed as conductive polymers [polypyrrole, polyaniline (PANI), polythiophene] improved device integration with flexible substrates, delivering good electrical properties for sensor applications. Incorporating graphene,[Reference Peng, Dongzhi, Jingjing, Hongyan, Yan and Nailiang13–Reference Kang, Wang, Wu, Aksay, Liu and Lin15] carbon nanotubes,[Reference Kumar Vashist, Zheng, Al-Rubeaan, Luong and Sheu16, Reference Jacobs, Peairs and Venton17] metal nanoparticles,[Reference Saha, Agasti, Kim, Li and Rotello18, Reference Luo, Morrin, Killard and Smyth19] and semiconductor materials into active layers improved electrical and mechanical properties[Reference Forrest20] of flexible devices. Issues around fouling and biomolecule interference have been alleviated with biomolecule-selective membranes, immobilization matrices, and antifouling layers.[Reference Liu, Shi, Wang, Li, Liu and Shilpa21–Reference Penga, Zhub, Liua and Qina23] Such technologies have contributed to advancement in wearable sensors. Electrochemical sensors offer distinct advantages over optical detection in conformal substrates for biomarker detection. For multiplex assays, multiple fluorophores or microarray approaches require complex optics (e.g., sources, lens, filters, sensor arrays) to be integrated on a single rigid substrate to maintain optical alignment. Flexible electrode systems facilitate bending and twisting having minimal signal impact. Microelectrode arrays manufactured on single substrates facilitate high-density multiplex detection. Signal-to-noise enhancement in optical systems often require long optical pathlengths (e.g., absorption) or high-power sources (e.g., fluorescence) to reach clinically relevant biomarker levels. Such approaches can increase system size, power, and may require specific thermal management. With electrochemical sensors, performance-enhancing approaches include target-selective membranes, materials (e.g., carbon nanotubes) enhancing electrical performance which can be incorporated without size or power impact. In this review, we highlight the applications of flexible substrates to multiplex biomarker monitoring with potential for health-monitoring applications.
Saliva, sweat, and tear liquids contain biomarkers (Fig. 1), which are easily accessed using wearable sensor technology, to diagnose and manage a range of clinical conditions. Significant potential for multiplex monitoring exists, due to biomarker diversity within each sample type. In this review, we highlight the applications of flexible substrates to multiplex biomarker monitoring with potential for health-monitoring applications. The potential for wearable biomarker devices to non-invasively monitor a range of physiologic conditions has generated a significant interest as outlined in Table 1, where clinically relevant biomarker ranges to monitor healthcare conditions are highlighted. For each flexible substrate type, device fabrication, assay implementation, and performance is outlined for a range of multiplex applications screening for cancer biomarkers, electrolyte imbalance, and proteins, etc. This review focuses on electrochemical detection methods as they have progressed more than optical techniques for wearable applications. The approach taken is to review the three main flexible substrate categories: (i) paper/paper hybrids, (ii) synthetic polymers, and (iii) fabrics as reported in the literature and to highlight multiplex biomarker combinations demonstrated with each substrate type.
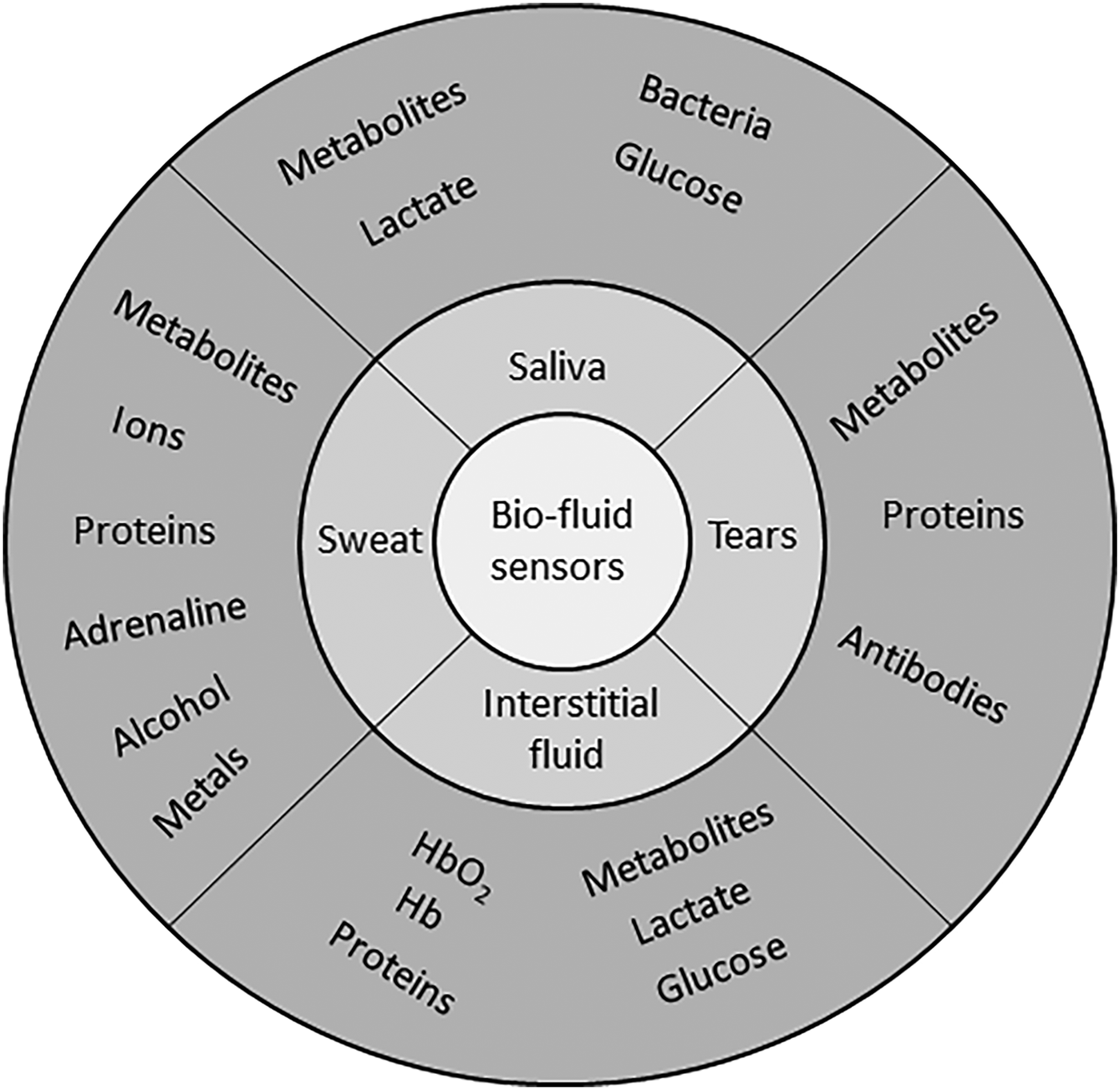
Figure 1. Overview of target biomarkers within saliva, tear, sweat, and interstitial fluid (ISF), to be monitored at the eye, skin, and mouth locations with potential for multiplex combinations.
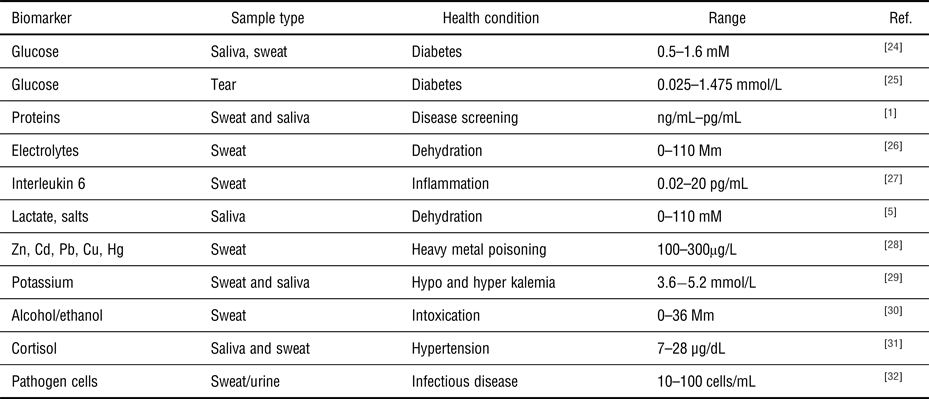
Table I. Examples of common target biomolecules, sample fluid, and clinical concentration ranges used as applications for wearable health-monitoring systems.
Paper/hybrid devices
Cellulose is an abundant, natural, low-cost polymer (trees, plants, bacteria, algae) extensively used in bioassays.[Reference Sher, Zhuang, Demirci and Asghar33] Paper assays generate significant research interest, they are inexpensive, easy to use, flexible, consume low reagent volume, and deliver rapid results.[Reference Comer34–Reference Martinez, Phillips, Wiley, Gupta and Whitesides36] In this section, we highlight paper and hybrid/paper devices applied to multiplex biomarker monitoring, in applications including cancer, metabolites, and pathogen detection. Microfluidic paper-based analytical devices (mPADs) is a term used for paper and hybrid test devices.[Reference Mukhopadhyay37–Reference Mukhopadhyay41] Capillary action makes paper an ideal material for wearable/point-of-care applications, avoiding the need for pumps, as local surface modification [e.g., wax,[Reference Lu, Shi, Jiang, Qin and Lin42] polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS)[Reference Tang and Whitesides43]] manipulates sample flow to reaction sites. Tests are primarily based on enzyme-linked immuno-assays (ELISA), where reagents can be directly adsorbed onto porous paper at reaction sites. Electrochemical detection is extensively used in low-cost printing techniques (inkjet) that dispense materials forming electrode patterns. Electrochemical detection is extensively used in portable systems due to low-power consumption and simple instrumentation, a significant advantage over optical systems.
