Published online by Cambridge University Press: 17 September 2018
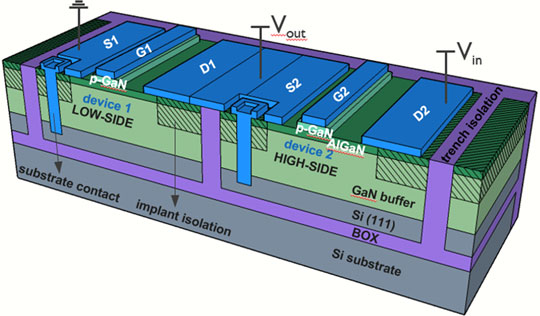
In this paper new materials and substrate approaches are discussed which have potential to provide (Al)GaN buffers with a better crystal quality, higher critical electrical field, or thickness and have the potential to offer co-integration of GaN switches at different reference potentials, while maintaining lower wafer bow and maintaining complementary metal–oxide semiconductor (CMOS) compatibility. Engineered silicon substrates, silicon on insulator (SOI) and coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE)-matched substrates have been investigated and benchmarked with respect to each other. SOI and CTE-matched offer benefits for scaling to higher voltage, while a trench isolation process combined with an oxide interlayer substrate allows co-integration of GaN components in a GaN-integrated circuit (IC).