Glucose, lactose, uric acid
Assays incorporating catalytic reactions and identifying multiple analytes have been demonstrated on paper substrates. A multiplex electrochemical device was demonstrated for glucose, lactose, and uric acid detection in human serum samples.[Reference Dungchai, Chailapakul and Henry44] Electrodes were screen printed from carbon ink containing Prussian blue (PB) for the working electrode (WE) and the counter electrode (CE); the reference electrode (RE) was Ag/AgCl. PB is extensively incorporated as a mediator into electrochemical assays, facilitating electro-potential shift to mitigate against competing biomolecules. Test areas were prepared by spotting 0.3 µL of GOx, lactate oxidase (LOx), and uricase solutions onto WE areas. Chrono-amperometric detection was used to monitor enzyme reactions within each target zone, at a sampling rate of 10 Hz. PB, as an electrode mediator, reduced catalytic reaction potentials over the range −0.2 to 0.2 mV (Ag/AgCl) minimizing interference from uric and ascorbic acid. Detection was based on the reduction of H2O2 at 0 V. The limits of detection (LODs) were: glucose 0.21 mM (range 0–100 mM), lactate 0.36 mM (range 0–50 mM), and uric acid 1.38 mM (range 0–35 mM) in human serum. Direct enzyme immobilization on WEs is a popular approach for electrochemical sensor implementation. However, incorporating three-dimensional (3D) structures can improve the performance and enhance specificity. A hydrogel–paper hybrid assay demonstrated the glucose and protein detection in urine.[Reference Martinez, Phillips, Butte and Whitesides35, Reference Martinez, Phillips, Carrilho, Thomas, Sindi and Whitesides45] Microfluidic channels were defined by patterning hydrophilic paper with hydrophobic polymer for controlled liquid flow, delivering a low-cost approach for multiplex biomarker detection. The paper substrate was soaked in SU8 polymer solution; following UV curing, non-cross-linked polymer was removed in a propylene glycol monomethyl ether acetate solution. Three-dimensional hydrogels enhance reagent immobilization and assay sensitivity, through increased target capture and optimizing enzyme activity.[Reference Kivlehan, Paolucci, Brennan, Ragoussis and Galvin46] A novel screen-printed mPAD, with all-carbon electrode-enabled electrochemical assay (SP-ACE-EC-μPAD), simultaneously detected glucose and uric acid in urine.[Reference Yao and Zhang47] Carbon ink electrodes were deposited on the substrate using low-cost screen printing. GOx and uricase were deposited in reservoir locations by spotting 2 µL of enzyme solution, followed by air drying (20 min).Glucose and uric acid were detected in urine using chrono-amperometry, providing fast and accurate results. Spiked glucose (0.25, 0.5, 0.75 Mm) and uric acid (0.1, 0.2, 0.3 mM) samples (20 µL) were evaluated on the device, delivering results within 3 min. This simple detection approach applied 300 mV step potential with current monitored over time and was highly suitable for wearable applications.
Proteins
Color change detection is an instrument-free approach, extensively used with lateral flow assays. Such tests usually identify a single target. In a novel approach of multiplex diagnostics, hydrogel was formed on a paper substrate using an aptamer cross-linker, trapping glucoamylase (GA).[Reference Wei, Tian, Jia, Zhu, Ma, Sun, Lin and Yang48] Glucose detection, based on enzymatic oxidation of iodide to iodine, altered test spot color from clear to brown. For protein detection, spots changed from yellow to blue following tetrabromophenol blue ionization. The device used a target-responsive aptamer cross-linked hydrogel, for selective target recognition. With the target present, the hydrogel collapsed releasing GA into the solution and amylose hydrolyzed by GA generated glucose as the liquid progressed along the paper. A catalytic GOx reaction along the channel converted glucose to gluconic acid and H2O2, resulting in a brown color change as horse radish peroxidase (HRP) catalyzed poly(DAB) from colorless 3,3′-diaminobenzidine (DAB). The resulting color change length along the test strip correlated with target concentrations. The flexibility of the hydrogel–aptamer structure facilitated multiple target detection in urine, i.e., glucose (0.7–10.5 mM), cocaine (0–100 µM), and adenosine detection (0 to 800 µM). Adenosine is a cancer biomarker used to monitor disease progression.[Reference Zheng, Xu, Liu, Xiong, Zhang, Zhang, Yang and Lv49] While color-based detection is fast, results are subjective and may suffer from reduced sensitivity. The authors highlight how distance-based color detection is less subjective compared with spot color change, and performance was comparable to commercially available dipstick tests.
Cell targets
Electrochemical luminescence (ECL) combines electrochemical activity with optical detection by incorporating a chemiluminescent molecule into the ELISA. This approach is useful for quantitative detection and gives enhanced sensitivity over purely color-based assays. Conventionally, ECL assays are implemented in microwells or on microfluidic devices; however, paper-based ECL has been demonstrated. A hybrid paper-PDMS device was manufactured for rapid multiplex pathogen detection.[Reference Zuo, Li, Dominguez and Yeb32] The hybrid approach offered a simple, biocompatible, 3D material for reagent storage and immobilization, without complex surface chemistry, while PDMS microfluidics defined reaction zones. Fluorescent aptamers functionalized with graphene oxide (GO) were deposited by pipette on chromatography paper. The aptamer–GO solution was adsorbed onto paper defining a probe microarray, screening for target pathogens. GO in close proximity to a fluorescence probe caused quenching, thus switching CY3-labeled aptamers to an “off” state. The aptamer became rigid with specific target binding, increasing GO–Cy3 separation, switching “on” fluorescence signal by reducing quenching. The simple test required sample loading followed by incubation (10 min), without washing prior to fluorescence detection. This approach offered direct pathogen-specific detection without nucleic acid screening techniques (e.g., PCR). Lactobacillus acidophilus detection was demonstrated over the range 0–300 cfu/mL with an estimated LOD of 11 cfu/mL. Multiplex pathogen detection was demonstrated for Staphylococcus aureus and Salmonella enterica, achieving good specificity (Fig. 2). The detection range for S. enterica was 42.2–675.0 cfu and for S. aureus 104–106 cfu/mL, with LOD of 61.0 cfu/mL (S. enterica) and 800.0 cfu/mL (S. aureus). Performance was comparable to cell culture and molecular diagnostic approaches.
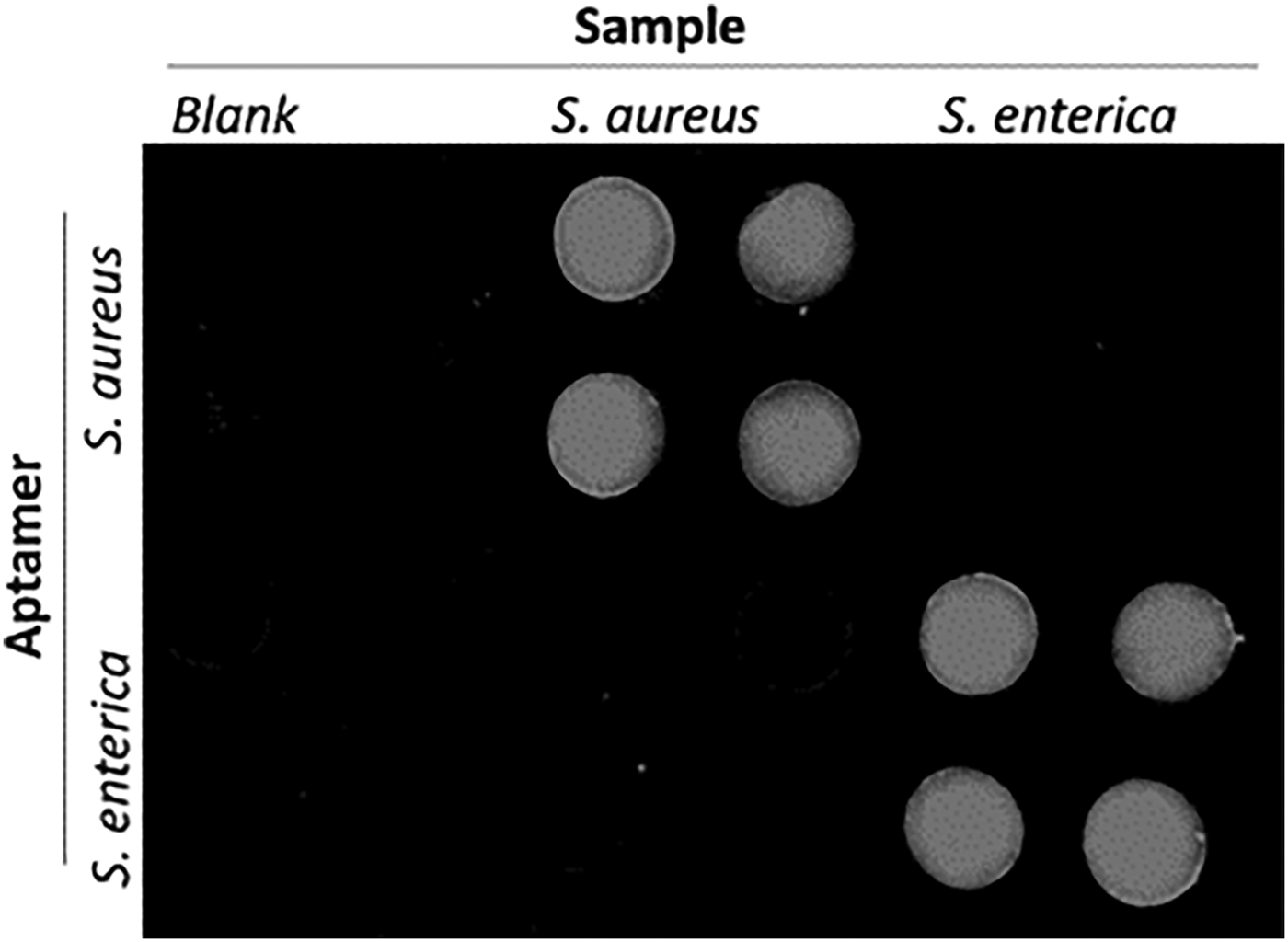
Figure 2. A cross-reaction assay incorporating Staphylococcus aureus (106 cfu/mL) and Salmonella enterica (1375 cfu/mL) demonstrates the selectivity of the sensor to multiple pathogen targets for each immobilized aptamer (reproduced from Ref. Reference Zuo, Li, Dominguez and Yeb32 with permission from Royal Society of Chemistry).
A novel laboratory-on-paper-based chemiluminescence assay was demonstrated for cancer biomarkers.[Reference Wang, Ge, Song, Yu, Ge, Huang and Zeng50] Reaction chambers were formed by screen printing hydrophobic wax layers into porous paper, with covalent immobilization of capture antibodies using a glutaraldehyde linker molecule. The assay consisted of: (i) immobilizing sample-specific capture antigens, (ii) addition of HRP-labeled signal antibodies to detection zones, and (iii) injection of luminol-p-iodophenol-H2O2, triggering chemiluminescence. Incubation time was optimized at 210 s. Increasing concentrations of three tumor markers were evaluated in phosphate-buffered saline buffer, delivering linear ECL responses for each target range: (i) α-fetoprotein (AFP) 0.1–35.0 ng/ml, (ii) carcinoma antigen 125 (CA125) 0.5–80.0 U/mL, and (iii) carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) 0.1–70.0 ng/mL. The LODs of the three targets were within clinically acceptable limits when evaluated with human serum, in agreement with a commercial ECL cancer test. A paper-based ECL assay was also implemented screening for four cancer biomarkers: AFP, CA125, carcinoma antigen 199, and CEA.[Reference Ge, Yan, Song, Yan, Ge and Yu51] ECL detection was demonstrated in human serum using TPA [tris-(bipyridine)-ruthenium(II)[Ru(bpy)32þ]-tri-n-propylamine]. Eight reaction chambers with feeder channels were defined by wax printing. Eight WEs incorporated into the device stimulated ECL during voltage sweeps (0.5–1.1 V). For manufacture, fluidics were first fabricated followed by electrode screen printing (Carbon WE, Ag/AgCl reference). Capture antibodies (2 µL, 20 mg/mL) were immobilized on each WE using chitosan coating and GA cross-linking. For target capture, sample was added to each electrode and incubated for 30 min. ECL detection was realized by adding TPA (0.01 mM) and monitored during voltage sweeps. The test was evaluated with blood serum from high-risk cancer patients; measured biomarker concentrations agreed with commercial cancer test results. An origami-like paper device was developed to simultaneously screen for four cancer cells (MCF-7, HL-60, K562, CCRF-CEM).[Reference Wu, Ma, Ge, Kong, Yan, Ge and Yu52]Target-specific aptamers were immobilized on gold electrodes, and porous AuPd nanoparticles labeled with concanavalin-A acted as probes. The nanoparticles selectively bound to mannose on the captured cell surface. Carbon WEs were screen printed in each capture reservoir with a single Ag/AgCl RE. Au nanoparticles were grown on WE surfaces before aptamer modification, forming an Au–thiol monolayer. Wax channel and chambers were defined for liquid handling. For detection, test solutions (10 µL) were delivered to each chamber and incubated for 15 min. After cell capture, the bio-conjugate solution (AuPd@Con-A) was added labeling captured cells. ECL measurements were performed by sweeping voltage (−0.3 to −1.8 V, scan rate 100 mV/s) on each electrode while the monitoring optical signal. A log relationship existed between ECL signals and cell concentration (working range 450–105 cells/mL) demonstrating potential for low-cost, rapid cancer cell screening. The test exhibited good specificity, with a slight signal increase, to non-targeted cancer cells. Test variation was <4% [coefficient of variation (CV)] and devices were viable for up to 5 weeks. Similar assays were also developed for specific cancerous cell screening.[Reference Su, Ge, Ge, Li, Yu, Yan and Huang53, Reference Su, Ge, Kong, Zheng, Ge, Li, Yu and Yan54] Paper stacking was demonstrated as a novel approach for assay implementation.[Reference Yang, Zhang, Yang, Hu, Cao, Zheng, Chen and Jiang55] Paper sheets, pre-incubated with biologic reagents, were skived into multiple test sheets facilitating mass device manufacture for multiplex applications. The width of a single paper sheet formed each reaction site, with multiple sheets assembled to implement multiplex barcode assays. Test readout was performed using a commercial barcode scanner and simultaneously distinguished positive results for HBV, HCV, HIV, TP over negative samples. Barcode assays were fabricated by gluing white paper, red paper, and paper immobilized with capture probes together in a defined manner. Lateral flow delivered target to immobilized capture probes, while AuNPs labels changed paper color (white to red) indicating a positive test. Devices evaluated with human samples demonstrated reproducible and specific virus detection at clinically relevant levels. An emerging area is paper-based molecular diagnostics using amperometric[Reference Cunningham, Brenes and Crooks56] and impedance[Reference Ihalainen, Pettersson, Pesonen, Viitala, Määttänen, Österbacka and Peltonen57] detection; however, multiplex assays using these detection methods on flexible substrates have yet to be demonstrated. A challenge for paper assays is valved fluidic control; a novel paper device (Fig. 3) incorporated active electromagnetic valving and timed incubation. Active on paper valving was implemented as a sample wicked between two electrodes, completing a circuit to activate electromagnetic valves. The device screened for multiple cancer biomarkers and programmed incubation times facilitated specific protein detection. Significant progress has also been made with mPAD multiplex devices, screening for specific biomarker combinations. Catalytic detection is the most popular technique adapted with mPADs assays, and aptamers are easily incorporated to enhance selectivity and sensitivity. ECL has enhanced signal benefits over visual color change assays, and electrochemical-based techniques offer potential for portable point-of-care and wearable biomarker detection. Challenges for paper-based assays include long-term biomolecule activity with refrigeration required to maintain viable assays. Paper assay manufacture is low cost and easy to implement in developing countries; however, humidity and temperature variation can impact reproducibility. Capillary flowrates can be modified by change in sample viscosity due to medication; thus, internal controls are required for test verification. Wearable paper devices have primarily focused on monitoring interstitial fluid and sweat constituents (e.g., electrolytes, glucose, lactate) using simple assays, while point-of-care paper applications extend to urine, saliva, and blood biomarkers. A future step will be to incorporate complete sample preparation and detection into a single test.
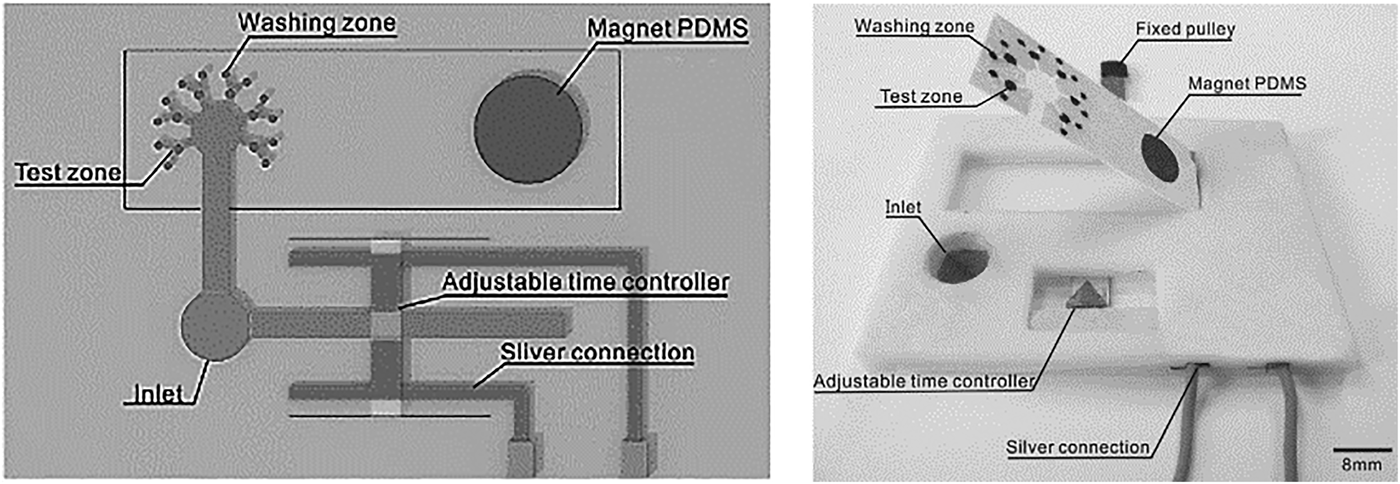
Figure 3. Programmed incubation time and active electromagnetic valving were implemented on a paper-based ECL assay, screening for protein cancer biomarkers α-fetoprotein (AFP) and carcinoma antigen 125 (CA-125) in human serum sample (reprinted from Ref. Reference Wang, Li, Ban, Du, Feng and Liu58 Copyright Sensors & Actuators B).
Polymer substrates
A diverse range of flexible synthetic polymer materials are available for sensor applications including polyimide (PI), polyethersulfone, polyetheretherketone, poly(ethylene napthalate), polycarbonate, and polyethylene terephthalate (PETE). Such materials are compatible with mass manufacture methods for thin flexible substrates (e.g., spin coating, extrusion, injection moulding). They are compatible with processing steps to deposit electroactive layers (organic or inorganic) for device fabrication [electrode, field effect transistor (FET), nanowire] and biochemistry protocols immobilizing capture biomolecules (antibodies, DNA) or enzymes, for target capture/recognition. Electroactive materials incorporated into flexible sensors include conductive polymers (polypyrrole, PANI, polythiophene), semiconductor materials (ZnO, In2O3, graphene), and nanowire/nanoparticle materials (carbon nanotubes). Microelectronic deposition techniques (chemical vapor deposition, evaporation) are extensively used to realize pure films defining devices and electrical contacts. Approaches where prepolymer liquids incorporate nanowire/nanoparticle materials have been implemented by electrospinning, micro-contact printing, spin-coating, etc. Such approaches produce robust devices amenable to substrate bending, twisting, and stretching.
Glucose, electrolytes, lactate
A flexible substrate for multi-target (glucose, lactate, Na+, K+) sweat screening was demonstrated for exercise monitoring.[Reference Gao, Emaminejad, Nyein, Challa, Chen, Peck, Fahad, Ota, Shiraki, Kiriya, Lien, Brooks, Davis and Javey59] Sensors were fabricated on flexible polyethylene terephthalate (PET) substrates conforming to skin contour. Gold electrodes were deposited on the substrates using a lift-off process. Enzymes (GOx, LOx) immobilized on the substrate using a polysaccharide chitosan membrane facilitated amperometric measurement. Ion-selective electrodes (ISEs) incorporating PEDOT:PSS as an ion-to-electrode transducer facilitated selective Na+ and K+ detection. The RE (Ag/AgCl) was coated with a polyvinylbutyral (PVB) membrane containing carbon nanotubes enhancing electrical properties. Such coatings facilitate long-term measurements and minimize signal drift. Incorporating PB dye shifted reduction potentials to 0 V removing the need for additional sensor power, an important consideration for wearable devices. The ion sensors demonstrated detection over physiologically relevant ranges (K+ 10−160 mM and Na+ 1–32 mM). Temperature variation was found to have a significant impact on enzyme activity, and thermal compensation addressed overestimation in glucose and lactate measurements. The system was evaluated during moderate activity on an exercise bike. After perspiration onset, decrease in measured glucose and lactate levels was observed; however, lactate levels stabilized as expected with continuous steady exertion. Na+ increased and K+ decreased as perspiration commenced and stabilized as exercise continued. When applied to different body locations (forehead, wrist), the system recorded different trends due to varied sweat volumes and skin characteristics. During high-intensity exercise, measured trends varied across four volunteers for Na+ and K+. During intense exercise, observed glucose trends were well correlated across subjects, however lactate levels varied between subjects. Highlighting how large scale population testing is required to establish biomarker relevance. A fully integrated autonomous platform (Fig. 4)[Reference Emaminejada, Gao, Wub, Davies, Nyein, Challaa, Ryan, Fahad, Chen, Shahpar, Talebia, Millaf, Javey and Davies60] was developed to quantify Na+, Cl−, and glucose in sweat samples for cystic fibrosis (CF) and diabetes monitoring. Iontophoresis electrodes coated with pilocarpine-loaded hydrogel were incorporated to locally stimulate sweat glands in sedentary patients. The measurement consisted of two phases: (i) application of a local current to generate sample and (ii) parameter measurement using ISEs.
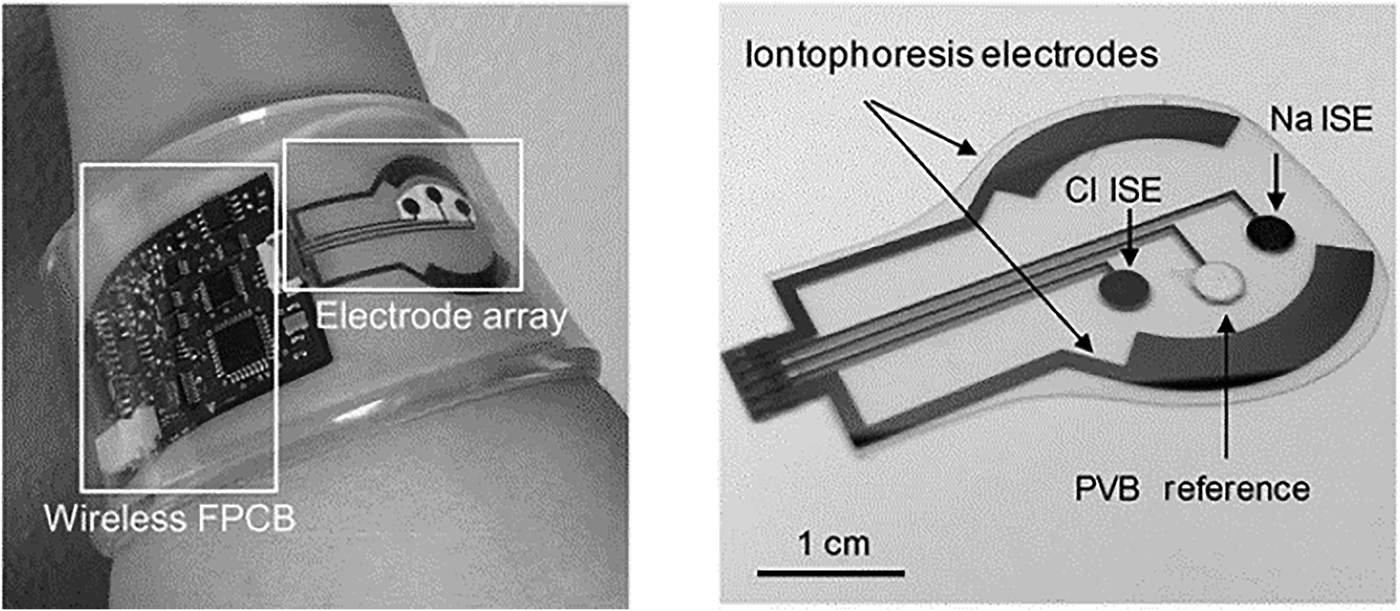
Figure 4. The flexible patch-type system incorporating electrodes and electronics for wireless Na+, Cl−, and glucose monitoring in sweat sample (reprinted from Ref. Reference Emaminejada, Gao, Wub, Davies, Nyein, Challaa, Ryan, Fahad, Chen, Shahpar, Talebia, Millaf, Javey and Davies60 Copyright PNAS 2017).
Ag electrodes were deposited on a PET substrate facilitating mechanical flexibility for direct skin contact. An Ag/AgCl electrode for Cl− detection was deposited by modifying an Ag electrode with a FeCl3 solution. The Na+ detection electrode was realized by depositing a Na+-selective layer upon an Ag electrode. PVB coatings saturated with chlorine ions were applied to formulate REs. For CF diagnostics, the system was evaluated by measuring sweat chloride concentration. Levels >60 mM indicated increased probability of disease. Measurements were made on three CF patients and six healthy volunteers; the average Na+ and Cl− for CF sufferers were 82.3 and 95.7 mM, respectively, while average healthy readings were 26.7 and 21.2 mM. For glucose measurements, a correlation between blood and sweat levels was demonstrated on a group of fasting and post fasting volunteers. A skin-mounted micro-analytical flow system was demonstrated[Reference Martín, Kim, Kurniawan, Sempionatto, Moreto, Tang, Campbell, Shin, Lee, Liu and Wang61] to monitor sweat lactate and glucose levels during light indoor cycling sessions. An optimized microfluidic sweat collection device was designed to deliver sweat sample collected from the skin to measure electrodes. This was the first time a microfluidic interface was optimized for sample collection on a skin wearable sensor. The device structure consisted of two PDMS layers, one incorporating the electrode substrate and the second defining fluidic channels. Gold electrodes (WE, CE) were modified with PB, GOx, and LOx for detection. The device also incorporated an Ag/AgCl RE. When evaluated with spiked artificial sweat sample, flowing at 200 mL/min, standard deviations of 1.2 and 1.6% were recorded for lactate (12 mM) and glucose (10 mM). The linear operating ranges for lactate was 4–20 mM and for glucose 2–10 mM. Detection sensitivity was 29.6 µM/μA. On body tests were undertaken with two healthy subjects over 20 min of moderate indoor cycling. Different signals were obtained compared with in vivo tests due to temperature, pH, and flowrate variation. Similar measured metabolite trends were previously reported.[Reference Gao, Emaminejad, Nyein, Challa, Chen, Peck, Fahad, Ota, Shiraki, Kiriya, Lien, Brooks, Davis and Javey59, Reference Parrilla, Ferr, Guinovart and Andrade62, Reference Matzeu, Quigley, McNamara, Zuliani, Fay, Glennon and Diamond63] Flexible conformal biosensor arrays were manufactured using printed ultrathin metal oxide semiconductor technology for pH and glucose detection.[Reference Rim, Bae, Chen, Yang, Kim, Andrews, Weiss, Yang and Tseng64] Arrays were manufactured from indium oxide films (3.5 nm) with low impurity concentration. The metal oxide films were robust to stress/strain caused by substrate bending, twisting, and stretching. The surface was easily modified for biomolecule immobilization, and the sensor demonstrated both pH and glucose detection for diabetes and wound monitoring. Flexible FET devices were formed on ultrathin PI films (2 µm); the active layer (In2O3) was spin coated and then annealed at 250 °C. Interdigitated electrode arrays were patterned on the metal oxide film defining metal contacts. Sensor thin films were released from support substrates by delamination in water, facilitating stretching and unfolding. Protonation of surface hydroxyl groups and primary amines of aminopropyltriethoxysilane occurred on the metal oxide surface, as pH decreased from pH5.5 to pH9. For glucose detection, GOx immobilized on FET surfaces produced hydrogen peroxide from glucose oxidation. Measured currents were recorded over a clinically relevant range (100–400 µM), and devices were suitable for simultaneous on-skin glucose and pH measurements. Flexible organic electrochemical transistors (OECTs) formed on a flexible substrate demonstrated simultaneous detection of uric acid and glucose.[Reference Liao, Mak, Zhang, Chan and Yan65] The device was formed by the deposition of electroactive PEDOT:PSS layers on a flexible PET substrate (50 µm) with platinum contact electrodes. Flexible devices could be attached to conformal surfaces and were robust to repeat bending cycles (1000 times). The device was sensitive to H2O2 formed during enzymatic reactions. To overcome the sensitivity of the platinum gate electrodes to interfering molecules [e.g., dopamine, glucose, uric acid (UA), and ascorbic acid], electrodes were modified with a bilayer consisting of graphite flakes and Nafion, then encapsulated with a conductive polymer (PANI). After surface modification, positively charged molecules (e.g., dopamine) were repelled from the surface (Nafion repelled UA and ascorbic acid), while larger molecules (e.g., glucose) could not penetrate the PANI nanometer-sized pores. Gate modification had minimal impact, as H2O2 penetrated the bilayer delivering good detection (LOD 10−9). Uricase (UOx) was immobilized on PANI using GO and oxidation of uric acid also generated H2O2. A physiologically relevant response range was recorded (100 × 10−9–500 × 10−6 M) for uric acid. The device detected UA in saliva at 173 ± 20 × 10−6 M and saliva glucose in a healthy individual (103 ± 10 × 10−6 M). The bilayer blocking effect was relevant only to potentiometric sensors as fields associated with amperometric detection negated bilayer charge blocking at the device surface. Blocking layer efficiency is an important parameter along with electrode poisoning, requiring consideration in catalytic sensor methods. A flexible multi-sensor patch was fabricated to simultaneously monitor sodium, pH, and lactate sweat during exercise sessions.[Reference Anastasova, Crewther, Bembnowicz, Curto, Ip, Rosa and Yang66] The patch adhered to skin on the lower back where a flexible microneedle array and microfluidic channel collected sweat sample for electrochemical measurement. The innovative sampling mechanism continuously drew sample across the sensors for real-time detection. The overall patch thickness was 180 µm facilitating comfortable long-term application. For Na+ detection, a poly(vinylchloride) ion-selective membrane was drop cast onto Pt/PEDOT electrode gasket, the RE was prepared by doping the polymeric membrane with a lipophilic salt. For lactate detection, the RE was treated with potassium dichromate. For pH detection, iridium oxide was electrochemically deposited on electrodes by chemical oxidation. LOx drop cast onto electrodes coated with sulphonated polyether-ether sulphone:polyethersulphone for selective lactate detection. Sensor signals were wirelessly transmitted to a mobile phone for data analysis. The system was evaluated on six male volunteers during exercise sessions. Temperature recalibration was applied to the sensors compensating for modified enzyme activity. Saliva samples were taken during exercise to determine cortisol concentration using a commercial immunoassay. Measured sodium, lactate, and pH levels were in agreement with the previous reported studies and in line with clinical levels for exercise sessions and were repeatable with CVs of 6% (Na), 7% (pH), and 9% (lactate). The sensors were robust to interfering sweat constituents, e.g., uric acid, ascorbic acid, and glucose. A disposable patch incorporating microfluidics and assay reagent implemented a passive test screening for Cl, Zn, and Na.[Reference Sekine, Kim, Zhang, Bandodkar, Xu, Choi, Irie, Ray, Kohli, Kozai, Sugita, Wu, Lee, Lee, Ghaffarid and Rogers67] The device was composed of three layers: (i) adhesive, (ii) microfluidic, and (iii) light shield. Microfluidic channels, valves, and chambers realized a passive pump mechanism delivering sweat sample from skin to assay reservoirs. Fluorescent probes reported target concentrations, with signals read using a smartphone via miniaturized optical fluorescence system. The fluidic system (Fig. 5) contained check valves to facilitate timed delivery of sweat sample to each reaction chamber once a threshold liquid pressure was achieved. The light shield layer protected the probes during skin application for sweat sampling and assay reaction. For Na and Zn detection, there was a direct relationship between intensity and target concentration correlating with physiologically relevant ranges (Na 20–60 mM, Zn 1.4–27 µM). An inverse fluorescent signal was correlated with increasing Cl sweat content over the physiologic range 20–60 mM.
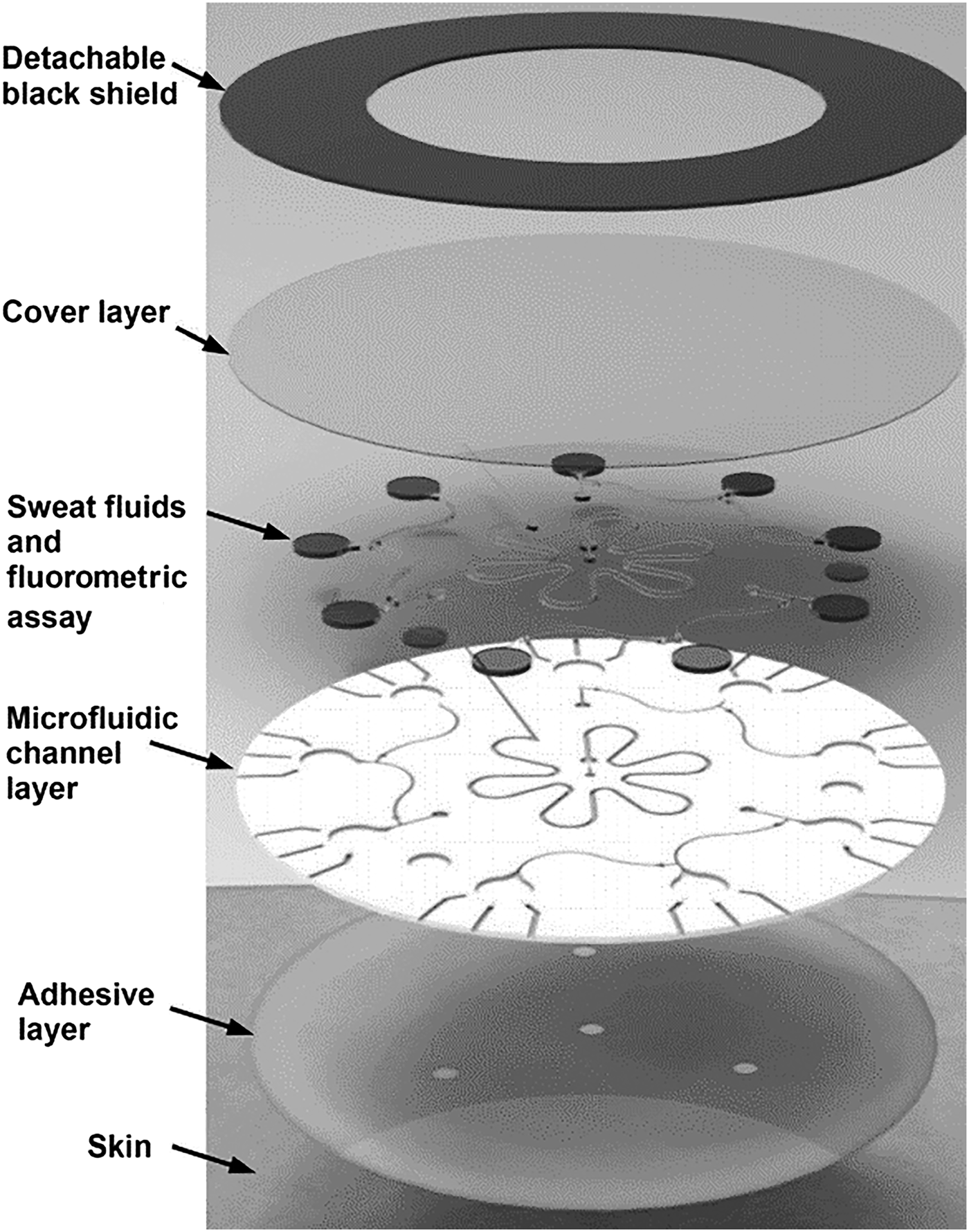
Figure 5. A multilayer patch incorporating adhesive, microfluidics, and assay reagents was demonstrated for the detection of Cl, Na, and Zn over clinically relevant ranges (reproduced from Ref. Reference Sekine, Kim, Zhang, Bandodkar, Xu, Choi, Irie, Ray, Kohli, Kozai, Sugita, Wu, Lee, Lee, Ghaffarid and Rogers67 with permission from Royal Society of Chemistry).
Alcohol, glucose
A flexible sensor was developed to simultaneously monitor alcohol and glucose with low sample volume (1–3 µL); this combination facilitated a wearable system to monitor correlation between alcohol consumption and diabetes.[Reference Bhide, Muthukumar, Saini and Prasad68] Flexible porous PI membranes were used as a substrate to fabricate zinc oxide electrodes. The porous polymer membrane wicked sweat away from the skin to the sensor surface. Selective biomolecule transport through the porous membrane enhanced the signal by minimizing interference from ions and lipids. The sensor was evaluated on synthetic sweat spiked with glucose and ethanol over clinically relevant ranges, with impedance measured over the frequency range 50–500 Hz. Variation in impedance due to electron charge transfer and electrical double-layer modulation modified electrode capacitance as target biomolecule concentration varied. Changes in imaginary impedance correlated with ethanol concentration over the range 0.01–200 mg/dL. Sweat pH variation (pH4–8) had an impact on ethanol estimates. The sensor also demonstrated selectivity against interfering biomolecules (e.g., uric acid, glucose, lactate, creatine, etc.). For combinatorial experiments, glucose measurements were made at 100 Hz, and the performance of glucose and alcohol measurements were comparable to commercial devices for glucose (Accu-Chek®) and alcohol (BACtrac®) and within acceptable limits of error.
Heartrate, lactate
Combining electrophysiologic and biochemical measurements on a single patch[Reference Imani, Bandodkar, Vinu Mohan, Kumar, Yu, Wang and Mercier69] augmented heartrate monitoring with lactate measurements, offering a more comprehensive fitness monitor compared with electrophysiologic measurements alone. The system was composed of a three electrode lactate sensors and a bipolar electrocardiogram sensor fabricated on a flexible substrate for skin adhesion. The device was fabricated by screen printing electrodes on a flexible polyester sheet. Portable instrumentation incorporated a potentiostat and an electrocardiogram with Bluetooth telemetry. The hybrid device was tested on three subjects during cycling exercise sessions. The patch size (7 cm × 2 cm) was set by electrocardiogram electrode separation. Placing the patch on the chest region was optimal for heartrate monitoring and also generated sufficient sweat sample for lactate measurement. The lactate electrodes were fabricated between the heartrate electrodes. PB ink was used to print the WEs, which were highly sensitive to hydrogen peroxide produced by enzymatic lactate oxidation. The Ag/AgCl RE was also screen printed. The sensors were separated by an ecoflex hydrophobic layer preventing signal distortion through multiple electrical pathways thus minimizing cross-talk between sensors. Results from continuous cycling highlighted heartrate measurements between 60 bpm (resting) and 120 bpm (full exertion); at exercise commencement, no variation in lactate was measured on the lactate sensor due to lack of perspiration; however, with sweat onset, the LOx sensor shows signal increase correlating with heartrate and exertion. Dilution of sweat lactate content after a period of time due to profuse sweating was also detected by the sensor. During exercise cooldown, the heartrate returned to normal and the lactate readings reduced as expected under normal clinical conditions.
Heavy metals
Metal detection is well established in electrochemistry[Reference Bansoda, Kumarb, Thakurc, Ranac and Singh70] and has been applied to environmental,[Reference March, Nguyen and Piro71] agriculture,[Reference Zhao, Sheng, Wang and Liu72] and health[Reference Yantasee, Lin, Hongsirikarn, Fryxell, Addleman and Timchalk73] applications. Portable amperometric technology is suitable for system miniaturization.[Reference Xuan, Hossain and Park74] Metal screening in wearable health devices has emerged as an area of interest as metal deficiency (e.g., Cu, Zn) causes disease,[Reference Fraga28, Reference Schaefer, Schellenberg, Merle, Weiss and Wilson75] while metal build-up has negative health implications. Screening sweat for heavy metals using electrochemical techniques[Reference Crew, Cowell and Hart76, Reference De Souza, Lima, Salles, Nascimento and Bertotti77] has been adapted by wearable technologies.[Reference Kim, de Araujo, Samek, Bandodkar, Jia, Brunetti, Paixao and Wang78] Heavy metal detection (Zn, Cd, Pb, Cu, Hg) in body fluids was demonstrated using square wave anodic stripping voltammetry on Au and Bi electrodes.[Reference Goa, Nyein, Shahpar, Fahad, Chen, Emaminejad, Goa, Tai, Ota, Wu, Bullock, Zeng, Lein and Javey79] A five-electrode microarray was evaporated and patterned (lift-off) on a PET substrate, then coated with a Nafion protective layer.[Reference Koh, Kang, Xue, Lee, Pielak, Kim, Hwang, Min, Banks, Bastien, Manco, Wang, Ammann, Jang, Won, Han, Ghaffari, Paik, Slepian, Balooch, Huang and Rogers80] A PDMS sample reservoir (20–30 µL) was sealed on the sensor substrate for sweat sample retention, providing a stable sensor liquid measurement interface and highlighting how microfluidic designs can be incorporated with flexible sensor substrates to enhance biomarker detection.
Proteins and DNA
Single-target immunoassays have limited diagnostic value as many biomarkers (e.g., proteins) are associated with a number of conditions (e.g., cancers); thus, there is a significant interest in implementing multiplex tests to improve diagnosis accuracy. Gold WE microarrays were deposited on flexible PI substrates for cytokine detection using impedance measurements.[Reference Baraket, Lee, Zine, Sigaud, Yaakoubi, Trivella, Zabala, Bausells, Jaffrezic-Renault and Errachid81] The same group fabricated poly(pyrrole) (PPy) microwires (PPYμWs) on flexible substrates including PETE, cyclic olefin copolymer, polyethylene naphthalate, and PI using microcontact printing (μCP).[Reference Garcia-Cruz, Lee, Zine, Sigaud, Bausells and Errachid82] The flexible sensors demonstrated multiplex cytokine detection by impedance spectroscopy. PPy is a good conductive polymer for electrical biosensors due to its electrical conductivity, environmental stability, biocompatibility, and easy synthesis.[Reference Kamakoti, Selvam, Shanmugam, Muthukum and Prasad83] Human interleukin-10 antibodies were chemically immobilized on PPyμWs using gluteraldehyde cross-linker. Impedance spectroscopy was used to detect rhIL-10 biomarkers over the range 1–50 pg/mL, with sensitivity 0.026 (pg/mL). This group also devised a PDMS μCP process defining PPy nanowires on flexible thermoplastic surfaces (PETE, polyether ether ketone), by covalent bonding. Carbodiimide cross-linker chemistry attached specific monoclonal antibodies (anti-human IL-6) to diazonium functionalized nanowires, defining impedance sensors for IL-6 detection. The LOD was 0.013 pg/mL with a linear operating range 1–50 pg/mL and demonstrated potential for multiplex cancer screening using IL-6 antibody biomarkers. Target-specific aptamers were combined with nanographene oxide (NGO) sensor arrays to selectively screen for nine cancer-related proteins using fluorescence detection[Reference Pei, Li, Lv, Wang, Gao, Lu, Li, Huang, Hu and Fan84] at nanomolar target concentrations. Multiple protein targets were also detected using aptamer/NGO substrates with NGO-modifying polymer substrate elasticity.[Reference Chou, De, Luo, Rotello, Huang and Dravid85] NGO also demonstrated superior limits of detection over graphene oxide due to increased oxygenated reactive sites delivering enhanced affinity for a wide range of protein biomarkers. OECT devices were also demonstrated for label-free DNA detection,[Reference Lin, Luo, Hsing and Yan86] where the device was fabricated on a PET substrate and integrated within a PDMS microfluidic channel. The transistor active layer was PEDOT:PSS with Au electrodes. The device electrical characteristics (I DS,V G) showed similar values before and during bending. The electrical transfer curve shifted positively after DNA hybridization and demonstrated sensitivity down to 10 pM target oligonucleotide with enhanced hybridization conditions. While multiplex target detection was not demonstrated, the potential microarray application could be realized.
Cell targets
Label-free electrochemical biomolecule detection has generated significant interest in recent years; removing reporter molecules can significantly reduce assay cost and complexity. OECTs have been demonstrated for the detection of sialic acid screening for cancer cells.[Reference Guo, Liu, Liu, She, Zheng, Tang, Ma and Yao87] Such approaches exploit the concept of field-effective transistors; detection is realized by monitoring a source to drain electrical characteristics as gate voltage is modified with biomolecule interaction. In a highly efficient approach for cancer cell detection, sialic acid was directly monitored at a p-aminobenzoic acid-modified gate counter electrode by exploiting direct binding between sialic acid (SA) and phenylboronic acid. The transistor active layer was based on PEDOT:PSS with screen-printed carbon source and drain electrodes. The OECT device showed a response to free SA test solution and HeLa cells with relative standard deviation of 6.3% (SA) and 12.9% (HeLa), respectively. The device has demonstrated a potential to distinguish between different cell types (Fig. 6).
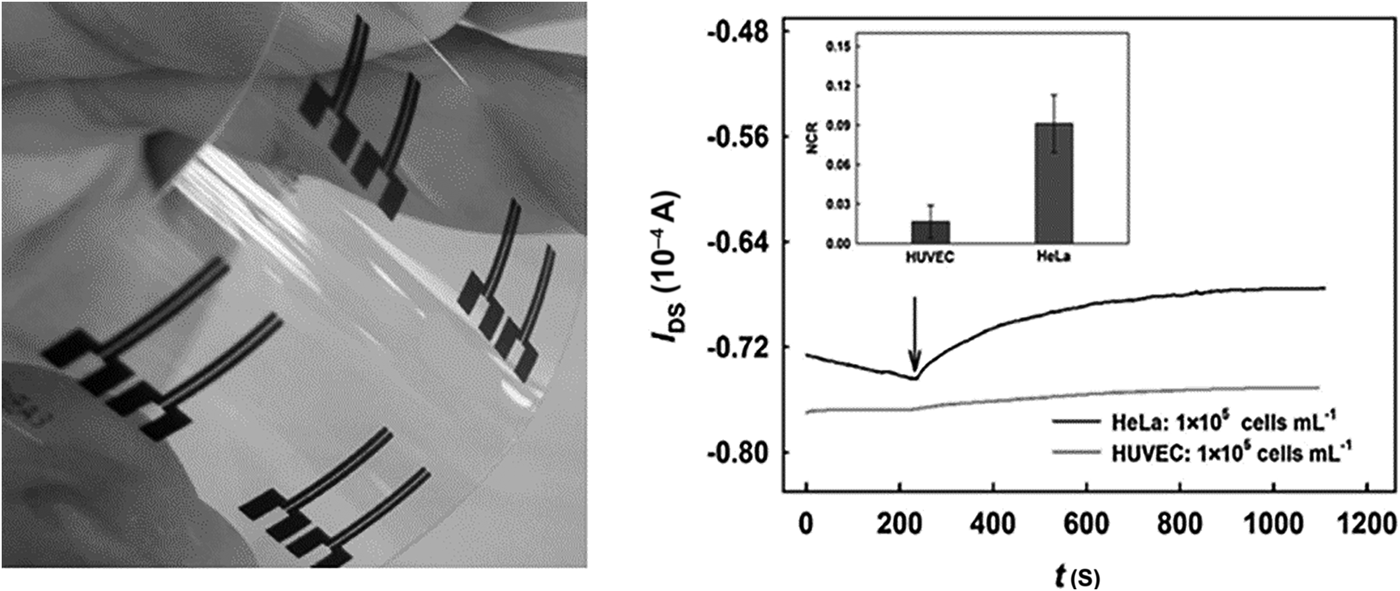
Figure 6. OECT devices were incorporated into a flexible transparent substrate (left) to screen for sialic acid. The potential to differentiate between different cancer (HeLa) and normal (HUVEC) cell types was demonstrated (right) (reprinted from Ref. Reference Guo, Liu, Liu, She, Zheng, Tang, Ma and Yao87 Copyright Sensors & Actuators B).
Fabric substrates
Textile-based sensors are a growing research area, most clothing materials are hydrophilic, biocompatible, and naturally conform to the body profile. Approaches to achieve woven fabric sensors include (i) modified fibers/threads, defining conductive paths in cloth or (ii) electrodes printed onto finished garments using flexible print/deposition approaches. Unlike paper and polymer substrates requiring multiple detection and fluid-handling layers, fibers are selectively woven into the fabric, defining sensor and fluidic functionality in a single-layer manufacture process. Textile manufacture incorporates a range of low-cost high-throughput techniques[Reference Castano and Flatau88] (embroidery, weaving, braiding, coating, and printing) compatible with multiplex biomarker screening devices. Fabrics incorporating measurement technologies are referred to as smart fabric sensors (SFSs).[Reference Castano and Flatau88] Stretchable SFSs can be realized by using elastic fibers/threads,[89] greatly enhancing suitability for wearable applications.
Electrolytes, pH
Fabric sensors are especially suited to skin applications monitoring sweat or interstitial fluid parameters (e.g., electrolytes). Commercial cotton yarn, dyed with carbon nanotube ink, defined an ion-selective membrane for target-specific measurement.[Reference Guinovart, Parilla, Crespo, Rius and Andrade90] The electrodes were woven into a band aid-type material (Fig. 7), with a commercial miniature RE incorporated into the structure measuring pH, potassium, and nitrates in liquid sample. Optimizing carbon nanotube ink concentrations achieved stable electrode dye for cotton-based applications.
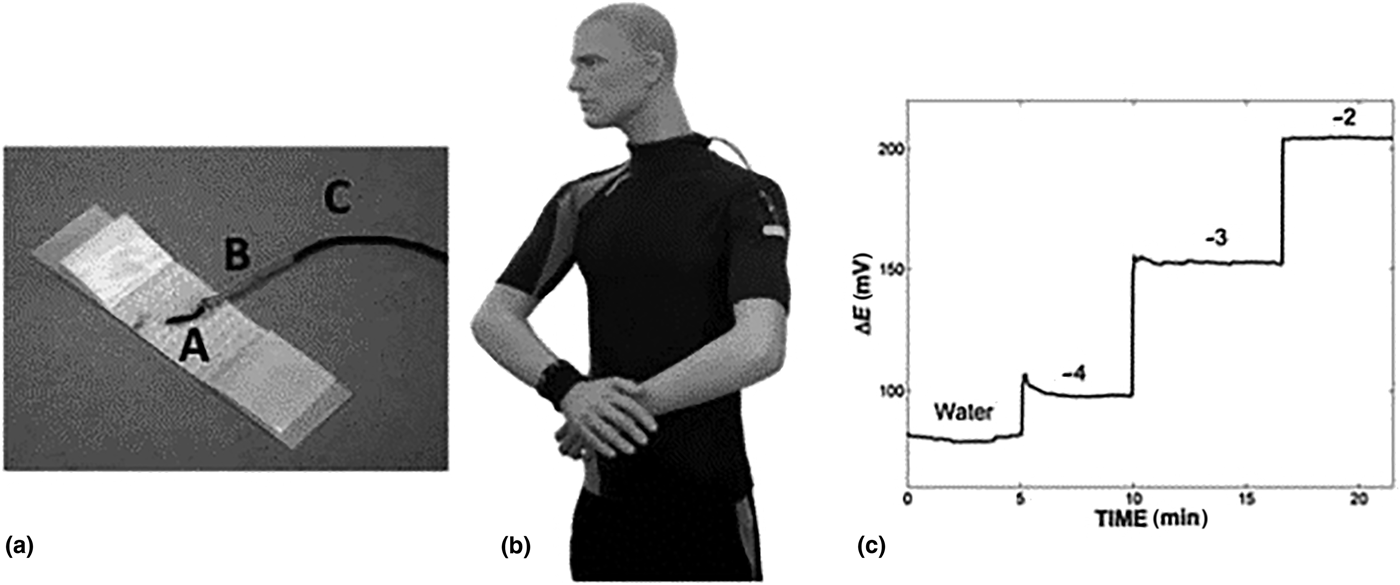
Figure 7. Band aid plaster material incorporating ion-selective membranes, designed to measure pH, potassium, and nitrates (reprinted from Ref. Reference Guinovart, Parilla, Crespo, Rius and Andrade90 with permission from Royal Society of Chemistry).
Impedance measurements were made using these band aid devices and yarn-based electrodes were found to be stable over extended time (1 month), with structure bending/stretching having minimal impact on performance. Selectivity and sensitivity of the yarn electrodes were similar to conventional planar electrodes. The device incorporated a cellulose interface between electrodes, which rapidly soaked sweat, eliminating direct skin contact. Device manufacture was convenient and suitable for low-resource countries, due its low manufacture cost and disposable nature. Silk is also an interesting material for fabric-based electrochemical sensors; individual threads were coated with conductive inks and woven into flexible fabric electrodes.[Reference Choudhary, Rajamanickam and Dendukuri91] Silk threads were coated with reagents and electrode materials before being incorporated into fabric patches realizing sensor arrays. This approach was preferred over conventional screen printing to reduce reagent waste, while incorporating hydrophilic and hydrophobic threads into the sensor design controlled fluid flow and miniaturized sensor footprint. An OECT formulated on a cotton fiber[Reference Coppede, Tarabella, Villani, Calestani, Lannotta and Zappettini92] simultaneously measured adrenaline and NaCl in sweat sample by oxidation at the gate electrode, forming adrenochrome. Metal wire was used as gate electrodes controlling charge on a PEDOT:PSS conduction channel formulated on a cotton fiber. When switched on, cations flowed from the electrolyte solution to the conductive channel reducing current flow between drain and source; the current amplitude was proportional to sweat adrenaline concentration. The sensor response was measured over the range from 10 nM to 10 mM, changing the gate electrode to silver-facilitated salt content measurement.
Glucose, lactate, hemoglobin
Electrochemical detection was used to detect glucose (chrono-amperometry) and hemoglobin (digital pulse voltammetry).[Reference Choudhary, Rajamanickam and Dendukuri91] This approach incorporated different reagents on electrodes, in a fashion not previously demonstrated with textile devices, also enhancing mechanical strength for incorporation into wearable devices. The glucose sensor consisted of carbon ink coated onto silk fiber (CE), with thread coated in a carbon ink/potassium ferricyanide mix for the WE, followed by GOx deposition. An Ag/AgCl thread coating was used for the RE. Identical materials and manufacture technique was used for the hemoglobin sensor, with a carbon RE replacing Ag/AgCl and WEs left uncoated. For multiplex detection, uncoated carbon REs were incorporated into a four-electrode design with common REs and CEs for multiplex detection. Each sensor was 2 cm × 1.2 cm × 0.1 cm. The multiplex sensor was evaluated with lysed blood sample of known glucose and hemoglobin content. For glucose detection, 5 µl of blood was delivered to the sensor and a 0.5 V fixed voltage was applied between WE and RE with current measured over time. Glucose was oxidized forming gluconic acid, while potassium ferricyanide reduction produced the measured current. The sensors showed good sensitivity over a clinically relevant range (80–600 mg/dL) with <5% CV. For hemoglobin detection, red blood cell lysis released target into solution. Carbon WEs were used to detect oxyhemoglobin by reduction at −0.42 V. Using digital peak voltammetry, peak size at −0.42 V increased with increasing oxyhemoglobin over the clinically relevant range 2.3–14 g/dL. Electrochemical sensors were embroidered into fabric, to monitor glucose and lactate in whole blood.[Reference Liu and Lillehoj93] Conductive thread was woven to define complex electrode designs using a commercial embroidery machine. Electrochemical detection using complex electrode design patterns was not previously demonstrated with weaved fabric. Carbon ink-coated thread defined the working and CEs, while Ag/AgCl ink was used for the RE. Passive enzyme adsorption (e.g., GOx or LOx) was undertaken on the WE for selective detection. Resistivity of the Ag/AgCl and carbon-coated threads were in line with the literature; to reduce oxidation resistance, the Ag/AgCl was flux-coated. The assays were stable, reproducible, and target-specific in liquids containing glucose, lactate, and uric acid. Blood spiked with glucose and lactate was measured over the range 0–40 mM, demonstrating suitability for clinical measurements. The sensor performance was stable against mechanical deformation, e.g., bending, stretching, and twisting. An array of graphene FET devices (Fig. 8) suitable for multiplex detection was fabricated on a silk substrate.[Reference You and Pak94] A thin silk film substrate (10 µm) was prepared from silk fibers. GOx was incorporated into silk solutions prior to drying achieving GOx (1%) loaded substrates. Graphene grown on a nicol (Ni) substrate was transferred to pure silk films using a PDMS stamp technique. Gold electrodes were deposited by low-temperature evaporation (40 °C) and patterned to realize source and drain electrodes on graphene channels. The GOx silk substrate was placed on the silk–graphene layer and adhered using water. The FET gate was then deposited and patterned on the silk–GOx layer. The glucose–GOx reactions modulated FET conductance, resulting in increased source drain current with increased glucose concentration. With V g = 0 V and V ds = 100 mV, the measured current (I ds) demonstrated a linear response over glucose concentration 0.1–10 mM (LOD = 0.1 mM), with average sensor sensitivity 2.5 A/mM. Sensor response time was <10 s, with up to ten sensors deposited per sensor patch, facilitating multiplex detection. The device was selective with minimal impact from uric acid (10 mM), bovine serum albumin (BSA), or ascorbic acid (10 mM).
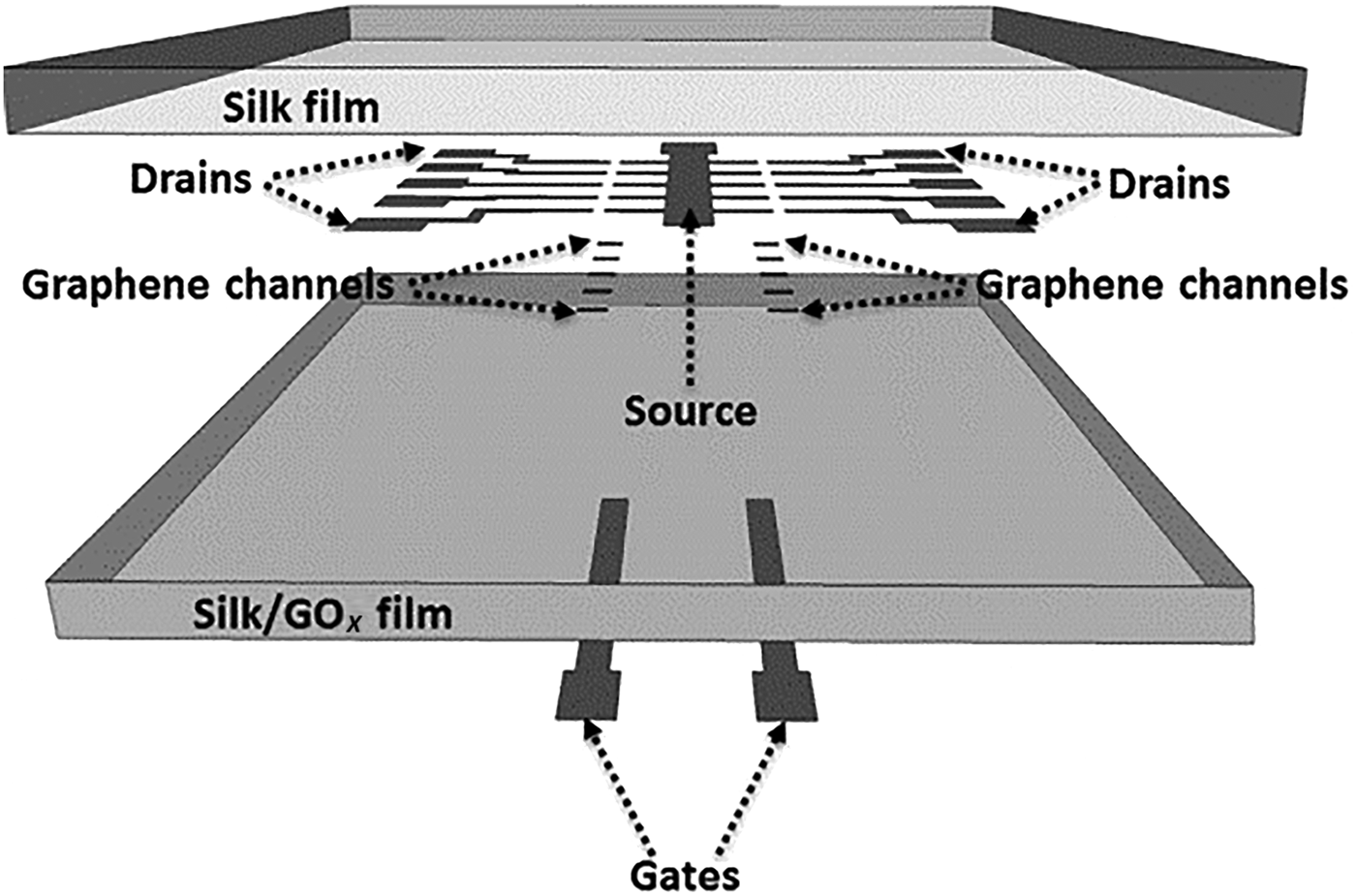
Figure 8. Outline of the incorporation graphene FET device array onto a silk substrate for spatial multiplex detection of glucose in a wearable system (reprinted from Ref. Reference You and Pak94 Copyright Sensors & Actuators B).
Flexible fabric sensors have been extensively deployed for electrophysiologic[Reference Chou, Nguyen, Chortos, To, Lu, Mei, Kurosawa, Bae, Tok and Bao95] and blood pressure[Reference Lee, Reuveny, Reeder, Lee, Jin, Liu, Yokota, Sekitani, Isoyama, Abe, Suo and Someya96] measurements, and a recent review[Reference Amjadi, Kyung, Park and Sitti97] on flexible strain sensors highlighted polymers and functional nanomaterials emerging in resistive/capacitive devices. They also highlighted how semiconductor materials significantly improve piezoresistivity over metals in flexible sensor applications; a similar trend is evident with flexible biomarker devices. However, for biomarker monitoring, additional challenges exist around surface fouling, sweat, and humidity. Sampling-appropriate volumes of target biomolecule is also a challenge in wearable devices and may require fluidic reservoir storage or pre-concentration prior to detection.
OECTs were fabricated by coating nylon fibers with multilayers of Cr/Au/PEDOT:PSS.[Reference Yang, Li, Yang, Fu, Wang, Li and Yan98] The stretchable fibers were incorporated into the fabric using a commercial weaving system, without any impact on performance. Bending the fiber had a small change in resistance (26–51 Ω/cm) compared with a fiber coated only with Cr/Au (39–401 Ω/cm). To define the gate electrode, Pt was deposited on the nylon fiber using a Ti adhesion layer. Detection of glucose (30–100 × 10−9 M), uric acid, and dopamine was demonstrated with the device. For glucose detection, GOx was deposited on the gate electrode with a modified blocking polymer layer. For UA detection, the gate electrode was modified with Nafion-graphine/PANI/uricase–GO multilayers and detection limits were similar to a planar device (30 × 10−9 M) with a linear response up to 300 × 10−6 M. The gate was modified with graphene flakes for dopamine detection with an LOD 10 × 10−9 M. To demonstrate the practical application, the OECT sensors were woven into diapers and used to determine glucose levels in spiked artificial urine.
Concluding remarks and future perspectives
In recent years, significant growth has occurred with consumer devices, monitoring physical activity (hearth rate, motion, etc.) for the fitness and well-being markets. Flexible substrate sensors based on piezoresistance, piezocapacitance, and piezoelectric technologies have been commercialized where product design delivers robust, easy to use, and comfortable devices. To date, less progress has been made in commercialization of wearable biomarker monitoring devices (e.g., glucose, Na+, etc.). Research and commercial devices have extensively demonstrated single-target biomarker detection; however, there is an increased activity around multiplex detection due to more representative diagnostics. New biomarkers emerging from genomic/proteomic research offers opportunities for real-time health monitoring in accessible biofluids (e.g., saliva, sweat, tear fluid). Flexible substrates facilitate on body wearable diagnostics enhancing non-invasive health monitoring. Materials progress has advanced wearable sensors through: (i) biocompatible polymers realizing flexible substrates for integrated electrodes/electronics, (ii) conductive nanomaterials defining flexible electrodes, (iii) target-selective interface layers (ionogels, hydrogels) addressing biofouling and enhancing biomarker selectivity. Integration of graphene, semiconductor, and nanowire materials with conductive polymers has delivered a significant progress in flexible sensor technology by enhancing electrical and mechanical performance. Microfluidics incorporated into flexible sensor devices improve liquid volume sampling[Reference Martín, Kim, Kurniawan, Sempionatto, Moreto, Tang, Campbell, Shin, Lee, Liu and Wang61] and deliver active device metering/valving.[Reference Wang, Li, Ban, Du, Feng and Liu58]
Challenges still exist, e.g., (i) analyte leaching from interface layers, (ii) long-term stability for bio-recognition molecules, and (iii) stable interface potentials between sample and sensor interfaces. Enzyme-free glucose detection has emerged as a key research topic, enabled by enhanced electro-catalytic nanostructure properties.[Reference Baloach, Tahira, Begum Mallah, Ishaq Abro, Uddin, Willander and Ibupoto99, Reference Bai, Yang, Sun and Sun100] These remove surface immobilization and ameliorate issues around enzyme stability and lifetime. However, device reproducibility is an issue with up to 50% signal variation reported across non-enzyme nanoparticle sensors.[Reference Bell, Nammari, Uttamchandani, Rai, Shahand and Moore101] Non-linear response/sensitivity and interference from electroactive species is also reported.[Reference Bell, Nammari, Uttamchandani, Rai, Shahand and Moore101] Enzyme-free electrochemical glucose detection has yet to impact flexible biomarker systems, and enzyme-mediated detection is still widely implemented. For future wearable flexible biomarker monitoring system, sampling will present challenges: (i) minimum sample volumes required to reliably detect target concentrations and (ii) sample/biomarker replenishment rates. Current wearable electrochemical devices have to overcome lifetime and stability issues. Biofouling and electrode poisoning (H2O2) impact long-term stability limiting measurements to <24 h, acceptable for short-term disposable devices (e.g., contact lens for glucose monitoring) but limiting long-term biomarker monitoring (e.g., days). A challenge for wearable potentiometric devices is avoiding interface equilibrium between RE material and the sample, resulting in a signal drift and limited sensor lifetime.[Reference Choi, Kim, Cutting and Searson102] Flexible substrate multiplex biomarker systems are a natural fit for wearable health-monitoring applications. They can provide rapid, reliable information for the end user, facilitating decision making on medication, performance, or lifestyle. In future developments, flexible polymers with physical characteristics (Young's modulus) similar to skin will advance comfort and robustness of skin-worn devices. For non-invasive monitoring, reliability and clinical performance[Reference Turner103] are key aspects for device performance. Blood diagnostics[Reference de Planell-Saguer and Celina Rodicio104–Reference Monbailliu, Goossens and Hachimi-Idrissi106] are the benchmark against which wearable systems are evaluated, and lower target concentration, lag times, and sample variation are challenges to be addressed. Progress in wearable sensor technology has been significant; flexible substrates have been facilitated by new nanomaterials, polymers, and novel fabrication technologies. To date, diabetes monitoring has been the commercial and technology benchmark,[107–109] with glucose and lactate extensively used to demonstrate proof of concept in research devices.[Reference Lee, Choi, Lee, Cho, Ghaffari, Wang, Choi, Chung, Lu, Hyeon, Choi and Kim110–Reference Ozana, Beiderman, Mico, Sanz, Garcia, Arnand, Baharam, Epstein and Zalevsky115] Emerging biomarkers from genome and proteome research are generating clinical interest as biomarkers linked to specific diseases. Currently, many commercial diagnostic assays monitor single biomarkers (e.g., glucose), but the possibility to monitor multiple biomarkers promises more efficient health monitoring where multiple parameters inform clinical diagnosis. The potential for non-invasive wearable biomedical sensors as alternatives to invasive monitoring is significant and the explosion in physical activity and lifestyle monitoring devices illustrate how issues around biofouling, calibration, and signal interference can be addressed.
Supplementary material
The supplementary material for this article can be found at https://doi.org/10.1557/mrc.2018.134.
Acknowledgments
CALIN––Ireland Wales InterReg Programme. SFI Insight Centre.















